Todd Hudson
Evaluating OCR Performance for Assistive Technology: Effects of Walking Speed, Camera Placement, and Camera Type
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Optical character recognition (OCR), which converts printed or handwritten text into machine-readable form, is widely used in assistive technology for people with blindness and low vision. Yet, most evaluations rely on static datasets that do not reflect the challenges of mobile use. In this study, we systematically evaluated OCR performance under both static and dynamic conditions. Static tests measured detection range across distances of 1-7 meters and viewing angles of 0-75 degrees horizontally. Dynamic tests examined the impact of motion by varying walking speed from slow (0.8 m/s) to very fast (1.8 m/s) and comparing three camera mounting positions: head-mounted, shoulder-mounted, and hand-held. We evaluated both a smartphone and smart glasses, using the phone's main and ultra-wide cameras. Four OCR engines were benchmarked to assess accuracy at different distances and viewing angles: Google Vision, PaddleOCR 3.0, EasyOCR, and Tesseract. PaddleOCR 3.0 was then used to evaluate accuracy at different walking speeds. Accuracy was computed at the character level using the Levenshtein ratio against manually defined ground truth. Results showed that recognition accuracy declined with increased walking speed and wider viewing angles. Google Vision achieved the highest overall accuracy, with PaddleOCR close behind as the strongest open-source alternative. Across devices, the phone's main camera achieved the highest accuracy, and a shoulder-mounted placement yielded the highest average among body positions; however, differences among shoulder, head, and hand were not statistically significant.
Network-Aware 5G Edge Computing for Object Detection: Augmenting Wearables to "See'' More, Farther and Faster
Dec 25, 2021


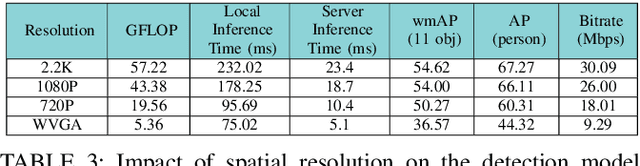
Abstract:Advanced wearable devices are increasingly incorporating high-resolution multi-camera systems. As state-of-the-art neural networks for processing the resulting image data are computationally demanding, there has been growing interest in leveraging fifth generation (5G) wireless connectivity and mobile edge computing for offloading this processing to the cloud. To assess this possibility, this paper presents a detailed simulation and evaluation of 5G wireless offloading for object detection within a powerful, new smart wearable called VIS4ION, for the Blind-and-Visually Impaired (BVI). The current VIS4ION system is an instrumented book-bag with high-resolution cameras, vision processing and haptic and audio feedback. The paper considers uploading the camera data to a mobile edge cloud to perform real-time object detection and transmitting the detection results back to the wearable. To determine the video requirements, the paper evaluates the impact of video bit rate and resolution on object detection accuracy and range. A new street scene dataset with labeled objects relevant to BVI navigation is leveraged for analysis. The vision evaluation is combined with a detailed full-stack wireless network simulation to determine the distribution of throughputs and delays with real navigation paths and ray-tracing from new high-resolution 3D models in an urban environment. For comparison, the wireless simulation considers both a standard 4G-Long Term Evolution (LTE) carrier and high-rate 5G millimeter-wave (mmWave) carrier. The work thus provides a thorough and realistic assessment of edge computing with mmWave connectivity in an application with both high bandwidth and low latency requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge