Manh Cuong Dao
Diffusion-Inspired Reconfiguration of Transformers for Uncertainty Calibration
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Uncertainty calibration in pre-trained transformers is critical for their reliable deployment in risk-sensitive applications. Yet, most existing pre-trained transformers do not have a principled mechanism for uncertainty propagation through their feature transformation stack. In this work, we propose a diffusion-inspired reconfiguration of transformers in which each feature transformation block is modeled as a probabilistic mapping. Composing these probabilistic mappings reveals a probability path that mimics the structure of a diffusion process, transporting data mass from the input distribution to the pre-trained feature distribution. This probability path can then be recompiled on a diffusion process with a unified transition model to enable principled propagation of representation uncertainty throughout the pre-trained model's architecture while maintaining its original predictive performance. Empirical results across a variety of vision and language benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves superior calibration and predictive accuracy compared to existing uncertainty-aware transformers.
Rethinking Cross-Modal Fine-Tuning: Optimizing the Interaction between Feature Alignment and Target Fitting
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Adapting pre-trained models to unseen feature modalities has become increasingly important due to the growing need for cross-disciplinary knowledge integration.~A key challenge here is how to align the representation of new modalities with the most relevant parts of the pre-trained model's representation space to enable accurate knowledge transfer.~This requires combining feature alignment with target fine-tuning, but uncalibrated combinations can exacerbate misalignment between the source and target feature-label structures and reduce target generalization.~Existing work however lacks a theoretical understanding of this critical interaction between feature alignment and target fitting.~To bridge this gap, we develop a principled framework that establishes a provable generalization bound on the target error, which explains the interaction between feature alignment and target fitting through a novel concept of feature-label distortion.~This bound offers actionable insights into how this interaction should be optimized for practical algorithm design. The resulting approach achieves significantly improved performance over state-of-the-art methods across a wide range of benchmark datasets.
Boosting Offline Optimizers with Surrogate Sensitivity
Mar 06, 2025


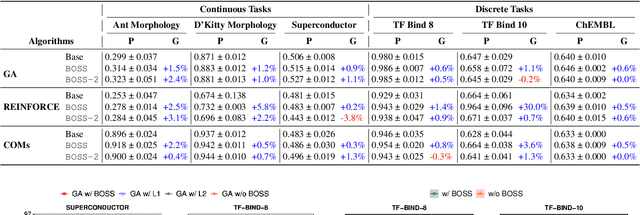
Abstract:Offline optimization is an important task in numerous material engineering domains where online experimentation to collect data is too expensive and needs to be replaced by an in silico maximization of a surrogate of the black-box function. Although such a surrogate can be learned from offline data, its prediction might not be reliable outside the offline data regime, which happens when the surrogate has narrow prediction margin and is (therefore) sensitive to small perturbations of its parameterization. This raises the following questions: (1) how to regulate the sensitivity of a surrogate model; and (2) whether conditioning an offline optimizer with such less sensitive surrogate will lead to better optimization performance. To address these questions, we develop an optimizable sensitivity measurement for the surrogate model, which then inspires a sensitivity-informed regularizer that is applicable to a wide range of offline optimizers. This development is both orthogonal and synergistic to prior research on offline optimization, which is demonstrated in our extensive experiment benchmark.
Incorporating Surrogate Gradient Norm to Improve Offline Optimization Techniques
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Offline optimization has recently emerged as an increasingly popular approach to mitigate the prohibitively expensive cost of online experimentation. The key idea is to learn a surrogate of the black-box function that underlines the target experiment using a static (offline) dataset of its previous input-output queries. Such an approach is, however, fraught with an out-of-distribution issue where the learned surrogate becomes inaccurate outside the offline data regimes. To mitigate this, existing offline optimizers have proposed numerous conditioning techniques to prevent the learned surrogate from being too erratic. Nonetheless, such conditioning strategies are often specific to particular surrogate or search models, which might not generalize to a different model choice. This motivates us to develop a model-agnostic approach instead, which incorporates a notion of model sharpness into the training loss of the surrogate as a regularizer. Our approach is supported by a new theoretical analysis demonstrating that reducing surrogate sharpness on the offline dataset provably reduces its generalized sharpness on unseen data. Our analysis extends existing theories from bounding generalized prediction loss (on unseen data) with loss sharpness to bounding the worst-case generalized surrogate sharpness with its empirical estimate on training data, providing a new perspective on sharpness regularization. Our extensive experimentation on a diverse range of optimization tasks also shows that reducing surrogate sharpness often leads to significant improvement, marking (up to) a noticeable 9.6% performance boost. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/cuong-dm/IGNITE
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge