Vittoria Vergani
School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, UK
Deep Learning-based Segmentation of Pleural Effusion From Ultrasound Using Coordinate Convolutions
Aug 05, 2022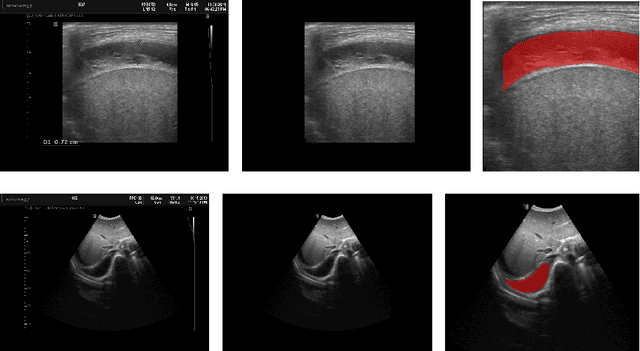
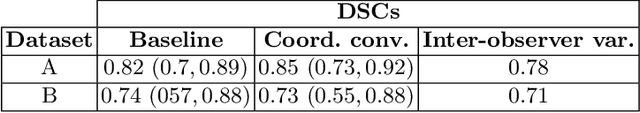
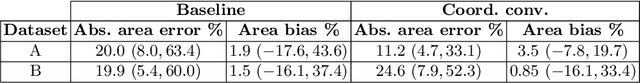
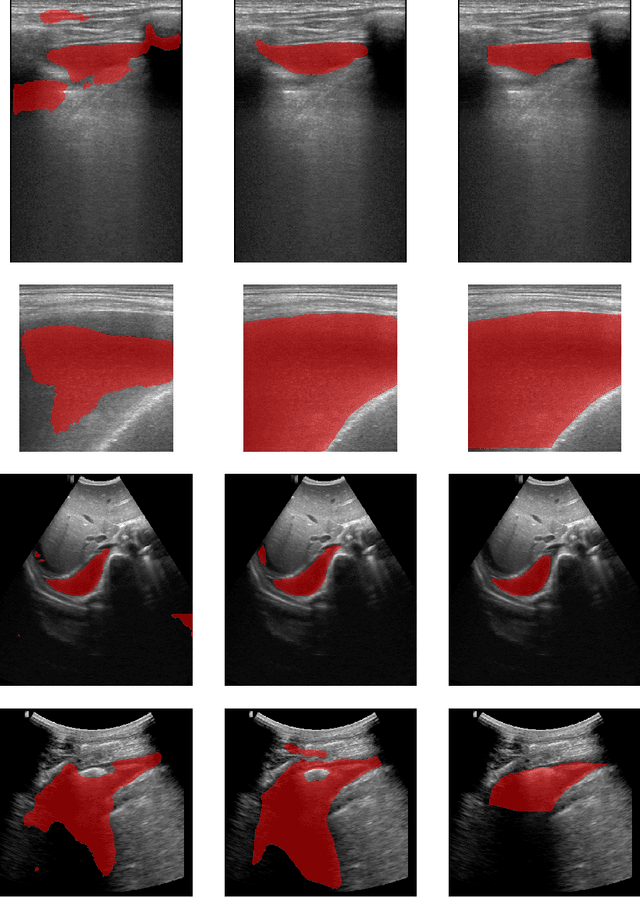
Abstract:In many low-to-middle income (LMIC) countries, ultrasound is used for assessment of pleural effusion. Typically, the extent of the effusion is manually measured by a sonographer, leading to significant intra-/inter-observer variability. In this work, we investigate the use of deep learning (DL) to automate the process of pleural effusion segmentation from ultrasound images. On two datasets acquired in a LMIC setting, we achieve median Dice Similarity Coefficients (DSCs) of 0.82 and 0.74 respectively using the nnU-net DL model. We also investigate the use of coordinate convolutions in the DL model and find that this results in a statistically significant improvement in the median DSC on the first dataset to 0.85, with no significant change on the second dataset. This work showcases, for the first time, the potential of DL in automating the process of effusion assessment from ultrasound in LMIC settings where there is often a lack of experienced radiologists to perform such tasks.
Large-scale, multi-centre, multi-disease validation of an AI clinical tool for cine CMR analysis
Jun 15, 2022



Abstract:INTRODUCTION: Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to facilitate the automation of CMR analysis for biomarker extraction. However, most AI algorithms are trained on a specific input domain (e.g., single scanner vendor or hospital-tailored imaging protocol) and lack the robustness to perform optimally when applied to CMR data from other input domains. METHODS: Our proposed framework consists of an AI-based algorithm for biventricular segmentation of short-axis images, followed by a post-analysis quality control to detect erroneous results. The segmentation algorithm was trained on a large dataset of clinical CMR scans from two NHS hospitals (n=2793) and validated on additional cases from this dataset (n=441) and on five external datasets (n=6808). The validation data included CMR scans of patients with a range of diseases acquired at 12 different centres using CMR scanners from all major vendors. RESULTS: Our method yielded median Dice scores over 87%, translating into median absolute errors in cardiac biomarkers within the range of inter-observer variability: <8.4mL (left ventricle), <9.2mL (right ventricle), <13.3g (left ventricular mass), and <5.9% (ejection fraction) across all datasets. Stratification of cases according to phenotypes of cardiac disease and scanner vendors showed good agreement. CONCLUSIONS: We show that our proposed tool, which combines a state-of-the-art AI algorithm trained on a large-scale multi-domain CMR dataset with a post-analysis quality control, allows us to robustly deal with routine clinical data from multiple centres, vendors, and cardiac diseases. This is a fundamental step for the clinical translation of AI algorithms. Moreover, our method yields a range of additional biomarkers of cardiac function (filling and ejection rates, regional wall motion, and strain) at no extra computational cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge