Vincent Tang
A General-Purpose Multimodal Foundation Model for Dermatology
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:Diagnosing and treating skin diseases require advanced visual skills across multiple domains and the ability to synthesize information from various imaging modalities. Current deep learning models, while effective at specific tasks such as diagnosing skin cancer from dermoscopic images, fall short in addressing the complex, multimodal demands of clinical practice. Here, we introduce PanDerm, a multimodal dermatology foundation model pretrained through self-supervised learning on a dataset of over 2 million real-world images of skin diseases, sourced from 11 clinical institutions across 4 imaging modalities. We evaluated PanDerm on 28 diverse datasets covering a range of clinical tasks, including skin cancer screening, phenotype assessment and risk stratification, diagnosis of neoplastic and inflammatory skin diseases, skin lesion segmentation, change monitoring, and metastasis prediction and prognosis. PanDerm achieved state-of-the-art performance across all evaluated tasks, often outperforming existing models even when using only 5-10% of labeled data. PanDerm's clinical utility was demonstrated through reader studies in real-world clinical settings across multiple imaging modalities. It outperformed clinicians by 10.2% in early-stage melanoma detection accuracy and enhanced clinicians' multiclass skin cancer diagnostic accuracy by 11% in a collaborative human-AI setting. Additionally, PanDerm demonstrated robust performance across diverse demographic factors, including different body locations, age groups, genders, and skin tones. The strong results in benchmark evaluations and real-world clinical scenarios suggest that PanDerm could enhance the management of skin diseases and serve as a model for developing multimodal foundation models in other medical specialties, potentially accelerating the integration of AI support in healthcare.
FNetAR: Mixing Tokens with Autoregressive Fourier Transforms
Jul 22, 2021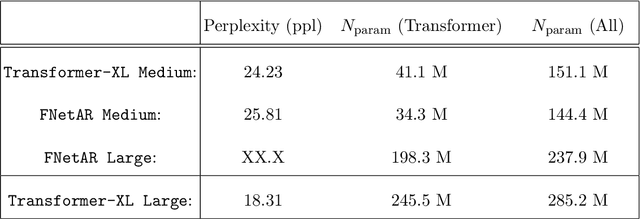
Abstract:In this note we examine the autoregressive generalization of the FNet algorithm, in which self-attention layers from the standard Transformer architecture are substituted with a trivial sparse-uniformsampling procedure based on Fourier transforms. Using the Wikitext-103 benchmark, we demonstratethat FNetAR retains state-of-the-art performance (25.8 ppl) on the task of causal language modelingcompared to a Transformer-XL baseline (24.2 ppl) with only half the number self-attention layers,thus providing further evidence for the superfluity of deep neural networks with heavily compoundedattention mechanisms. The autoregressive Fourier transform could likely be used for parameterreduction on most Transformer-based time-series prediction models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge