Thi Ngoc Trang Tran
Sustainability Evaluation Metrics for Recommender Systems
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Sustainability-oriented evaluation metrics can help to assess the quality of recommender systems beyond wide-spread metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and satisfaction. Following the United Nations`s sustainable development goals (SDGs), such metrics can help to analyse the impact of recommender systems on environmental, social, and economic aspects. We discuss different basic sustainability evaluation metrics for recommender systems and analyze their applications.
Recommender Systems for Sustainability: Overview and Research Issues
Dec 04, 2024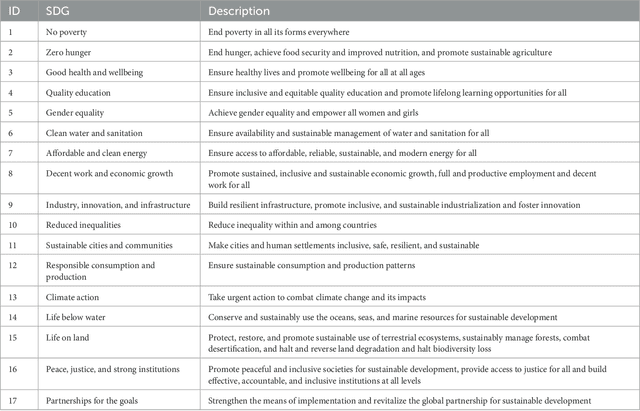
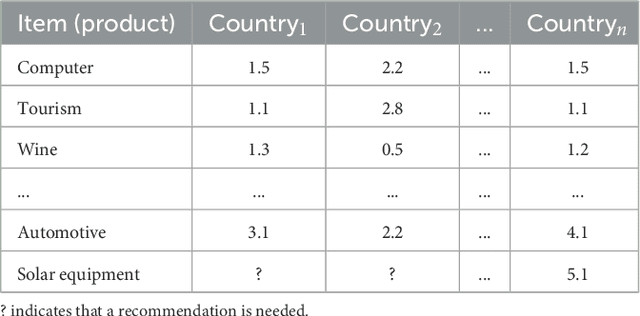

Abstract:Sustainability development goals (SDGs) are regarded as a universal call to action with the overall objectives of planet protection, ending of poverty, and ensuring peace and prosperity for all people. In order to achieve these objectives, different AI technologies play a major role. Specifically, recommender systems can provide support for organizations and individuals to achieve the defined goals. Recommender systems integrate AI technologies such as machine learning, explainable AI (XAI), case-based reasoning, and constraint solving in order to find and explain user-relevant alternatives from a potentially large set of options. In this article, we summarize the state of the art in applying recommender systems to support the achievement of sustainability development goals. In this context, we discuss open issues for future research.
Less is More: Towards Sustainability-Aware Persuasive Explanations in Recommender Systems
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Recommender systems play an important role in supporting the achievement of the United Nations sustainable development goals (SDGs). In recommender systems, explanations can support different goals, such as increasing a user's trust in a recommendation, persuading a user to purchase specific items, or increasing the understanding of the reasons behind a recommendation. In this paper, we discuss the concept of "sustainability-aware persuasive explanations" which we regard as a major concept to support the achievement of the mentioned SDGs. Such explanations are orthogonal to most existing explanation approaches since they focus on a "less is more" principle, which per se is not included in existing e-commerce platforms. Based on a user study in three item domains, we analyze the potential impacts of sustainability-aware persuasive explanations. The study results are promising regarding user acceptance and the potential impacts of such explanations.
Sports Recommender Systems: Overview and Research Issues
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Sports recommender systems receive an increasing attention due to their potential of fostering healthy living, improving personal well-being, and increasing performances in sport. These systems support people in sports, for example, by the recommendation of healthy and performance boosting food items, the recommendation of training practices, talent and team recommendation, and the recommendation of specific tactics in competitions. With applications in the virtual world, for example, the recommendation of maps or opponents in e-sports, these systems already transcend conventional sports scenarios where physical presence is needed. On the basis of different working examples, we present an overview of sports recommender systems applications and techniques. Overall, we analyze the related state-of-the-art and discuss open research issues.
Concentrating on the Impact: Consequence-based Explanations in Recommender Systems
Aug 31, 2023
Abstract:Recommender systems assist users in decision-making, where the presentation of recommended items and their explanations are critical factors for enhancing the overall user experience. Although various methods for generating explanations have been proposed, there is still room for improvement, particularly for users who lack expertise in a specific item domain. In this study, we introduce the novel concept of \textit{consequence-based explanations}, a type of explanation that emphasizes the individual impact of consuming a recommended item on the user, which makes the effect of following recommendations clearer. We conducted an online user study to examine our assumption about the appreciation of consequence-based explanations and their impacts on different explanation aims in recommender systems. Our findings highlight the importance of consequence-based explanations, which were well-received by users and effectively improved user satisfaction in recommender systems. These results provide valuable insights for designing engaging explanations that can enhance the overall user experience in decision-making.
FastDiagP: An Algorithm for Parallelized Direct Diagnosis
May 11, 2023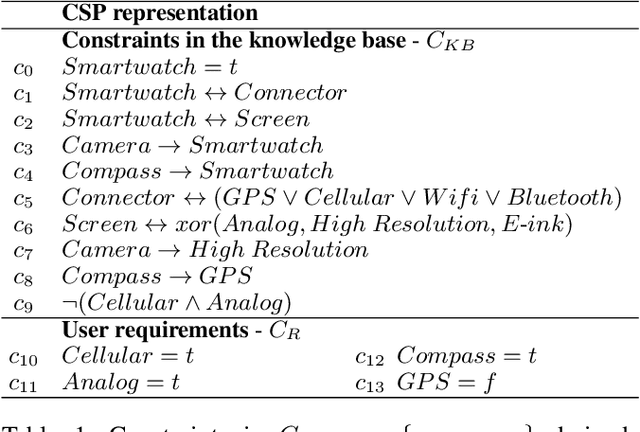
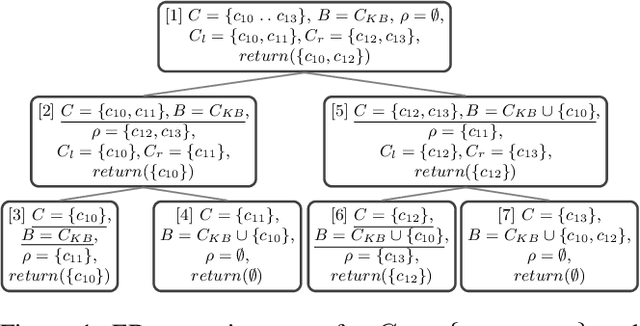
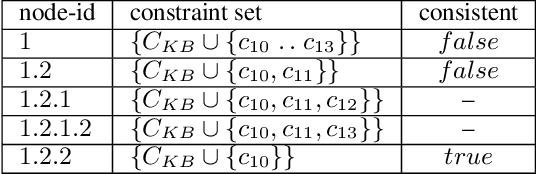
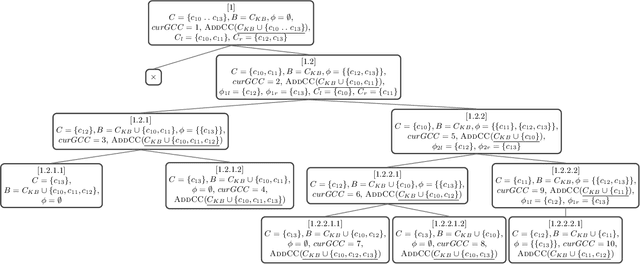
Abstract:Constraint-based applications attempt to identify a solution that meets all defined user requirements. If the requirements are inconsistent with the underlying constraint set, algorithms that compute diagnoses for inconsistent constraints should be implemented to help users resolve the "no solution could be found" dilemma. FastDiag is a typical direct diagnosis algorithm that supports diagnosis calculation without predetermining conflicts. However, this approach faces runtime performance issues, especially when analyzing complex and large-scale knowledge bases. In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm, so-called FastDiagP, which is based on the idea of speculative programming. This algorithm extends FastDiag by integrating a parallelization mechanism that anticipates and pre-calculates consistency checks requested by FastDiag. This mechanism helps to provide consistency checks with fast answers and boosts the algorithm's runtime performance. The performance improvements of our proposed algorithm have been shown through empirical results using the Linux-2.6.3.33 configuration knowledge base.
Configuring Multiple Instances with Multi-Configuration
Sep 20, 2021Abstract:Configuration is a successful application area of Artificial Intelligence. In the majority of the cases, configuration systems focus on configuring one solution (configuration) that satisfies the preferences of a single user or a group of users. In this paper, we introduce a new configuration approach - multi-configuration - that focuses on scenarios where the outcome of a configuration process is a set of configurations. Example applications thereof are the configuration of personalized exams for individual students, the configuration of project teams, reviewer-to-paper assignment, and hotel room assignments including individualized city trips for tourist groups. For multi-configuration scenarios, we exemplify a constraint satisfaction problem representation in the context of configuring exams. The paper is concluded with a discussion of open issues for future work.
An Overview of Recommender Systems and Machine Learning in Feature Modeling and Configuration
Feb 12, 2021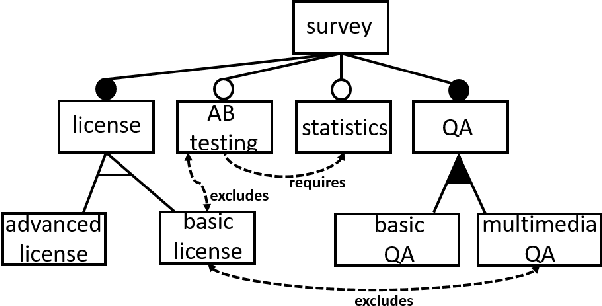
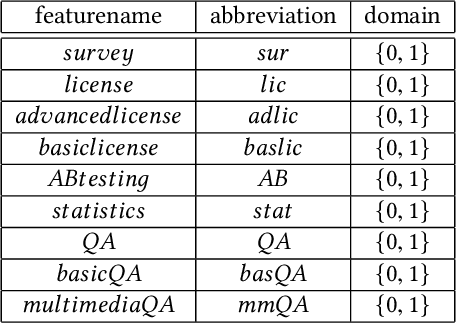
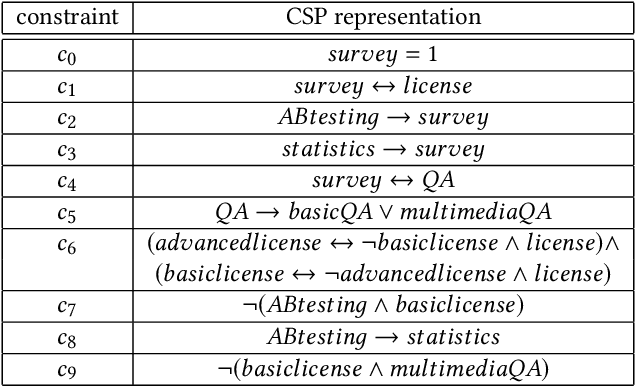

Abstract:Recommender systems support decisions in various domains ranging from simple items such as books and movies to more complex items such as financial services, telecommunication equipment, and software systems. In this context, recommendations are determined, for example, on the basis of analyzing the preferences of similar users. In contrast to simple items which can be enumerated in an item catalog, complex items have to be represented on the basis of variability models (e.g., feature models) since a complete enumeration of all possible configurations is infeasible and would trigger significant performance issues. In this paper, we give an overview of a potential new line of research which is related to the application of recommender systems and machine learning techniques in feature modeling and configuration. In this context, we give examples of the application of recommender systems and machine learning and discuss future research issues.
DirectDebug: Automated Testing and Debugging of Feature Models
Feb 11, 2021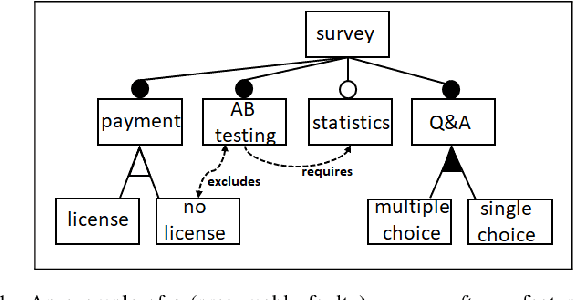
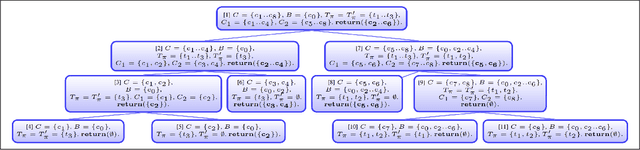

Abstract:Variability models (e.g., feature models) are a common way for the representation of variabilities and commonalities of software artifacts. Such models can be translated to a logical representation and thus allow different operations for quality assurance and other types of model property analysis. Specifically, complex and often large-scale feature models can become faulty, i.e., do not represent the expected variability properties of the underlying software artifact. In this paper, we introduce DirectDebug which is a direct diagnosis approach to the automated testing and debugging of variability models. The algorithm helps software engineers by supporting an automated identification of faulty constraints responsible for an unintended behavior of a variability model. This approach can significantly decrease development and maintenance efforts for such models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge