Ulugbek Salaev
UzMorphAnalyser: A Morphological Analysis Model for the Uzbek Language Using Inflectional Endings
May 23, 2024Abstract:As Uzbek language is agglutinative, has many morphological features which words formed by combining root and affixes. Affixes play an important role in the morphological analysis of words, by adding additional meanings and grammatical functions to words. Inflectional endings are utilized to express various morphological features within the language. This feature introduces numerous possibilities for word endings, thereby significantly expanding the word vocabulary and exacerbating issues related to data sparsity in statistical models. This paper present modeling of the morphological analysis of Uzbek words, including stemming, lemmatizing, and the extraction of morphological information while considering morpho-phonetic exceptions. Main steps of the model involve developing a complete set of word-ending with assigned morphological information, and additional datasets for morphological analysis. The proposed model was evaluated using a curated test set comprising 5.3K words. Through manual verification of stemming, lemmatizing, and morphological feature corrections carried out by linguistic specialists, it obtained a word-level accuracy of over 91%. The developed tool based on the proposed model is available as a web-based application and an open-source Python library.
Design and Implementation of a Tool for Extracting Uzbek Syllables
Dec 25, 2023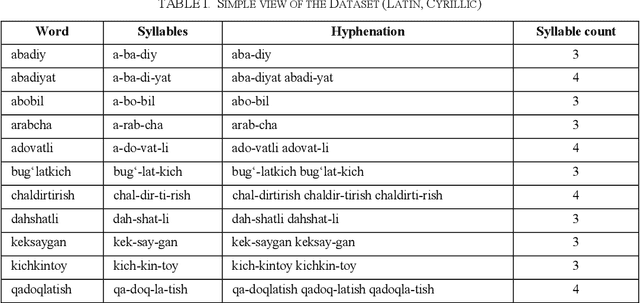
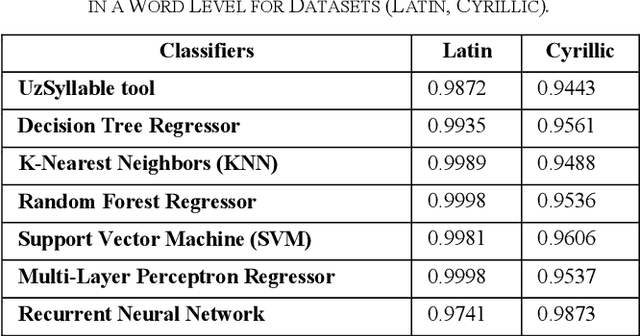
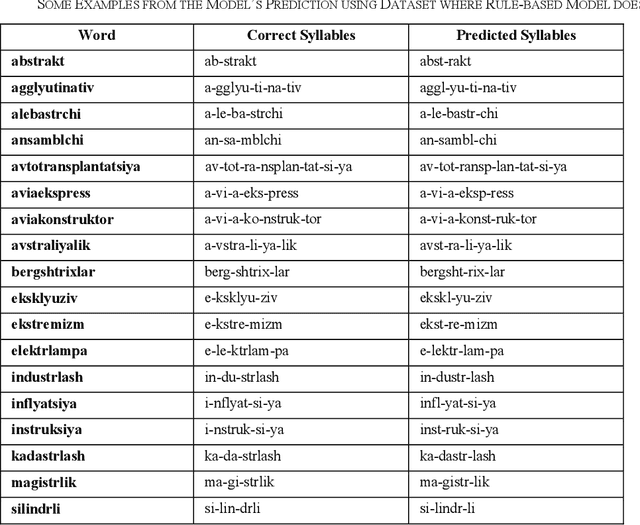
Abstract:The accurate syllabification of words plays a vital role in various Natural Language Processing applications. Syllabification is a versatile linguistic tool with applications in linguistic research, language technology, education, and various fields where understanding and processing language is essential. In this paper, we present a comprehensive approach to syllabification for the Uzbek language, including rule-based techniques and machine learning algorithms. Our rule-based approach utilizes advanced methods for dividing words into syllables, generating hyphenations for line breaks and count of syllables. Additionally, we collected a dataset for evaluating and training using machine learning algorithms comprising word-syllable mappings, hyphenations, and syllable counts to predict syllable counts as well as for the evaluation of the proposed model. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of both approaches in achieving accurate syllabification. The results of our experiments show that both approaches achieved a high level of accuracy, exceeding 99%. This study provides valuable insights and recommendations for future research on syllabification and related areas in not only the Uzbek language itself, but also in other closely-related Turkic languages with low-resource factor.
Text classification dataset and analysis for Uzbek language
Feb 28, 2023Abstract:Text classification is an important task in Natural Language Processing (NLP), where the goal is to categorize text data into predefined classes. In this study, we analyse the dataset creation steps and evaluation techniques of multi-label news categorisation task as part of text classification. We first present a newly obtained dataset for Uzbek text classification, which was collected from 10 different news and press websites and covers 15 categories of news, press and law texts. We also present a comprehensive evaluation of different models, ranging from traditional bag-of-words models to deep learning architectures, on this newly created dataset. Our experiments show that the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based models outperform the rule-based models. The best performance is achieved by the BERTbek model, which is a transformer-based BERT model trained on the Uzbek corpus. Our findings provide a good baseline for further research in Uzbek text classification.
Uzbek affix finite state machine for stemming
May 20, 2022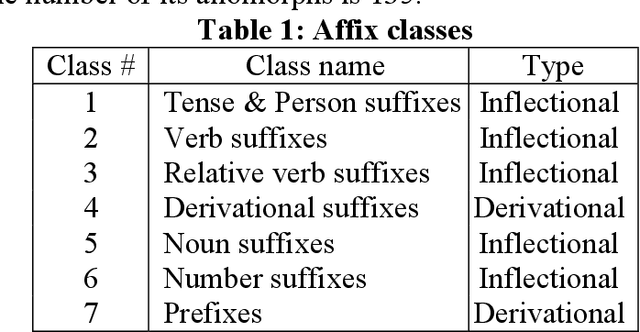
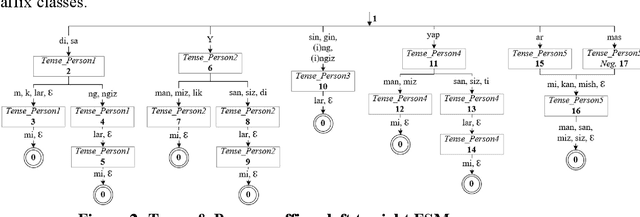
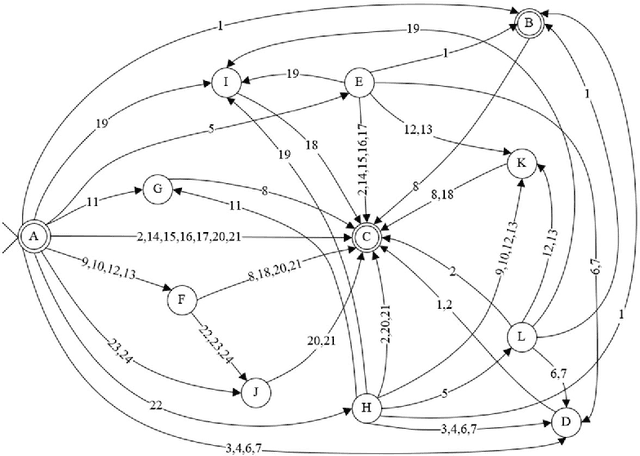

Abstract:This work presents a morphological analyzer for the Uzbek language using a finite state machine. The proposed methodology is a morphologic analysis of Uzbek words by using an affix striping to find a root and without including any lexicon. This method helps to perform morphological analysis of words from a large amount of text at high speed as well as it is not required using of memory for keeping vocabulary. According to Uzbek, an agglutinative language can be designed with finite state machines (FSMs). In contrast to the previous works, this study modeled the completed FSMs for all word classes by using the Uzbek language's morphotactic rules in right to left order. This paper shows the stages of this methodology including the classification of the affixes, the generation of the FSMs for each affix class, and the combination into a head machine to make analysis a word.
A machine transliteration tool between Uzbek alphabets
May 19, 2022

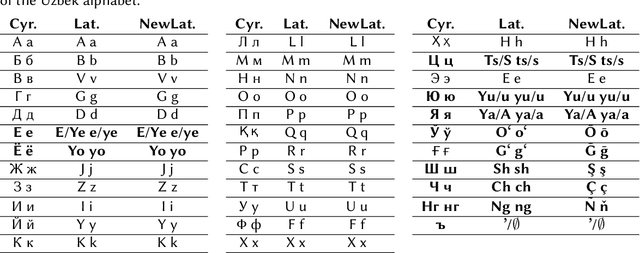

Abstract:Machine transliteration, as defined in this paper, is a process of automatically transforming written script of words from a source alphabet into words of another target alphabet within the same language, while preserving their meaning, as well as pronunciation. The main goal of this paper is to present a machine transliteration tool between three common scripts used in low-resource Uzbek language: the old Cyrillic, currently official Latin, and newly announced New Latin alphabets. The tool has been created using a combination of rule-based and fine-tuning approaches. The created tool is available as an open-source Python package, as well as a web-based application including a public API. To our knowledge, this is the first machine transliteration tool that supports the newly announced Latin alphabet of the Uzbek language.
SimRelUz: Similarity and Relatedness scores as a Semantic Evaluation dataset for Uzbek language
May 12, 2022
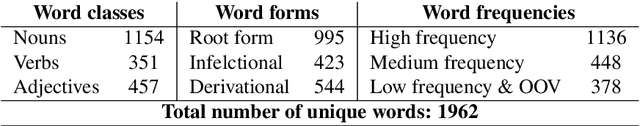
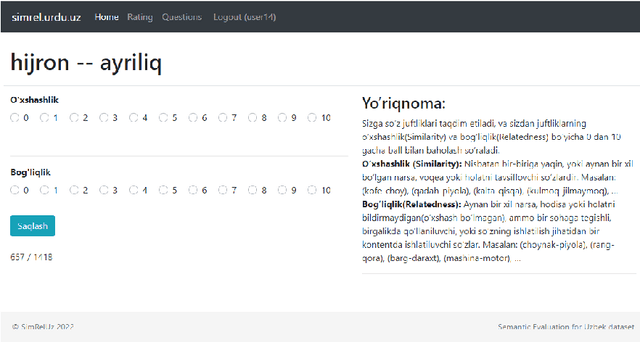

Abstract:Semantic relatedness between words is one of the core concepts in natural language processing, thus making semantic evaluation an important task. In this paper, we present a semantic model evaluation dataset: SimRelUz - a collection of similarity and relatedness scores of word pairs for the low-resource Uzbek language. The dataset consists of more than a thousand pairs of words carefully selected based on their morphological features, occurrence frequency, semantic relation, as well as annotated by eleven native Uzbek speakers from different age groups and gender. We also paid attention to the problem of dealing with rare words and out-of-vocabulary words to thoroughly evaluate the robustness of semantic models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge