Terence Lim
Position: Thematic Analysis of Unstructured Clinical Transcripts with Large Language Models
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:This position paper examines how large language models (LLMs) can support thematic analysis of unstructured clinical transcripts, a widely used but resource-intensive method for uncovering patterns in patient and provider narratives. We conducted a systematic review of recent studies applying LLMs to thematic analysis, complemented by an interview with a practicing clinician. Our findings reveal that current approaches remain fragmented across multiple dimensions including types of thematic analysis, datasets, prompting strategies and models used, most notably in evaluation. Existing evaluation methods vary widely (from qualitative expert review to automatic similarity metrics), hindering progress and preventing meaningful benchmarking across studies. We argue that establishing standardized evaluation practices is critical for advancing the field. To this end, we propose an evaluation framework centered on three dimensions: validity, reliability, and interpretability.
TAMA: A Human-AI Collaborative Thematic Analysis Framework Using Multi-Agent LLMs for Clinical Interviews
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Thematic analysis (TA) is a widely used qualitative approach for uncovering latent meanings in unstructured text data. TA provides valuable insights in healthcare but is resource-intensive. Large Language Models (LLMs) have been introduced to perform TA, yet their applications in healthcare remain unexplored. Here, we propose TAMA: A Human-AI Collaborative Thematic Analysis framework using Multi-Agent LLMs for clinical interviews. We leverage the scalability and coherence of multi-agent systems through structured conversations between agents and coordinate the expertise of cardiac experts in TA. Using interview transcripts from parents of children with Anomalous Aortic Origin of a Coronary Artery (AAOCA), a rare congenital heart disease, we demonstrate that TAMA outperforms existing LLM-assisted TA approaches, achieving higher thematic hit rate, coverage, and distinctiveness. TAMA demonstrates strong potential for automated TA in clinical settings by leveraging multi-agent LLM systems with human-in-the-loop integration by enhancing quality while significantly reducing manual workload.
LLM-TA: An LLM-Enhanced Thematic Analysis Pipeline for Transcripts from Parents of Children with Congenital Heart Disease
Feb 03, 2025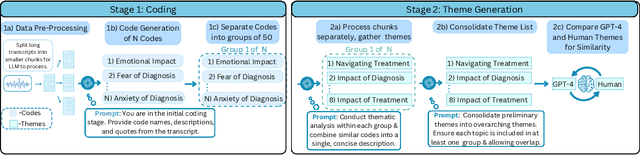
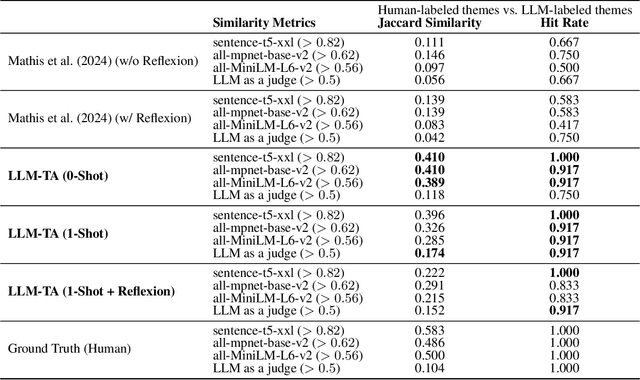
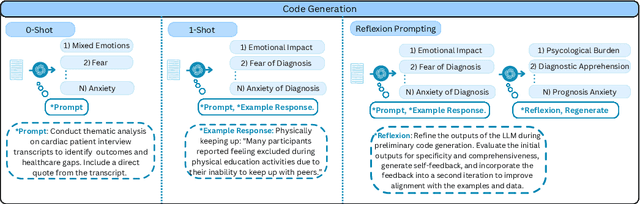
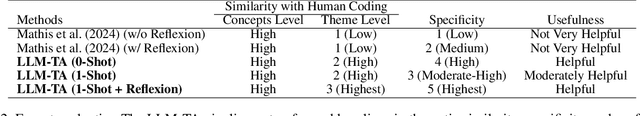
Abstract:Thematic Analysis (TA) is a fundamental method in healthcare research for analyzing transcript data, but it is resource-intensive and difficult to scale for large, complex datasets. This study investigates the potential of large language models (LLMs) to augment the inductive TA process in high-stakes healthcare settings. Focusing on interview transcripts from parents of children with Anomalous Aortic Origin of a Coronary Artery (AAOCA), a rare congenital heart disease, we propose an LLM-Enhanced Thematic Analysis (LLM-TA) pipeline. Our pipeline integrates an affordable state-of-the-art LLM (GPT-4o mini), LangChain, and prompt engineering with chunking techniques to analyze nine detailed transcripts following the inductive TA framework. We evaluate the LLM-generated themes against human-generated results using thematic similarity metrics, LLM-assisted assessments, and expert reviews. Results demonstrate that our pipeline outperforms existing LLM-assisted TA methods significantly. While the pipeline alone has not yet reached human-level quality in inductive TA, it shows great potential to improve scalability, efficiency, and accuracy while reducing analyst workload when working collaboratively with domain experts. We provide practical recommendations for incorporating LLMs into high-stakes TA workflows and emphasize the importance of close collaboration with domain experts to address challenges related to real-world applicability and dataset complexity. https://github.com/jiaweixu98/LLM-TA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge