Tom Francart
A Multi-decoder Neural Tracking Method for Accurately Predicting Speech Intelligibility
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Objective: EEG-based methods can predict speech intelligibility, but their accuracy and robustness lag behind behavioral tests, which typically show test-retest differences under 1 dB. We introduce the multi-decoder method to predict speech reception thresholds (SRTs) from EEG recordings, enabling objective assessment for populations unable to perform behavioral tests; such as those with disorders of consciousness or during hearing aid fitting. Approach: The method aggregates data from hundreds of decoders, each trained on different speech features and EEG preprocessing setups to quantify neural tracking (NT) of speech signals. Using data from 39 participants (ages 18-24), we recorded 29 minutes of EEG per person while they listened to speech at six signal-to-noise ratios and a quiet story. NT values were combined into a high-dimensional feature vector per subject, and a support vector regression model was trained to predict SRTs from these vectors. Main Result: Predictions correlated significantly with behavioral SRTs (r = 0.647, p < 0.001; NRMSE = 0.19), with all differences under 1 dB. SHAP analysis showed theta/delta bands and early lags had slightly greater influence. Using pretrained subject-independent decoders reduced required EEG data collection to 15 minutes (3 minutes of story, 12 minutes across six SNR conditions) without losing accuracy.
Unsupervised EEG-based decoding of absolute auditory attention with canonical correlation analysis
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:We propose a fully unsupervised algorithm that detects from encephalography (EEG) recordings when a subject actively listens to sound, versus when the sound is ignored. This problem is known as absolute auditory attention decoding (aAAD). We propose an unsupervised discriminative CCA model for feature extraction and combine it with an unsupervised classifier called minimally informed linear discriminant analysis (MILDA) for aAAD classification. Remarkably, the proposed unsupervised algorithm performs significantly better than a state-of-the-art supervised model. A key reason is that the unsupervised algorithm can successfully adapt to the non-stationary test data at a low computational cost. This opens the door to the analysis of the auditory attention of a subject using EEG signals with a model that automatically tunes itself to the subject without requiring an arduous supervised training session beforehand.
Performance Modeling for Correlation-based Neural Decoding of Auditory Attention to Speech
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Correlation-based auditory attention decoding (AAD) algorithms exploit neural tracking mechanisms to determine listener attention among competing speech sources via, e.g., electroencephalography signals. The correlation coefficients between the decoded neural responses and encoded speech stimuli of the different speakers then serve as AAD decision variables. A critical trade-off exists between the temporal resolution (the decision window length used to compute these correlations) and the AAD accuracy. This trade-off is typically characterized by evaluating AAD accuracy across multiple window lengths, leading to the performance curve. We propose a novel method to model this trade-off curve using labeled correlations from only a single decision window length. Our approach models the (un)attended correlations with a normal distribution after applying the Fisher transformation, enabling accurate AAD accuracy prediction across different window lengths. We validate the method on two distinct AAD implementations: a linear decoder and the non-linear VLAAI deep neural network, evaluated on separate datasets. Results show consistently low modeling errors of approximately 2 percent points, with 94% of true accuracies falling within estimated 95%-confidence intervals. The proposed method enables efficient performance curve modeling without extensive multi-window length evaluation, facilitating practical applications in, e.g., performance tracking in neuro-steered hearing devices to continuously adapt the system parameters over time.
Linear stimulus reconstruction works on the KU Leuven audiovisual, gaze-controlled auditory attention decoding dataset
Dec 02, 2024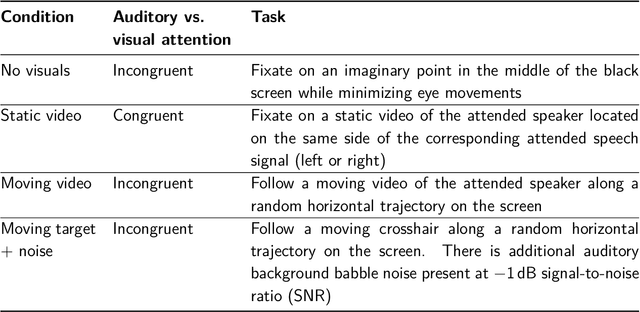
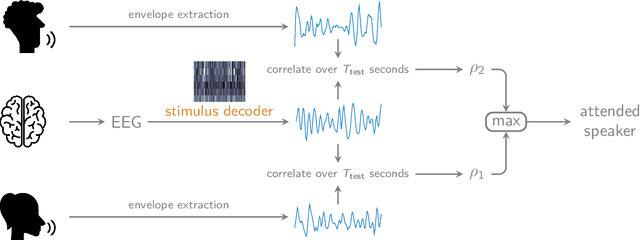
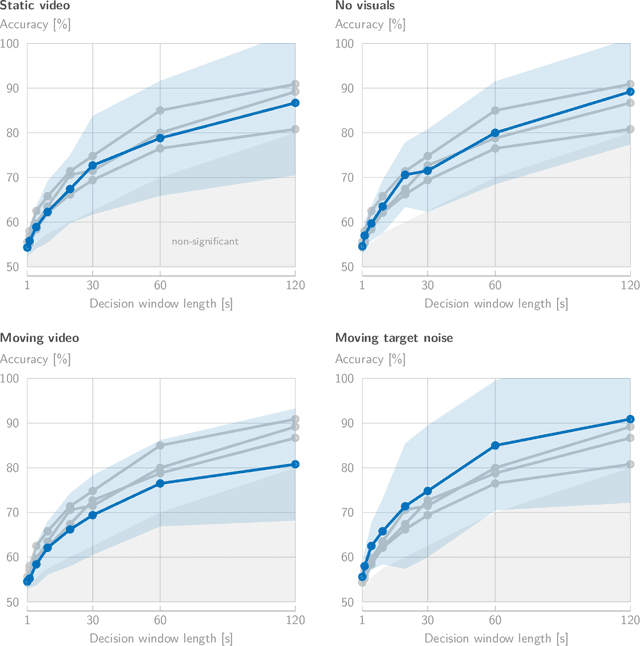
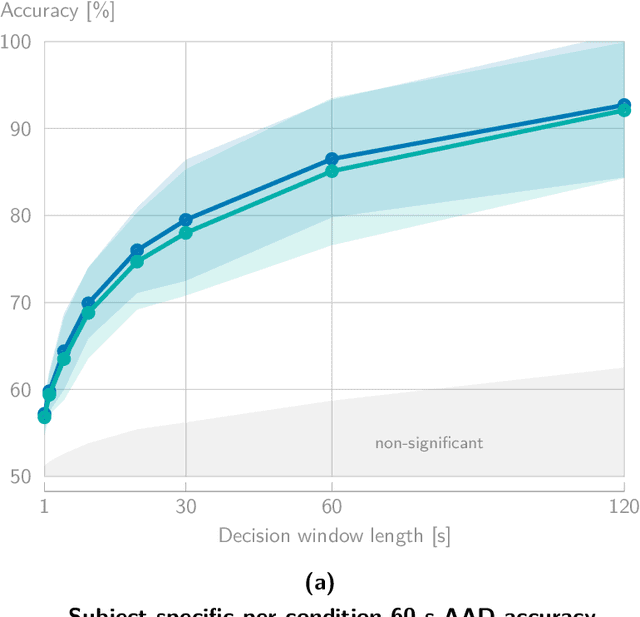
Abstract:In a recent paper, we presented the KU Leuven audiovisual, gaze-controlled auditory attention decoding (AV-GC-AAD) dataset, in which we recorded electroencephalography (EEG) signals of participants attending to one out of two competing speakers under various audiovisual conditions. The main goal of this dataset was to disentangle the direction of gaze from the direction of auditory attention, in order to reveal gaze-related shortcuts in existing spatial AAD algorithms that aim to decode the (direction of) auditory attention directly from the EEG. Various methods based on spatial AAD do not achieve significant above-chance performances on our AV-GC-AAD dataset, indicating that previously reported results were mainly driven by eye gaze confounds in existing datasets. Still, these adverse outcomes are often discarded for reasons that are attributed to the limitations of the AV-GC-AAD dataset, such as the limited amount of data to train a working model, too much data heterogeneity due to different audiovisual conditions, or participants allegedly being unable to focus their auditory attention under the complex instructions. In this paper, we present the results of the linear stimulus reconstruction AAD algorithm and show that high AAD accuracy can be obtained within each individual condition and that the model generalizes across conditions, across new subjects, and even across datasets. Therefore, we eliminate any doubts that the inadequacy of the AV-GC-AAD dataset is the primary reason for the (spatial) AAD algorithms failing to achieve above-chance performance when compared to other datasets. Furthermore, this report provides a simple baseline evaluation procedure (including source code) that can serve as the minimal benchmark for all future AAD algorithms evaluated on this dataset.
Stimulus-Informed Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis for Group Analysis of Neural Responses
Jan 31, 2024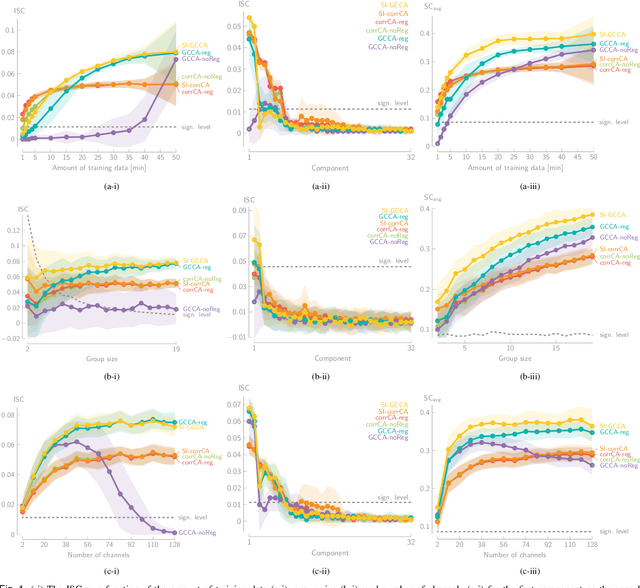
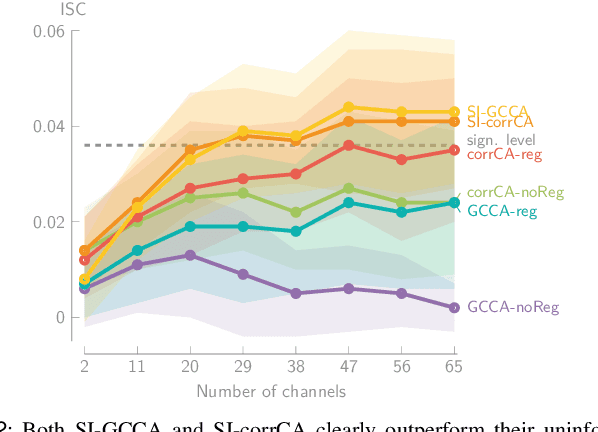
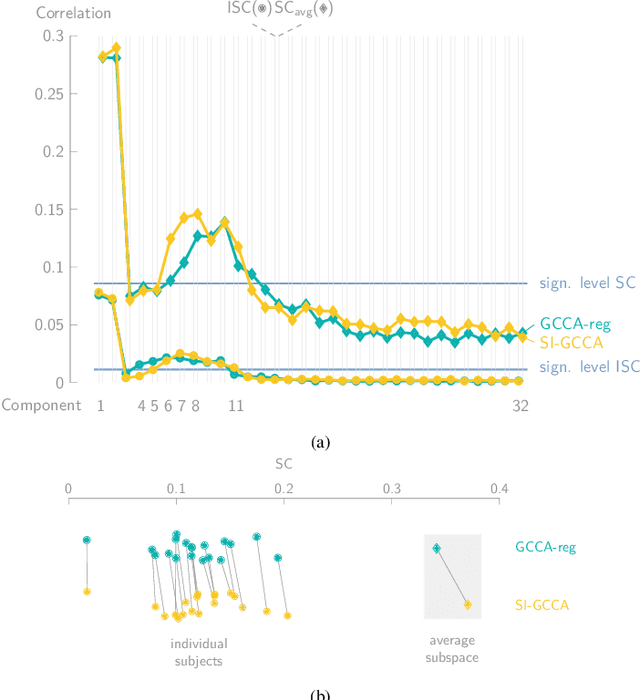
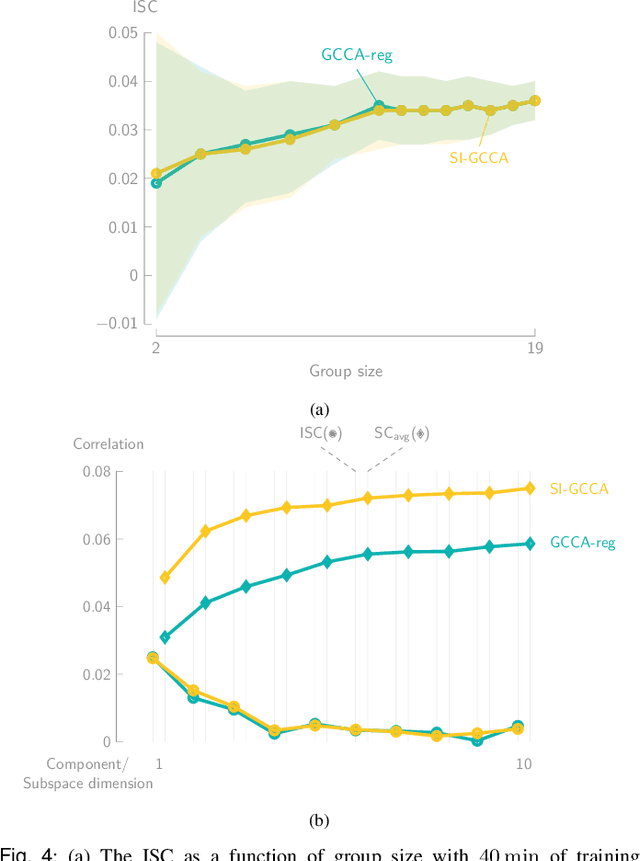
Abstract:Various new brain-computer interface technologies or neuroscience applications require decoding stimulus-following neural responses to natural stimuli such as speech and video from, e.g., electroencephalography (EEG) signals. In this context, generalized canonical correlation analysis (GCCA) is often used as a group analysis technique, which allows the extraction of correlated signal components from the neural activity of multiple subjects attending to the same stimulus. GCCA can be used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the stimulus-following neural responses relative to all other irrelevant (non-)neural activity, or to quantify the correlated neural activity across multiple subjects in a group-wise coherence metric. However, the traditional GCCA technique is stimulus-unaware: no information about the stimulus is used to estimate the correlated components from the neural data of several subjects. Therefore, the GCCA technique might fail to extract relevant correlated signal components in practical situations where the amount of information is limited, for example, because of a limited amount of training data or group size. This motivates a new stimulus-informed GCCA (SI-GCCA) framework that allows taking the stimulus into account to extract the correlated components. We show that SI-GCCA outperforms GCCA in various practical settings, for both auditory and visual stimuli. Moreover, we showcase how SI-GCCA can be used to steer the estimation of the components towards the stimulus. As such, SI-GCCA substantially improves upon GCCA for various purposes, ranging from preprocessing to quantifying attention.
Detecting Post-Stroke Aphasia Via Brain Responses to Speech in a Deep Learning Framework
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:Aphasia, a language disorder primarily caused by a stroke, is traditionally diagnosed using behavioral language tests. However, these tests are time-consuming, require manual interpretation by trained clinicians, suffer from low ecological validity, and diagnosis can be biased by comorbid motor and cognitive problems present in aphasia. In this study, we introduce an automated screening tool for speech processing impairments in aphasia that relies on time-locked brain responses to speech, known as neural tracking, within a deep learning framework. We modeled electroencephalography (EEG) responses to acoustic, segmentation, and linguistic speech representations of a story using convolutional neural networks trained on a large sample of healthy participants, serving as a model for intact neural tracking of speech. Subsequently, we evaluated our models on an independent sample comprising 26 individuals with aphasia (IWA) and 22 healthy controls. Our results reveal decreased tracking of all speech representations in IWA. Utilizing a support vector machine classifier with neural tracking measures as input, we demonstrate high accuracy in aphasia detection at the individual level (85.42\%) in a time-efficient manner (requiring 9 minutes of EEG data). Given its high robustness, time efficiency, and generalizability to unseen data, our approach holds significant promise for clinical applications.
Minimally Informed Linear Discriminant Analysis: training an LDA model with unlabelled data
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is one of the oldest and most popular linear methods for supervised classification problems. In this paper, we demonstrate that it is possible to compute the exact projection vector from LDA models based on unlabelled data, if some minimal prior information is available. More precisely, we show that only one of the following three pieces of information is actually sufficient to compute the LDA projection vector if only unlabelled data are available: (1) the class average of one of the two classes, (2) the difference between both class averages (up to a scaling), or (3) the class covariance matrices (up to a scaling). These theoretical results are validated in numerical experiments, demonstrating that this minimally informed Linear Discriminant Analysis (MILDA) model closely matches the performance of a supervised LDA model. Furthermore, we show that the MILDA projection vector can be computed in a closed form with a computational cost comparable to LDA and is able to quickly adapt to non-stationary data, making it well-suited to use as an adaptive classifier.
The role of vowel and consonant onsets in neural tracking of natural speech
Jul 31, 2023Abstract:To investigate how the auditory system processes natural speech, models have been created to relate the electroencephalography (EEG) signal of a person listening to speech to various representations of the speech. Mainly the speech envelope has been used, but also phonetic representations. We investigated to which degree of granularity phonetic representations can be related to the EEG signal. We used recorded EEG signals from 105 subjects while they listened to fairy tale stories. We utilized speech representations, including onset of any phone, vowel-consonant onsets, broad phonetic class (BPC) onsets, and narrow phonetic class (NPC) onsets, and related them to EEG using forward modeling and match-mismatch tasks. In forward modeling, we used a linear model to predict EEG from speech representations. In the match-mismatch task, we trained a long short term memory (LSTM) based model to determine which of two candidate speech segments matches with a given EEG segment. Our results show that vowel-consonant onsets outperform onsets of any phone in both tasks, which suggests that neural tracking of the vowel vs. consonant exists in the EEG to some degree. We also observed that vowel (syllable nucleus) onsets are better related to EEG compared to syllable onsets. Finally, our findings suggest that neural tracking previously thought to be associated with broad phonetic classes might actually originate from vowel-consonant onsets rather than the differentiation between different phonetic classes.
Detecting post-stroke aphasia using EEG-based neural envelope tracking of natural speech
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:[Objective]. After a stroke, one-third of patients suffer from aphasia, a language disorder that impairs communication ability. The standard behavioral tests used to diagnose aphasia are time-consuming and have low ecological validity. Neural tracking of the speech envelope is a promising tool for investigating brain responses to natural speech. The speech envelope is crucial for speech understanding, encompassing cues for processing linguistic units. In this study, we aimed to test the potential of the neural envelope tracking technique for detecting language impairments in individuals with aphasia (IWA). [Approach]. We recorded EEG from 27 IWA in the chronic phase after stroke and 22 controls while they listened to a story. We quantified neural envelope tracking in a broadband frequency range as well as in the delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma frequency bands using mutual information analysis. Besides group differences in neural tracking measures, we also tested its suitability for detecting aphasia using a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. We further investigated the required recording length for the SVM to detect aphasia and to obtain reliable outcomes. [Results]. IWA displayed decreased neural envelope tracking compared to controls in the broad, delta, theta, and gamma band. Neural tracking in these frequency bands effectively captured aphasia at the individual level (SVM accuracy 84%, AUC 88%). High-accuracy and reliable detection could be obtained with 5-7 minutes of recording time. [Significance]. Our study shows that neural tracking of speech is an effective biomarker for aphasia. We demonstrated its potential as a diagnostic tool with high reliability, individual-level detection of aphasia, and time-efficient assessment. This work represents a significant step towards more automatic, objective, and ecologically valid assessments of language impairments in aphasia.
Relating EEG to continuous speech using deep neural networks: a review
Feb 06, 2023Abstract:Objective. When a person listens to continuous speech, a corresponding response is elicited in the brain and can be recorded using electroencephalography (EEG). Linear models are presently used to relate the EEG recording to the corresponding speech signal. The ability of linear models to find a mapping between these two signals is used as a measure of neural tracking of speech. Such models are limited as they assume linearity in the EEG-speech relationship, which omits the nonlinear dynamics of the brain. As an alternative, deep learning models have recently been used to relate EEG to continuous speech, especially in auditory attention decoding (AAD) and single-speech-source paradigms. Approach. This paper reviews and comments on deep-learning-based studies that relate EEG to continuous speech in AAD and single-speech-source paradigms. We point out recurrent methodological pitfalls and the need for a standard benchmark of model analysis. Main results. We gathered 28 studies. The main methodological issues we found are biased cross-validations, data leakage leading to over-fitted models, or disproportionate data size compared to the model's complexity. In addition, we address requirements for a standard benchmark model analysis, such as public datasets, common evaluation metrics, and good practices for the match-mismatch task. Significance. We are the first to present a review paper summarizing the main deep-learning-based studies that relate EEG to speech while addressing methodological pitfalls and important considerations for this newly expanding field. Our study is particularly relevant given the growing application of deep learning in EEG-speech decoding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge