UAV-assisted Distributed Learning for Environmental Monitoring in Rural Environments
Paper and Code
Jul 02, 2024
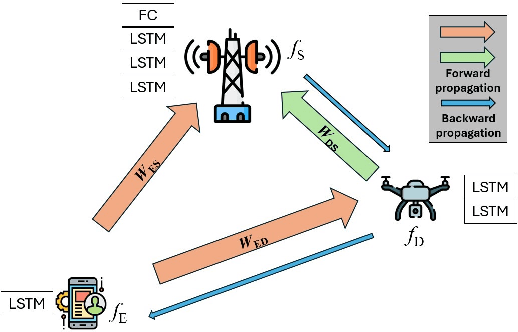
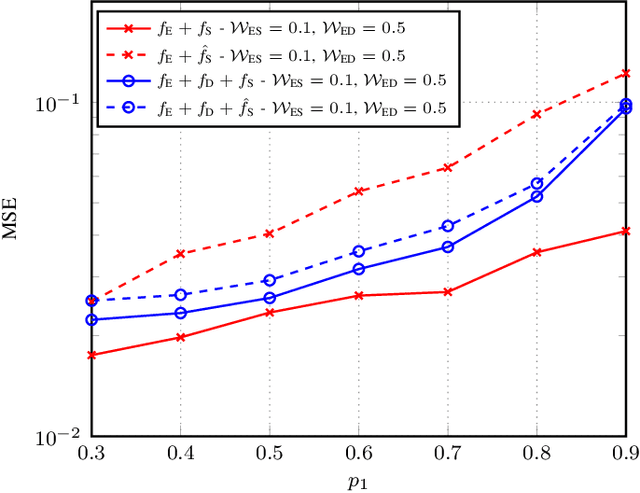

Distributed learning and inference algorithms have become indispensable for IoT systems, offering benefits such as workload alleviation, data privacy preservation, and reduced latency. This paper introduces an innovative approach that utilizes unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) as a coverage extension relay for IoT environmental monitoring in rural areas. Our method integrates a split learning (SL) strategy between edge devices, a UAV and a server to enhance adaptability and performance of inference mechanisms. By employing UAVs as a relay and by incorporating SL, we address connectivity and resource constraints for applications of learning in IoT in remote settings. Our system model accounts for diverse channel conditions to determine the most suitable transmission strategy for optimal system behaviour. Through simulation analysis, the proposed approach demonstrates its robustness and adaptability, even excelling under adverse channel conditions. Integrating UAV relaying and the SL paradigm offers significant flexibility to the server, enabling adaptive strategies that consider various trade-offs beyond simply minimizing overall inference quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge