Viacheslav Sinii
Steering LLM Reasoning Through Bias-Only Adaptation
May 24, 2025Abstract:Recent work on reasoning-oriented language models, exemplified by o1-like systems, suggests that reinforcement-learning (RL) finetuning does not create new capabilities but instead strengthens reasoning patterns already latent in the pretrained network. We test this claim by training steering vectors: layer-wise biases that additively amplify selected hidden features while leaving all original weights unchanged. Experiments on four base models across the GSM8K and MATH benchmarks show that steering vectors recover, and in several cases exceed, the accuracy of fully-tuned counterparts. This result supports the view that the required reasoning skills pre-exist in the base model. Further, logit-lens analysis reveals that the trained vectors consistently boost token groups linked to structured languages and logical connectors, providing an interpretable account that aligns with the demands of quantitative reasoning tasks.
You Do Not Fully Utilize Transformer's Representation Capacity
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:In contrast to RNNs, which compress previous tokens into a single hidden state, Transformers can attend to all previous tokens directly. However, standard Transformers only use representations from the immediately preceding layer. In this paper, we show that this design choice causes representation collapse and leads to suboptimal performance. To address this issue, we introduce Layer-Integrated Memory (LIMe), a simple yet powerful approach that preserves the model's overall memory footprint while expanding its representational capacity by allowing access to hidden states from earlier layers. Through extensive experiments across various architectures and different lookup mechanisms, we demonstrate consistent performance improvements on a wide range of tasks. Moreover, our analysis of the learned representation dynamics and our exploration of depthwise circuits reveal how LIMe integrates information across layers, pointing to promising directions for future research.
The Differences Between Direct Alignment Algorithms are a Blur
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Direct Alignment Algorithms (DAAs) simplify language model alignment by replacing reinforcement learning (RL) and reward modeling (RM) in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with direct policy optimization. DAAs can be classified by their ranking losses (pairwise vs. pointwise), by the rewards used in those losses (e.g., likelihood ratios of policy and reference policy, or odds ratios), or by whether a Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) phase is required (two-stage vs. one-stage). We first show that one-stage methods underperform two-stage methods. To address this, we incorporate an explicit SFT phase and introduce the $\beta$ parameter, controlling the strength of preference optimization, into single-stage ORPO and ASFT. These modifications improve their performance in Alpaca Eval 2 by +$3.46$ (ORPO) and +$8.27$ (ASFT), matching two-stage methods like DPO. Further analysis reveals that the key factor is whether the approach uses pairwise or pointwise objectives, rather than the specific implicit reward or loss function. These results highlight the importance of careful evaluation to avoid premature claims of performance gains or overall superiority in alignment algorithms.
XLand-100B: A Large-Scale Multi-Task Dataset for In-Context Reinforcement Learning
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Following the success of the in-context learning paradigm in large-scale language and computer vision models, the recently emerging field of in-context reinforcement learning is experiencing a rapid growth. However, its development has been held back by the lack of challenging benchmarks, as all the experiments have been carried out in simple environments and on small-scale datasets. We present \textbf{XLand-100B}, a large-scale dataset for in-context reinforcement learning based on the XLand-MiniGrid environment, as a first step to alleviate this problem. It contains complete learning histories for nearly $30,000$ different tasks, covering $100$B transitions and $2.5$B episodes. It took $50,000$ GPU hours to collect the dataset, which is beyond the reach of most academic labs. Along with the dataset, we provide the utilities to reproduce or expand it even further. With this substantial effort, we aim to democratize research in the rapidly growing field of in-context reinforcement learning and provide a solid foundation for further scaling. The code is open-source and available under Apache 2.0 licence at https://github.com/dunno-lab/xland-minigrid-datasets.
In-Context Reinforcement Learning for Variable Action Spaces
Dec 20, 2023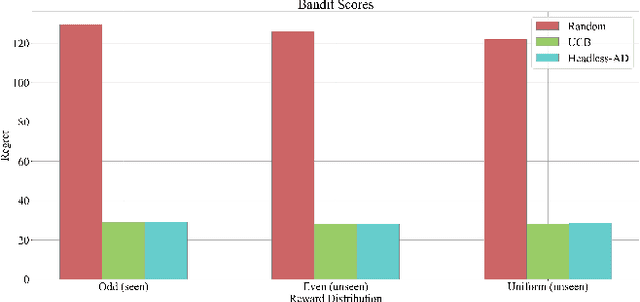
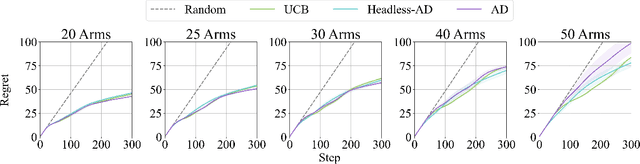
Abstract:Recent work has shown that supervised pre-training on learning histories of RL algorithms results in a model that captures the learning process and is able to improve in-context on novel tasks through interactions with an environment. Despite the progress in this area, there is still a gap in the existing literature, particularly in the in-context generalization to new action spaces. While existing methods show high performance on new tasks created by different reward distributions, their architectural design and training process are not suited for the introduction of new actions during evaluation. We aim to bridge this gap by developing an architecture and training methodology specifically for the task of generalizing to new action spaces. Inspired by Headless LLM, we remove the dependence on the number of actions by directly predicting the action embeddings. Furthermore, we use random embeddings to force the semantic inference of actions from context and to prepare for the new unseen embeddings during test time. Using multi-armed bandit environments with a variable number of arms, we show that our model achieves the performance of the data generation algorithm without requiring retraining for each new environment.
Emergence of In-Context Reinforcement Learning from Noise Distillation
Dec 19, 2023
Abstract:In-Context Reinforcement Learning is an emerging field with great potential for advancing Artificial Intelligence. Its core capability lies in generalizing to unseen tasks through interaction with the environment. To master these capabilities, an agent must be trained on specifically curated data that includes a policy improvement that an algorithm seeks to extract and then apply in context in the environment. However, for numerous tasks, training RL agents may be unfeasible, while obtaining human demonstrations can be relatively easy. Additionally, it is rare to be given the optimal policy, typically, only suboptimal demonstrations are available. We propose $AD^{\epsilon}$, a method that leverages demonstrations without policy improvement and enables multi-task in-context learning in the presence of a suboptimal demonstrator. This is achieved by artificially creating a history of incremental improvement, wherein noise is systematically introduced into the demonstrator's policy. Consequently, each successive transition illustrates a marginally better trajectory than the previous one. Our approach was tested on the Dark Room and Dark Key-to-Door environments, resulting in over a $\textbf{2}$x improvement compared to the best available policy in the data.
XLand-MiniGrid: Scalable Meta-Reinforcement Learning Environments in JAX
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:We present XLand-MiniGrid, a suite of tools and grid-world environments for meta-reinforcement learning research inspired by the diversity and depth of XLand and the simplicity and minimalism of MiniGrid. XLand-Minigrid is written in JAX, designed to be highly scalable, and can potentially run on GPU or TPU accelerators, democratizing large-scale experimentation with limited resources. To demonstrate the generality of our library, we have implemented some well-known single-task environments as well as new meta-learning environments capable of generating $10^8$ distinct tasks. We have empirically shown that the proposed environments can scale up to $2^{13}$ parallel instances on the GPU, reaching tens of millions of steps per second.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge