Thomas Swiger
Improved Planetary Rover Inertial Navigation and Wheel Odometry Performance through Periodic Use of Zero-Type Constraints
Jun 20, 2019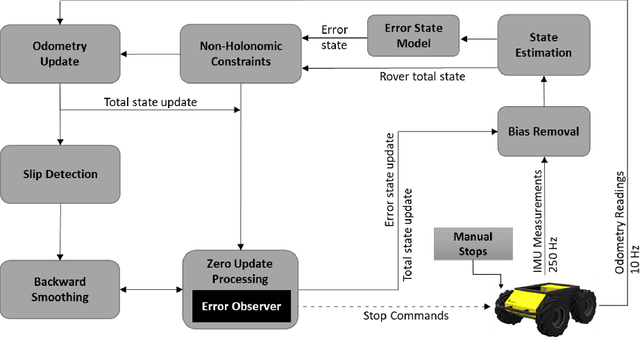

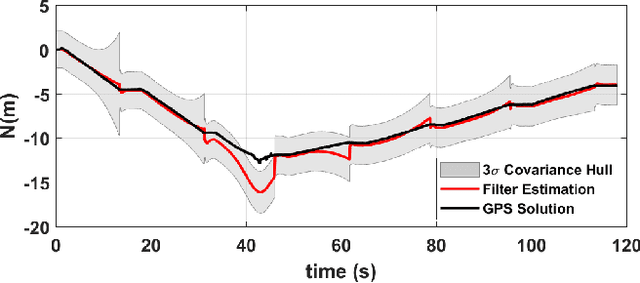
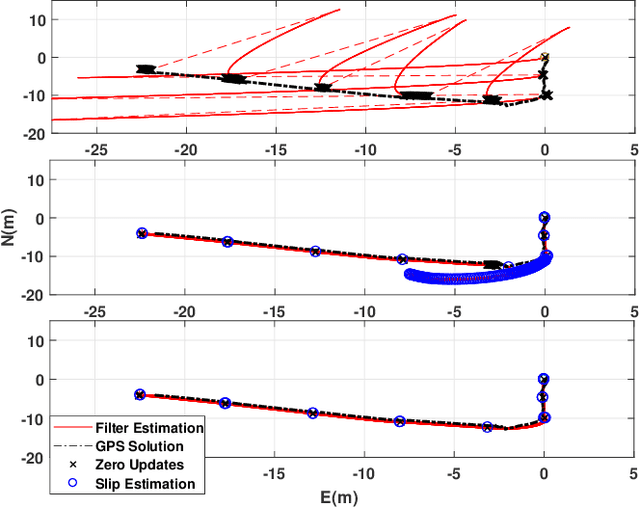
Abstract:We present an approach to enhance wheeled planetary rover dead-reckoning localization performance by leveraging the use of zero-type constraint equations in the navigation filter. Without external aiding, inertial navigation solutions inherently exhibit cubic error growth. Furthermore, for planetary rovers that are traversing diverse types of terrain, wheel odometry is often unreliable for use in localization, due to wheel slippage. For current Mars rovers, computer vision-based approaches are generally used whenever there is a high possibility of positioning error; however, these strategies require additional computational power, energy resources, and significantly slow down the rover traverse speed. To this end, we propose a navigation approach that compensates for the high likelihood of odometry errors by providing a reliable navigation solution that leverages non-holonomic vehicle constraints as well as state-aware pseudo-measurements (e.g., zero velocity and zero angular rate) updates during periodic stops. By using this, computationally expensive visual-based corrections could be performed less often. Experimental tests that compare against GPS-based localization are used to demonstrate the accuracy of the proposed approach. The source code, post-processing scripts, and example datasets associated with the paper are published in a public repository.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge