Thomas Britton
eLog analysis for accelerators: status and future outlook
Jun 15, 2025
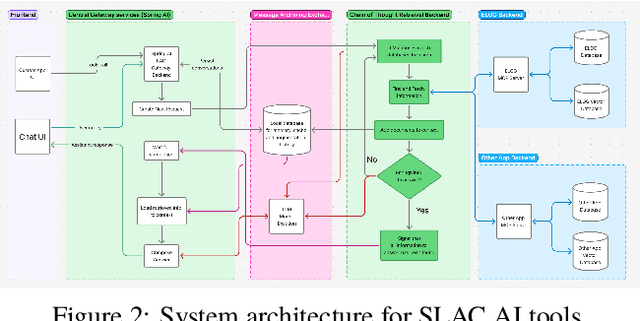
Abstract:This work demonstrates electronic logbook (eLog) systems leveraging modern AI-driven information retrieval capabilities at the accelerator facilities of Fermilab, Jefferson Lab, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. We evaluate contemporary tools and methodologies for information retrieval with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAGs), focusing on operational insights and integration with existing accelerator control systems. The study addresses challenges and proposes solutions for state-of-the-art eLog analysis through practical implementations, demonstrating applications and limitations. We present a framework for enhancing accelerator facility operations through improved information accessibility and knowledge management, which could potentially lead to more efficient operations.
Hydra: Computer Vision for Data Quality Monitoring
Mar 01, 2024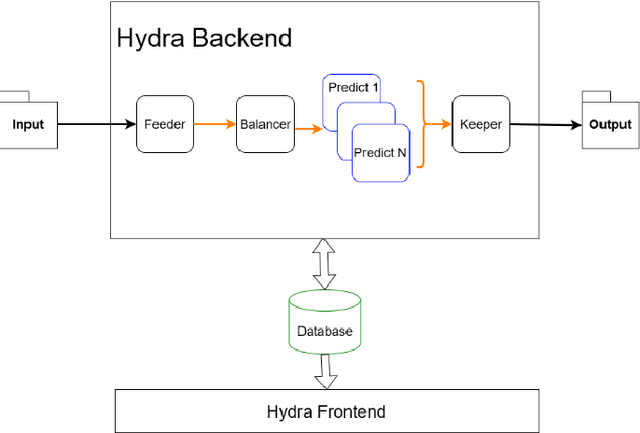
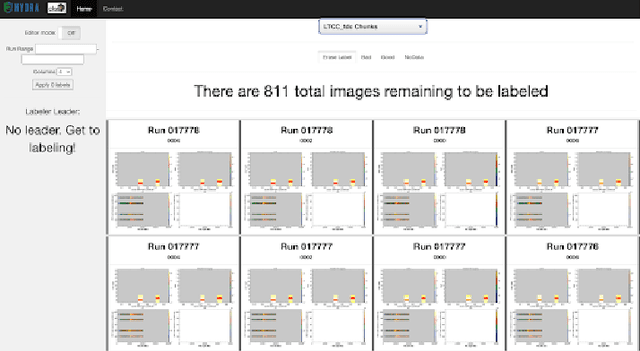
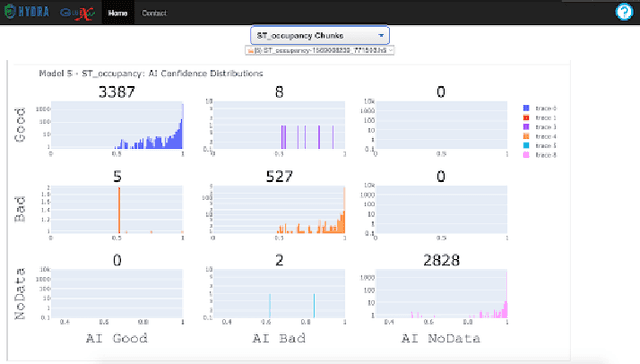
Abstract:Hydra is a system which utilizes computer vision to perform near real time data quality management, initially developed for Hall-D in 2019. Since then, it has been deployed across all experimental halls at Jefferson Lab, with the CLAS12 collaboration in Hall-B being the first outside of GlueX to fully utilize Hydra. The system comprises back end processes that manage the models, their inferences, and the data flow. The front-end components, accessible via web pages, allow detector experts and shift crews to view and interact with the system. This talk will give an overview of the Hydra system as well as highlight significant developments in Hydra's feature set, acute challenges with operating Hydra in all halls, and lessons learned along the way.
Distance Preserving Machine Learning for Uncertainty Aware Accelerator Capacitance Predictions
Jul 05, 2023Abstract:Providing accurate uncertainty estimations is essential for producing reliable machine learning models, especially in safety-critical applications such as accelerator systems. Gaussian process models are generally regarded as the gold standard method for this task, but they can struggle with large, high-dimensional datasets. Combining deep neural networks with Gaussian process approximation techniques have shown promising results, but dimensionality reduction through standard deep neural network layers is not guaranteed to maintain the distance information necessary for Gaussian process models. We build on previous work by comparing the use of the singular value decomposition against a spectral-normalized dense layer as a feature extractor for a deep neural Gaussian process approximation model and apply it to a capacitance prediction problem for the High Voltage Converter Modulators in the Oak Ridge Spallation Neutron Source. Our model shows improved distance preservation and predicts in-distribution capacitance values with less than 1% error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge