Tuan-Duy H. Nguyen
Conditional Support Alignment for Domain Adaptation with Label Shift
May 29, 2023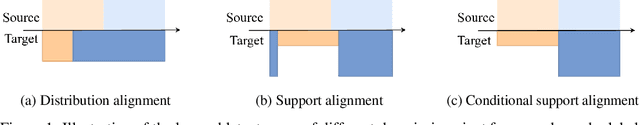



Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) refers to a domain adaptation framework in which a learning model is trained based on the labeled samples on the source domain and unlabelled ones in the target domain. The dominant existing methods in the field that rely on the classical covariate shift assumption to learn domain-invariant feature representation have yielded suboptimal performance under the label distribution shift between source and target domains. In this paper, we propose a novel conditional adversarial support alignment (CASA) whose aim is to minimize the conditional symmetric support divergence between the source's and target domain's feature representation distributions, aiming at a more helpful representation for the classification task. We also introduce a novel theoretical target risk bound, which justifies the merits of aligning the supports of conditional feature distributions compared to the existing marginal support alignment approach in the UDA settings. We then provide a complete training process for learning in which the objective optimization functions are precisely based on the proposed target risk bound. Our empirical results demonstrate that CASA outperforms other state-of-the-art methods on different UDA benchmark tasks under label shift conditions.
Robust Bayesian Recourse
Jun 22, 2022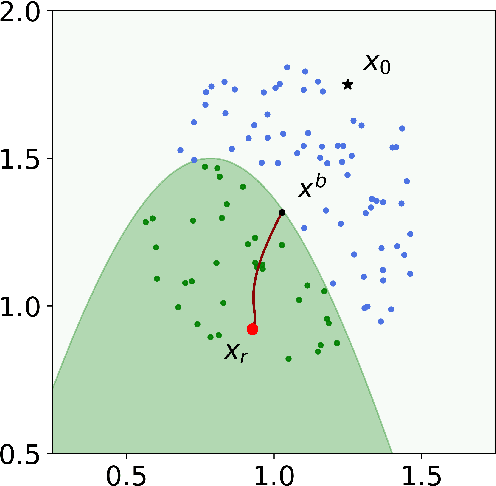
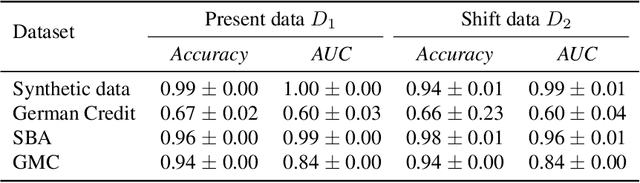
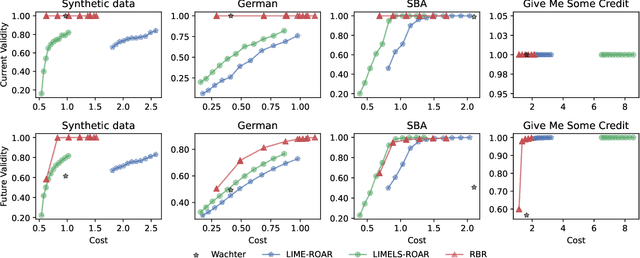
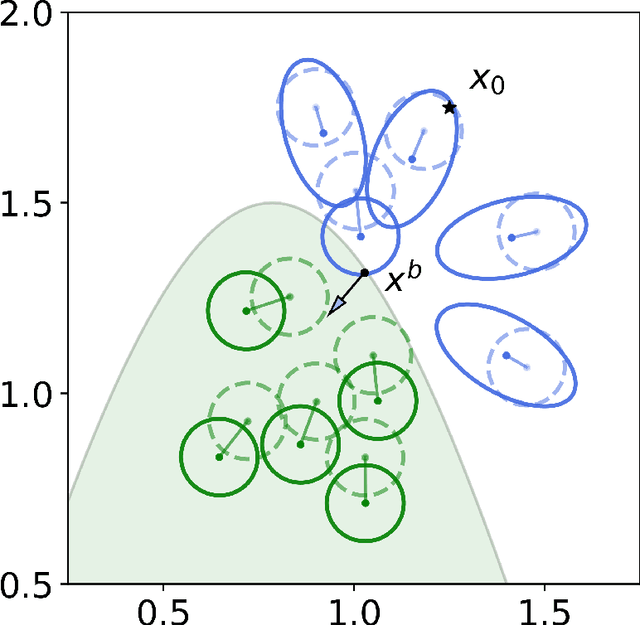
Abstract:Algorithmic recourse aims to recommend an informative feedback to overturn an unfavorable machine learning decision. We introduce in this paper the Bayesian recourse, a model-agnostic recourse that minimizes the posterior probability odds ratio. Further, we present its min-max robust counterpart with the goal of hedging against future changes in the machine learning model parameters. The robust counterpart explicitly takes into account possible perturbations of the data in a Gaussian mixture ambiguity set prescribed using the optimal transport (Wasserstein) distance. We show that the resulting worst-case objective function can be decomposed into solving a series of two-dimensional optimization subproblems, and the min-max recourse finding problem is thus amenable to a gradient descent algorithm. Contrary to existing methods for generating robust recourses, the robust Bayesian recourse does not require a linear approximation step. The numerical experiment demonstrates the effectiveness of our proposed robust Bayesian recourse facing model shifts. Our code is available at https://github.com/VinAIResearch/robust-bayesian-recourse.
Towards a Robust WiFi-based Fall Detection with Adversarial Data Augmentation
May 25, 2020

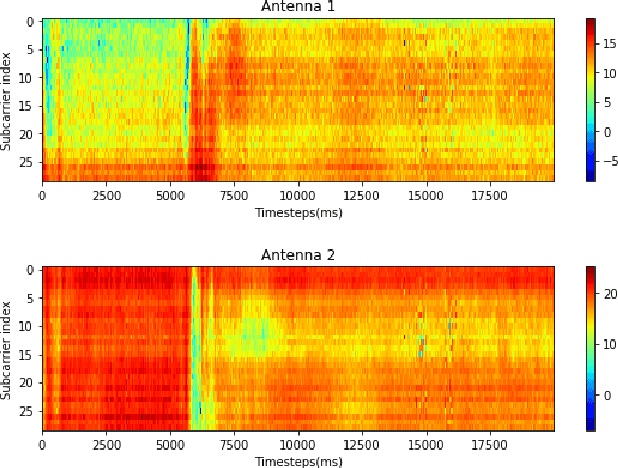

Abstract:Recent WiFi-based fall detection systems have drawn much attention due to their advantages over other sensory systems. Various implementations have achieved impressive progress in performance, thanks to machine learning and deep learning techniques. However, many of such high accuracy systems have low reliability as they fail to achieve robustness in unseen environments. To address that, this paper investigates a method of generalization through adversarial data augmentation. Our results show a slight improvement in deep learning-systems in unseen domains, though the performance is not significant.
* Will appear in Proceedings of the 54th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS2020)
Recognizing Families through Images with Pretrained Encoder
May 24, 2020
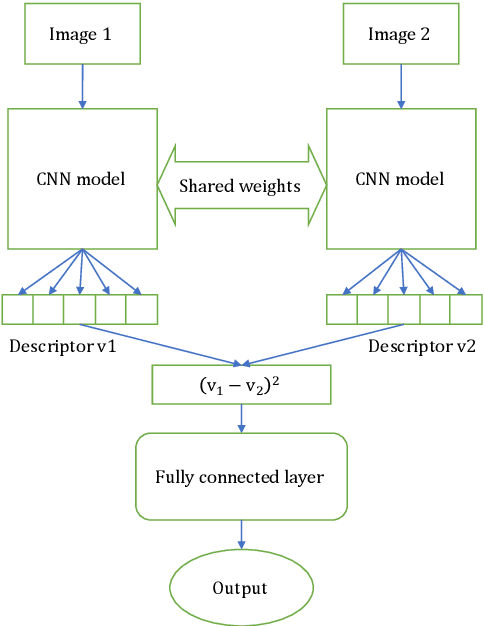
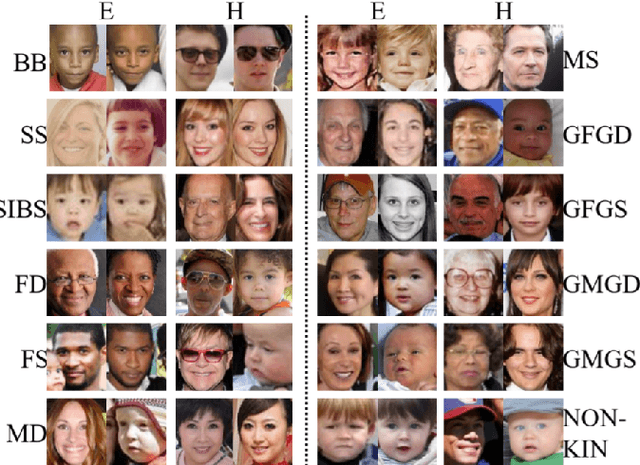
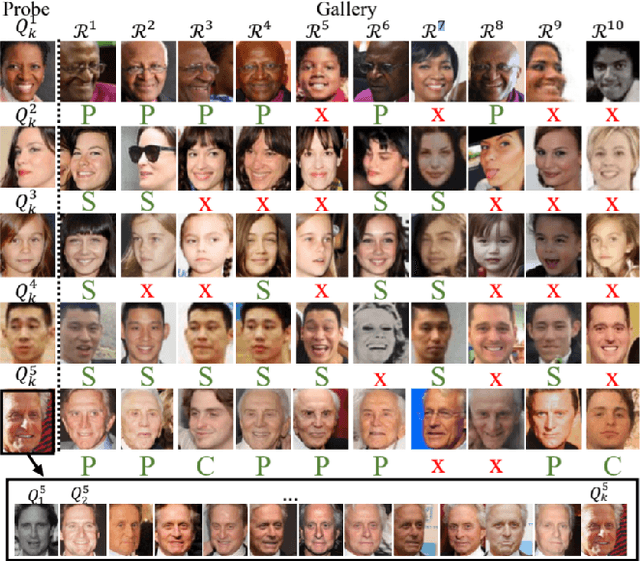
Abstract:Kinship verification and kinship retrieval are emerging tasks in computer vision. Kinship verification aims at determining whether two facial images are from related people or not, while kinship retrieval is the task of retrieving possible related facial images to a person from a gallery of images. They introduce unique challenges because of the hidden relations and features that carry inherent characteristics between the facial images. We employ 3 methods, FaceNet, Siamese VGG-Face, and a combination of FaceNet and VGG-Face models as feature extractors, to achieve the 9th standing for kinship verification and the 5th standing for kinship retrieval in the Recognizing Family in The Wild 2020 competition. We then further experimented using StyleGAN2 as another encoder, with no improvement in the result.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge