Thao Nguyen Truong
Diffusion-Inspired Reconfiguration of Transformers for Uncertainty Calibration
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Uncertainty calibration in pre-trained transformers is critical for their reliable deployment in risk-sensitive applications. Yet, most existing pre-trained transformers do not have a principled mechanism for uncertainty propagation through their feature transformation stack. In this work, we propose a diffusion-inspired reconfiguration of transformers in which each feature transformation block is modeled as a probabilistic mapping. Composing these probabilistic mappings reveals a probability path that mimics the structure of a diffusion process, transporting data mass from the input distribution to the pre-trained feature distribution. This probability path can then be recompiled on a diffusion process with a unified transition model to enable principled propagation of representation uncertainty throughout the pre-trained model's architecture while maintaining its original predictive performance. Empirical results across a variety of vision and language benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves superior calibration and predictive accuracy compared to existing uncertainty-aware transformers.
Causal Graph Learning via Distributional Invariance of Cause-Effect Relationship
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:This paper introduces a new framework for recovering causal graphs from observational data, leveraging the observation that the distribution of an effect, conditioned on its causes, remains invariant to changes in the prior distribution of those causes. This insight enables a direct test for potential causal relationships by checking the variance of their corresponding effect-cause conditional distributions across multiple downsampled subsets of the data. These subsets are selected to reflect different prior cause distributions, while preserving the effect-cause conditional relationships. Using this invariance test and exploiting an (empirical) sparsity of most causal graphs, we develop an algorithm that efficiently uncovers causal relationships with quadratic complexity in the number of observational variables, reducing the processing time by up to 25x compared to state-of-the-art methods. Our empirical experiments on a varied benchmark of large-scale datasets show superior or equivalent performance compared to existing works, while achieving enhanced scalability.
Rethinking Cross-Modal Fine-Tuning: Optimizing the Interaction between Feature Alignment and Target Fitting
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Adapting pre-trained models to unseen feature modalities has become increasingly important due to the growing need for cross-disciplinary knowledge integration.~A key challenge here is how to align the representation of new modalities with the most relevant parts of the pre-trained model's representation space to enable accurate knowledge transfer.~This requires combining feature alignment with target fine-tuning, but uncalibrated combinations can exacerbate misalignment between the source and target feature-label structures and reduce target generalization.~Existing work however lacks a theoretical understanding of this critical interaction between feature alignment and target fitting.~To bridge this gap, we develop a principled framework that establishes a provable generalization bound on the target error, which explains the interaction between feature alignment and target fitting through a novel concept of feature-label distortion.~This bound offers actionable insights into how this interaction should be optimized for practical algorithm design. The resulting approach achieves significantly improved performance over state-of-the-art methods across a wide range of benchmark datasets.
PADM: A Physics-aware Diffusion Model for Attenuation Correction
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Attenuation artifacts remain a significant challenge in cardiac Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (MPI) using Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), often compromising diagnostic accuracy and reducing clinical interpretability. While hybrid SPECT/CT systems mitigate these artifacts through CT-derived attenuation maps, their high cost, limited accessibility, and added radiation exposure hinder widespread clinical adoption. In this study, we propose a novel CT-free solution to attenuation correction in cardiac SPECT. Specifically, we introduce Physics-aware Attenuation Correction Diffusion Model (PADM), a diffusion-based generative method that incorporates explicit physics priors via a teacher--student distillation mechanism. This approach enables attenuation artifact correction using only Non-Attenuation-Corrected (NAC) input, while still benefiting from physics-informed supervision during training. To support this work, we also introduce CardiAC, a comprehensive dataset comprising 424 patient studies with paired NAC and Attenuation-Corrected (AC) reconstructions, alongside high-resolution CT-based attenuation maps. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PADM outperforms state-of-the-art generative models, delivering superior reconstruction fidelity across both quantitative metrics and visual assessment.
Boosting Offline Optimizers with Surrogate Sensitivity
Mar 06, 2025


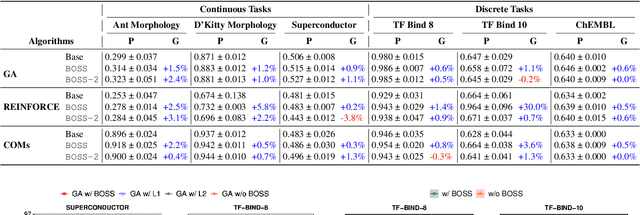
Abstract:Offline optimization is an important task in numerous material engineering domains where online experimentation to collect data is too expensive and needs to be replaced by an in silico maximization of a surrogate of the black-box function. Although such a surrogate can be learned from offline data, its prediction might not be reliable outside the offline data regime, which happens when the surrogate has narrow prediction margin and is (therefore) sensitive to small perturbations of its parameterization. This raises the following questions: (1) how to regulate the sensitivity of a surrogate model; and (2) whether conditioning an offline optimizer with such less sensitive surrogate will lead to better optimization performance. To address these questions, we develop an optimizable sensitivity measurement for the surrogate model, which then inspires a sensitivity-informed regularizer that is applicable to a wide range of offline optimizers. This development is both orthogonal and synergistic to prior research on offline optimization, which is demonstrated in our extensive experiment benchmark.
Incorporating Surrogate Gradient Norm to Improve Offline Optimization Techniques
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Offline optimization has recently emerged as an increasingly popular approach to mitigate the prohibitively expensive cost of online experimentation. The key idea is to learn a surrogate of the black-box function that underlines the target experiment using a static (offline) dataset of its previous input-output queries. Such an approach is, however, fraught with an out-of-distribution issue where the learned surrogate becomes inaccurate outside the offline data regimes. To mitigate this, existing offline optimizers have proposed numerous conditioning techniques to prevent the learned surrogate from being too erratic. Nonetheless, such conditioning strategies are often specific to particular surrogate or search models, which might not generalize to a different model choice. This motivates us to develop a model-agnostic approach instead, which incorporates a notion of model sharpness into the training loss of the surrogate as a regularizer. Our approach is supported by a new theoretical analysis demonstrating that reducing surrogate sharpness on the offline dataset provably reduces its generalized sharpness on unseen data. Our analysis extends existing theories from bounding generalized prediction loss (on unseen data) with loss sharpness to bounding the worst-case generalized surrogate sharpness with its empirical estimate on training data, providing a new perspective on sharpness regularization. Our extensive experimentation on a diverse range of optimization tasks also shows that reducing surrogate sharpness often leads to significant improvement, marking (up to) a noticeable 9.6% performance boost. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/cuong-dm/IGNITE
CT to PET Translation: A Large-scale Dataset and Domain-Knowledge-Guided Diffusion Approach
Oct 29, 2024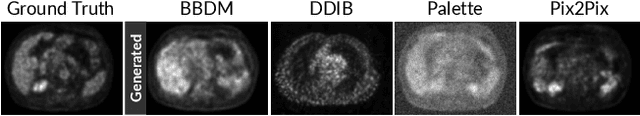



Abstract:Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT) are essential for diagnosing, staging, and monitoring various diseases, particularly cancer. Despite their importance, the use of PET/CT systems is limited by the necessity for radioactive materials, the scarcity of PET scanners, and the high cost associated with PET imaging. In contrast, CT scanners are more widely available and significantly less expensive. In response to these challenges, our study addresses the issue of generating PET images from CT images, aiming to reduce both the medical examination cost and the associated health risks for patients. Our contributions are twofold: First, we introduce a conditional diffusion model named CPDM, which, to our knowledge, is one of the initial attempts to employ a diffusion model for translating from CT to PET images. Second, we provide the largest CT-PET dataset to date, comprising 2,028,628 paired CT-PET images, which facilitates the training and evaluation of CT-to-PET translation models. For the CPDM model, we incorporate domain knowledge to develop two conditional maps: the Attention map and the Attenuation map. The former helps the diffusion process focus on areas of interest, while the latter improves PET data correction and ensures accurate diagnostic information. Experimental evaluations across various benchmarks demonstrate that CPDM surpasses existing methods in generating high-quality PET images in terms of multiple metrics. The source code and data samples are available at https://github.com/thanhhff/CPDM.
High Accurate and Explainable Multi-Pill Detection Framework with Graph Neural Network-Assisted Multimodal Data Fusion
Mar 17, 2023


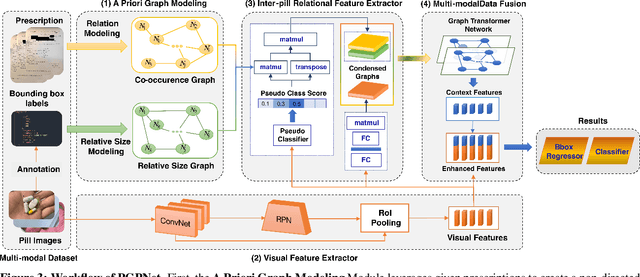
Abstract:Due to the significant resemblance in visual appearance, pill misuse is prevalent and has become a critical issue, responsible for one-third of all deaths worldwide. Pill identification, thus, is a crucial concern needed to be investigated thoroughly. Recently, several attempts have been made to exploit deep learning to tackle the pill identification problem. However, most published works consider only single-pill identification and fail to distinguish hard samples with identical appearances. Also, most existing pill image datasets only feature single pill images captured in carefully controlled environments under ideal lighting conditions and clean backgrounds. In this work, we are the first to tackle the multi-pill detection problem in real-world settings, aiming at localizing and identifying pills captured by users in a pill intake. Moreover, we also introduce a multi-pill image dataset taken in unconstrained conditions. To handle hard samples, we propose a novel method for constructing heterogeneous a priori graphs incorporating three forms of inter-pill relationships, including co-occurrence likelihood, relative size, and visual semantic correlation. We then offer a framework for integrating a priori with pills' visual features to enhance detection accuracy. Our experimental results have proved the robustness, reliability, and explainability of the proposed framework. Experimentally, it outperforms all detection benchmarks in terms of all evaluation metrics. Specifically, our proposed framework improves COCO mAP metrics by 9.4% over Faster R-CNN and 12.0% compared to vanilla YOLOv5. Our study opens up new opportunities for protecting patients from medication errors using an AI-based pill identification solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge