Tomoyuki Suzuki
MG-Gen: Single Image to Motion Graphics Generation with Layer Decomposition
Apr 03, 2025
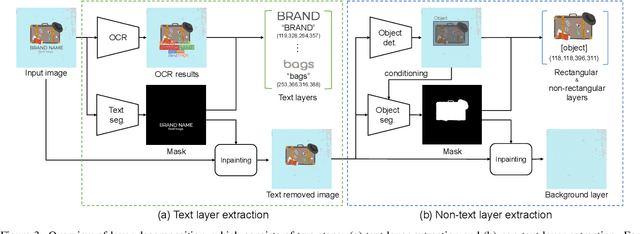


Abstract:General image-to-video generation methods often produce suboptimal animations that do not meet the requirements of animated graphics, as they lack active text motion and exhibit object distortion. Also, code-based animation generation methods typically require layer-structured vector data which are often not readily available for motion graphic generation. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework named MG-Gen that reconstructs data in vector format from a single raster image to extend the capabilities of code-based methods to enable motion graphics generation from a raster image in the framework of general image-to-video generation. MG-Gen first decomposes the input image into layer-wise elements, reconstructs them as HTML format data and then generates executable JavaScript code for the reconstructed HTML data. We experimentally confirm that \ours{} generates motion graphics while preserving text readability and input consistency. These successful results indicate that combining layer decomposition and animation code generation is an effective strategy for motion graphics generation.
Fast Sprite Decomposition from Animated Graphics
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents an approach to decomposing animated graphics into sprites, a set of basic elements or layers. Our approach builds on the optimization of sprite parameters to fit the raster video. For efficiency, we assume static textures for sprites to reduce the search space while preventing artifacts using a texture prior model. To further speed up the optimization, we introduce the initialization of the sprite parameters utilizing a pre-trained video object segmentation model and user input of single frame annotations. For our study, we construct the Crello Animation dataset from an online design service and define quantitative metrics to measure the quality of the extracted sprites. Experiments show that our method significantly outperforms baselines for similar decomposition tasks in terms of the quality/efficiency tradeoff.
Video Ads Content Structuring by Combining Scene Confidence Prediction and Tagging
Aug 20, 2021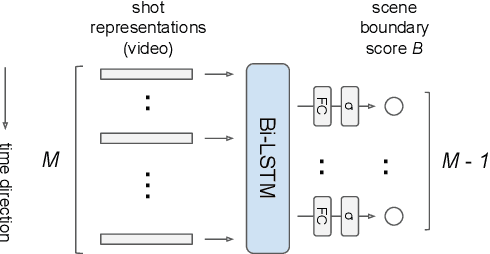

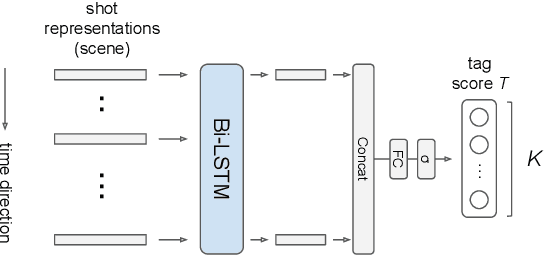
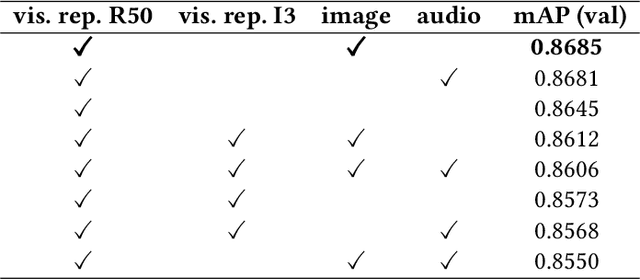
Abstract:Video ads segmentation and tagging is a challenging task due to two main reasons: (1) the video scene structure is complex and (2) it includes multiple modalities (e.g., visual, audio, text.). While previous work focuses mostly on activity videos (e.g. "cooking", "sports"), it is not clear how they can be leveraged to tackle the task of video ads content structuring. In this paper, we propose a two-stage method that first provides the boundaries of the scenes, and then combines a confidence score for each segmented scene and the tag classes predicted for that scene. We provide extensive experimental results on the network architectures and modalities used for the proposed method. Our combined method improves the previous baselines on the challenging "Tencent Advertisement Video" dataset.
Anticipating Traffic Accidents with Adaptive Loss and Large-scale Incident DB
Apr 08, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel approach for traffic accident anticipation through (i) Adaptive Loss for Early Anticipation (AdaLEA) and (ii) a large-scale self-annotated incident database for anticipation. The proposed AdaLEA allows a model to gradually learn an earlier anticipation as training progresses. The loss function adaptively assigns penalty weights depending on how early the model can an- ticipate a traffic accident at each epoch. Additionally, we construct a Near-miss Incident DataBase for anticipation. This database contains an enormous number of traffic near- miss incident videos and annotations for detail evaluation of two tasks, risk anticipation and risk-factor anticipation. In our experimental results, we found our proposal achieved the highest scores for risk anticipation (+6.6% better on mean average precision (mAP) and 2.36 sec earlier than previous work on the average time-to-collision (ATTC)) and risk-factor anticipation (+4.3% better on mAP and 0.70 sec earlier than previous work on ATTC).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge