Tomás Angles
Deep Network classification by Scattering and Homotopy dictionary learning
Oct 08, 2019
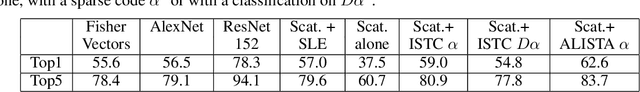
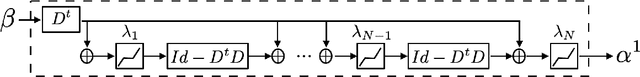
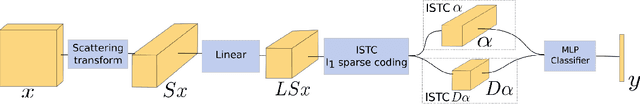
Abstract:We introduce a sparse scattering deep convolutional neural network, which provides a simple model to analyze properties of deep representation learning for classification. Learning a single dictionary matrix with a classifier yields a higher classification accuracy than AlexNet over the ImageNet ILSVRC2012 dataset. The network first applies a scattering transform which linearizes variabilities due to geometric transformations such as translations and small deformations. A sparse l1 dictionary coding reduces intra-class variability while preserving class separation through projections over unions of linear spaces. It is implemented in a deep convolutional network with a homotopy algorithm having an exponential convergence. A convergence proof is given in a general framework including ALISTA. Classification results are analyzed over ImageNet.
Kymatio: Scattering Transforms in Python
Dec 28, 2018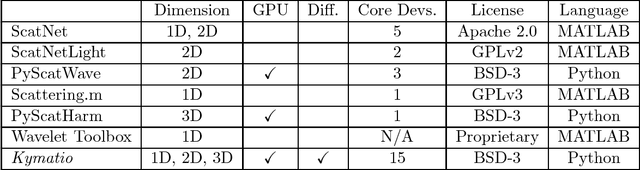
Abstract:The wavelet scattering transform is an invariant signal representation suitable for many signal processing and machine learning applications. We present the Kymatio software package, an easy-to-use, high-performance Python implementation of the scattering transform in 1D, 2D, and 3D that is compatible with modern deep learning frameworks. All transforms may be executed on a GPU (in addition to CPU), offering a considerable speed up over CPU implementations. The package also has a small memory footprint, resulting inefficient memory usage. The source code, documentation, and examples are available undera BSD license at https://www.kymat.io/
Generative networks as inverse problems with Scattering transforms
May 17, 2018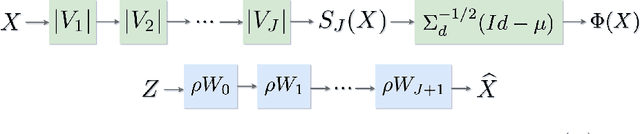
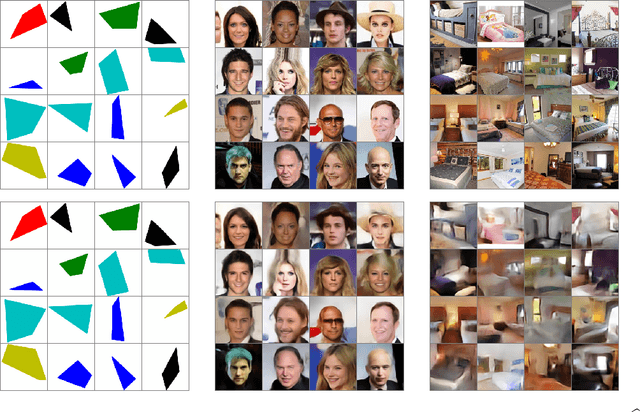
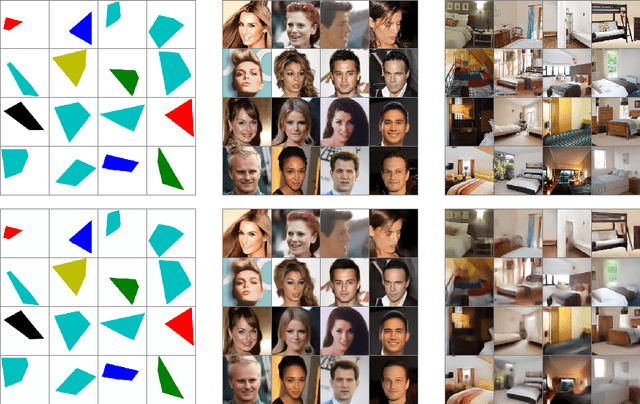


Abstract:Generative Adversarial Nets (GANs) and Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs) provide impressive image generations from Gaussian white noise, but the underlying mathematics are not well understood. We compute deep convolutional network generators by inverting a fixed embedding operator. Therefore, they do not require to be optimized with a discriminator or an encoder. The embedding is Lipschitz continuous to deformations so that generators transform linear interpolations between input white noise vectors into deformations between output images. This embedding is computed with a wavelet Scattering transform. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the resulting Scattering generators have similar properties as GANs or VAEs, without learning a discriminative network or an encoder.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge