Tianyi Jiang
Explore Briefly, Then Decide: Mitigating LLM Overthinking via Cumulative Entropy Regulation
Oct 02, 2025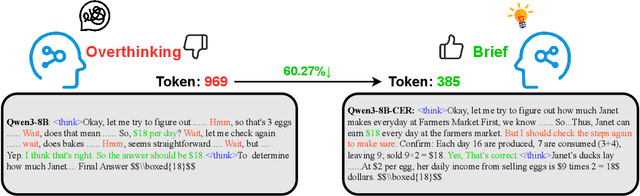
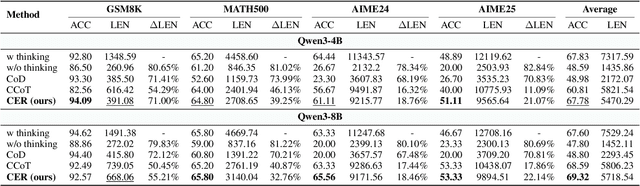
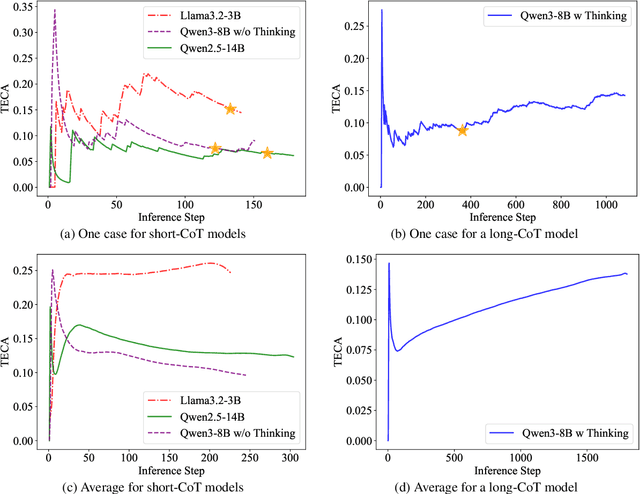
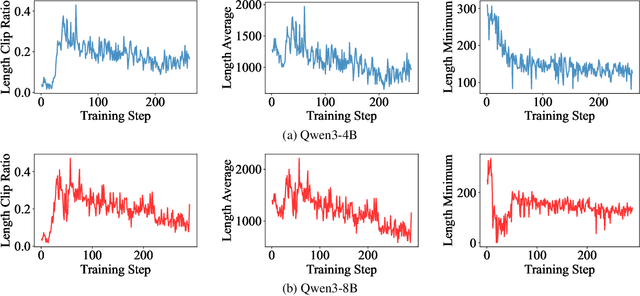
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning abilities on complex problems using long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. However, they often suffer from overthinking, meaning generating unnecessarily lengthy reasoning steps for simpler problems. This issue may degrade the efficiency of the models and make them difficult to adapt the reasoning depth to the complexity of problems. To address this, we introduce a novel metric Token Entropy Cumulative Average (TECA), which measures the extent of exploration throughout the reasoning process. We further propose a novel reasoning paradigm -- Explore Briefly, Then Decide -- with an associated Cumulative Entropy Regulation (CER) mechanism. This paradigm leverages TECA to help the model dynamically determine the optimal point to conclude its thought process and provide a final answer, thus achieving efficient reasoning. Experimental results across diverse mathematical benchmarks show that our approach substantially mitigates overthinking without sacrificing problem-solving ability. With our thinking paradigm, the average response length decreases by up to 71% on simpler datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method in creating a more efficient and adaptive reasoning process.
Adaptive Substructure-Aware Expert Model for Molecular Property Prediction
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Molecular property prediction is essential for applications such as drug discovery and toxicity assessment. While Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown promising results by modeling molecules as molecular graphs, their reliance on data-driven learning limits their ability to generalize, particularly in the presence of data imbalance and diverse molecular substructures. Existing methods often overlook the varying contributions of different substructures to molecular properties, treating them uniformly. To address these challenges, we propose ASE-Mol, a novel GNN-based framework that leverages a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) approach for molecular property prediction. ASE-Mol incorporates BRICS decomposition and significant substructure awareness to dynamically identify positive and negative substructures. By integrating a MoE architecture, it reduces the adverse impact of negative motifs while improving adaptability to positive motifs. Experimental results on eight benchmark datasets demonstrate that ASE-Mol achieves state-of-the-art performance, with significant improvements in both accuracy and interpretability.
Knowledge-enhanced Relation Graph and Task Sampling for Few-shot Molecular Property Prediction
May 24, 2024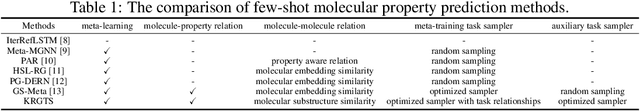
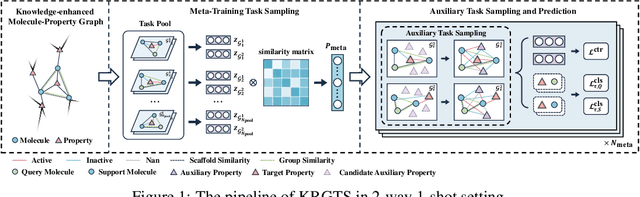
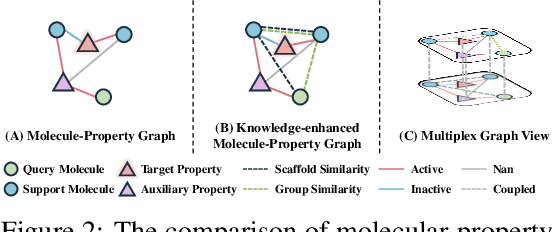
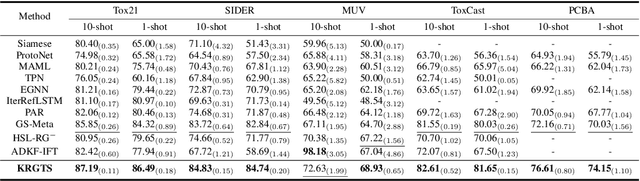
Abstract:Recently, few-shot molecular property prediction (FSMPP) has garnered increasing attention. Despite impressive breakthroughs achieved by existing methods, they often overlook the inherent many-to-many relationships between molecules and properties, which limits their performance. For instance, similar substructures of molecules can inspire the exploration of new compounds. Additionally, the relationships between properties can be quantified, with high-related properties providing more information in exploring the target property than those low-related. To this end, this paper proposes a novel meta-learning FSMPP framework (KRGTS), which comprises the Knowledge-enhanced Relation Graph module and the Task Sampling module. The knowledge-enhanced relation graph module constructs the molecule-property multi-relation graph (MPMRG) to capture the many-to-many relationships between molecules and properties. The task sampling module includes a meta-training task sampler and an auxiliary task sampler, responsible for scheduling the meta-training process and sampling high-related auxiliary tasks, respectively, thereby achieving efficient meta-knowledge learning and reducing noise introduction. Empirically, extensive experiments on five datasets demonstrate the superiority of KRGTS over a variety of state-of-the-art methods. The code is available in https://github.com/Vencent-Won/KRGTS-public.
Multi-Modal Representation Learning for Molecular Property Prediction: Sequence, Graph, Geometry
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:Molecular property prediction refers to the task of labeling molecules with some biochemical properties, playing a pivotal role in the drug discovery and design process. Recently, with the advancement of machine learning, deep learning-based molecular property prediction has emerged as a solution to the resource-intensive nature of traditional methods, garnering significant attention. Among them, molecular representation learning is the key factor for molecular property prediction performance. And there are lots of sequence-based, graph-based, and geometry-based methods that have been proposed. However, the majority of existing studies focus solely on one modality for learning molecular representations, failing to comprehensively capture molecular characteristics and information. In this paper, a novel multi-modal representation learning model, which integrates the sequence, graph, and geometry characteristics, is proposed for molecular property prediction, called SGGRL. Specifically, we design a fusion layer to fusion the representation of different modalities. Furthermore, to ensure consistency across modalities, SGGRL is trained to maximize the similarity of representations for the same molecule while minimizing similarity for different molecules. To verify the effectiveness of SGGRL, seven molecular datasets, and several baselines are used for evaluation and comparison. The experimental results demonstrate that SGGRL consistently outperforms the baselines in most cases. This further underscores the capability of SGGRL to comprehensively capture molecular information. Overall, the proposed SGGRL model showcases its potential to revolutionize molecular property prediction by leveraging multi-modal representation learning to extract diverse and comprehensive molecular insights. Our code is released at https://github.com/Vencent-Won/SGGRL.
Development of a Swarm UAV Simulator Integrating Realistic Motion Control Models For Disaster Operations
Nov 01, 2017

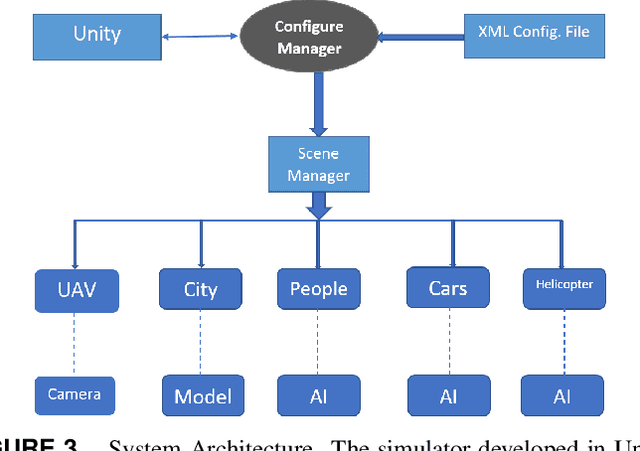
Abstract:Simulation environments for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) can be very useful for prototyping user interfaces and training personnel that will operate UAVs in the real world. The realistic operation of such simulations will only enhance the value of such training. In this paper, we present the integration of a model-based waypoint navigation controller into the Reno Rescue Simulator for the purposes of providing a more realistic user interface in simulated environments. We also present potential uses for such simulations, even for real-world operation of UAVs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge