Seda Polat-Erdeniz
Recommender Systems for Sustainability: Overview and Research Issues
Dec 04, 2024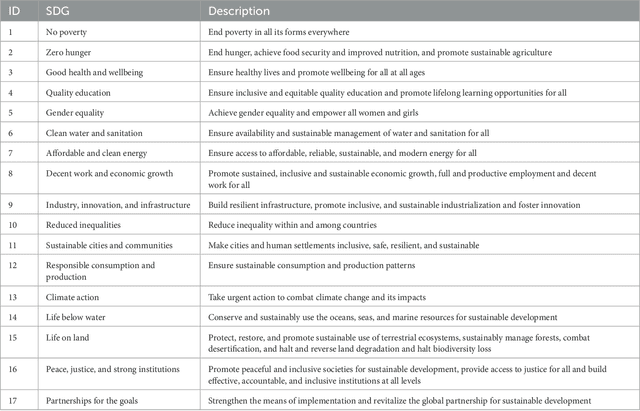
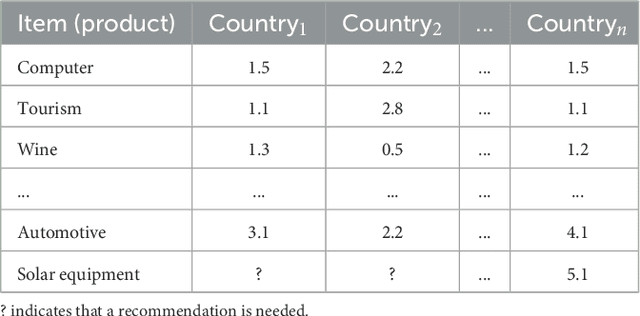

Abstract:Sustainability development goals (SDGs) are regarded as a universal call to action with the overall objectives of planet protection, ending of poverty, and ensuring peace and prosperity for all people. In order to achieve these objectives, different AI technologies play a major role. Specifically, recommender systems can provide support for organizations and individuals to achieve the defined goals. Recommender systems integrate AI technologies such as machine learning, explainable AI (XAI), case-based reasoning, and constraint solving in order to find and explain user-relevant alternatives from a potentially large set of options. In this article, we summarize the state of the art in applying recommender systems to support the achievement of sustainability development goals. In this context, we discuss open issues for future research.
Sports Recommender Systems: Overview and Research Issues
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Sports recommender systems receive an increasing attention due to their potential of fostering healthy living, improving personal well-being, and increasing performances in sport. These systems support people in sports, for example, by the recommendation of healthy and performance boosting food items, the recommendation of training practices, talent and team recommendation, and the recommendation of specific tactics in competitions. With applications in the virtual world, for example, the recommendation of maps or opponents in e-sports, these systems already transcend conventional sports scenarios where physical presence is needed. On the basis of different working examples, we present an overview of sports recommender systems applications and techniques. Overall, we analyze the related state-of-the-art and discuss open research issues.
Configuring Multiple Instances with Multi-Configuration
Sep 20, 2021Abstract:Configuration is a successful application area of Artificial Intelligence. In the majority of the cases, configuration systems focus on configuring one solution (configuration) that satisfies the preferences of a single user or a group of users. In this paper, we introduce a new configuration approach - multi-configuration - that focuses on scenarios where the outcome of a configuration process is a set of configurations. Example applications thereof are the configuration of personalized exams for individual students, the configuration of project teams, reviewer-to-paper assignment, and hotel room assignments including individualized city trips for tourist groups. For multi-configuration scenarios, we exemplify a constraint satisfaction problem representation in the context of configuring exams. The paper is concluded with a discussion of open issues for future work.
Anytime Diagnosis for Reconfiguration
Feb 19, 2021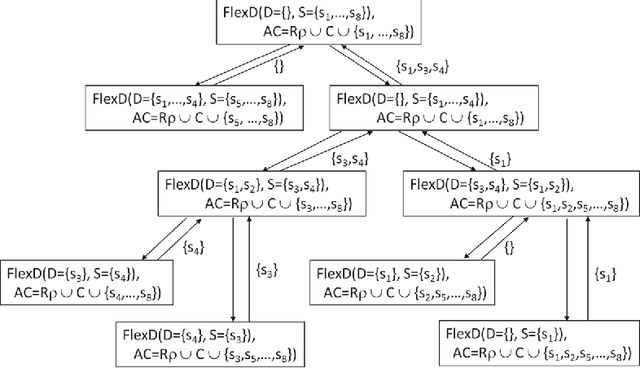
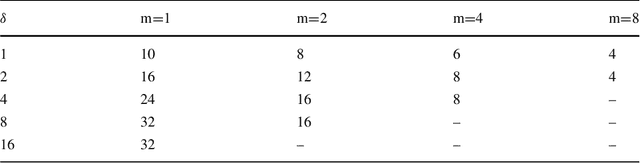
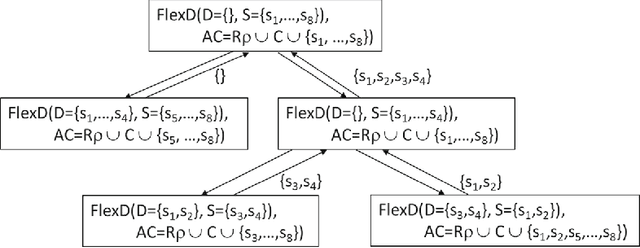
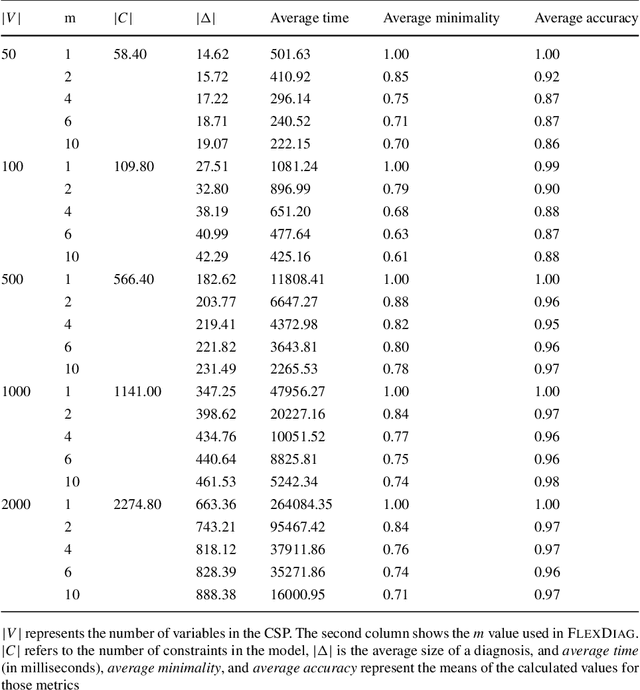
Abstract:Many domains require scalable algorithms that help to determine diagnoses efficiently and often within predefined time limits. Anytime diagnosis is able to determine solutions in such a way and thus is especially useful in real-time scenarios such as production scheduling, robot control, and communication networks management where diagnosis and corresponding reconfiguration capabilities play a major role. Anytime diagnosis in many cases comes along with a trade-off between diagnosis quality and the efficiency of diagnostic reasoning. In this paper we introduce and analyze FlexDiag which is an anytime direct diagnosis approach. We evaluate the algorithm with regard to performance and diagnosis quality using a configuration benchmark from the domain of feature models and an industrial configuration knowledge base from the automotive domain. Results show that FlexDiag helps to significantly increase the performance of direct diagnosis search with corresponding quality tradeoffs in terms of minimality and accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge