Syed Safwan Khalid
NPT-Loss: A Metric Loss with Implicit Mining for Face Recognition
Mar 05, 2021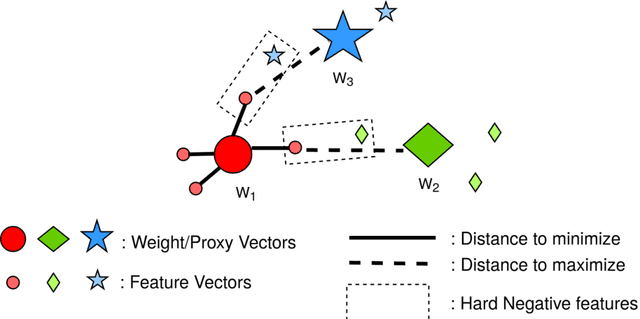

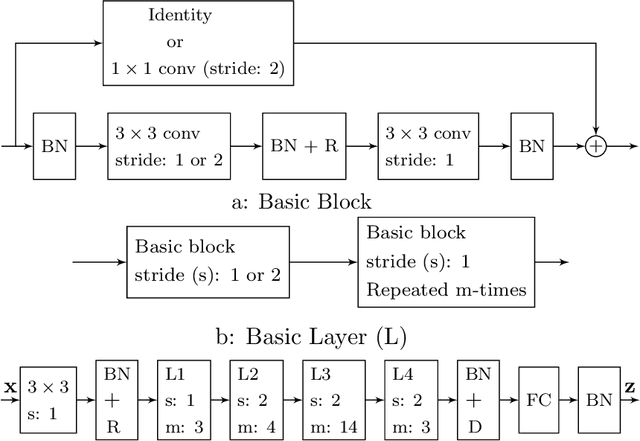
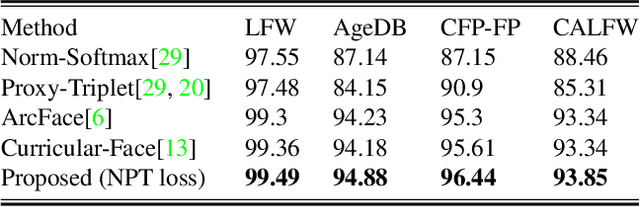
Abstract:Face recognition (FR) using deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) has seen remarkable success in recent years. One key ingredient of DCNN-based FR is the appropriate design of a loss function that ensures discrimination between various identities. The state-of-the-art (SOTA) solutions utilise normalised Softmax loss with additive and/or multiplicative margins. Despite being popular, these Softmax+margin based losses are not theoretically motivated and the effectiveness of a margin is justified only intuitively. In this work, we utilise an alternative framework that offers a more direct mechanism of achieving discrimination among the features of various identities. We propose a novel loss that is equivalent to a triplet loss with proxies and an implicit mechanism of hard-negative mining. We give theoretical justification that minimising the proposed loss ensures a minimum separability between all identities. The proposed loss is simple to implement and does not require heavy hyper-parameter tuning as in the SOTA solutions. We give empirical evidence that despite its simplicity, the proposed loss consistently achieves SOTA performance in various benchmarks for both high-resolution and low-resolution FR tasks.
AXM-Net: Cross-Modal Context Sharing Attention Network for Person Re-ID
Jan 19, 2021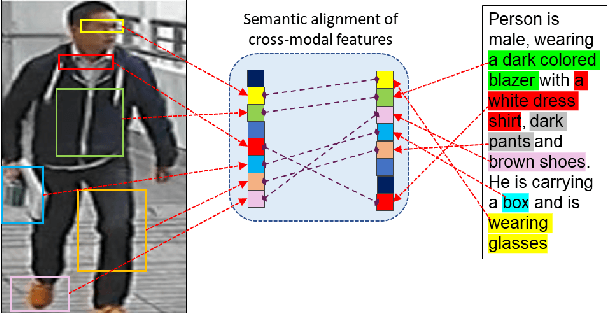
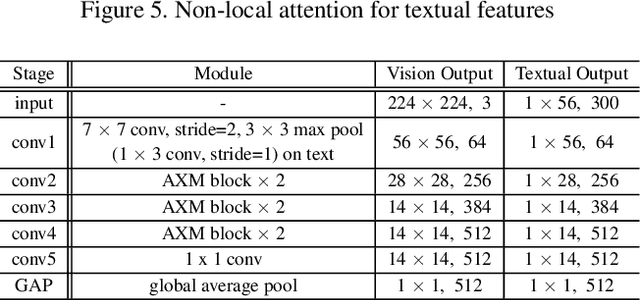
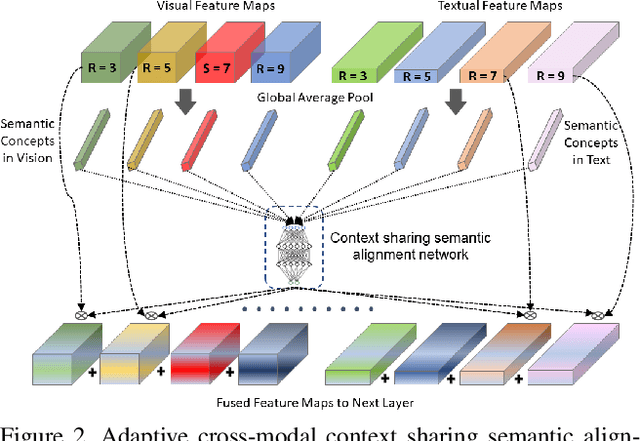
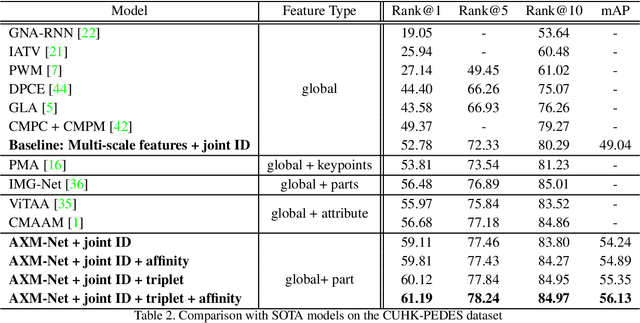
Abstract:Cross-modal person re-identification (Re-ID) is critical for modern video surveillance systems. The key challenge is to align inter-modality representations according to semantic information present for a person and ignore background information. In this work, we present AXM-Net, a novel CNN based architecture designed for learning semantically aligned visual and textual representations. The underlying building block consists of multiple streams of feature maps coming from visual and textual modalities and a novel learnable context sharing semantic alignment network. We also propose complementary intra modal attention learning mechanisms to focus on more fine-grained local details in the features along with a cross-modal affinity loss for robust feature matching. Our design is unique in its ability to implicitly learn feature alignments from data. The entire AXM-Net can be trained in an end-to-end manner. We report results on both person search and cross-modal Re-ID tasks. Extensive experimentation validates the proposed framework and demonstrates its superiority by outperforming the current state-of-the-art methods by a significant margin.
A Convolutional Baseline for Person Re-Identification Using Vision and Language Descriptions
Feb 20, 2020

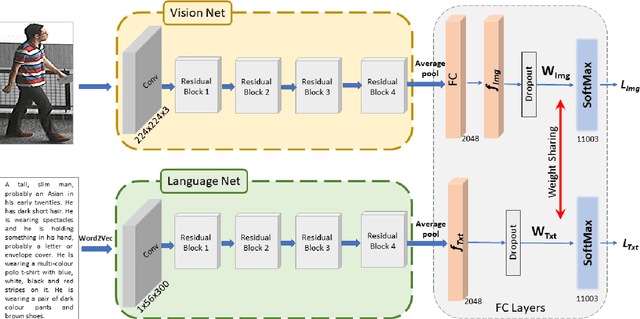

Abstract:Classical person re-identification approaches assume that a person of interest has appeared across different cameras and can be queried by one of the existing images. However, in real-world surveillance scenarios, frequently no visual information will be available about the queried person. In such scenarios, a natural language description of the person by a witness will provide the only source of information for retrieval. In this work, person re-identification using both vision and language information is addressed under all possible gallery and query scenarios. A two stream deep convolutional neural network framework supervised by cross entropy loss is presented. The weights connecting the second last layer to the last layer with class probabilities, i.e., logits of softmax layer are shared in both networks. Canonical Correlation Analysis is performed to enhance the correlation between the two modalities in a joint latent embedding space. To investigate the benefits of the proposed approach, a new testing protocol under a multi modal ReID setting is proposed for the test split of the CUHK-PEDES and CUHK-SYSU benchmarks. The experimental results verify the merits of the proposed system. The learnt visual representations are more robust and perform 22\% better during retrieval as compared to a single modality system. The retrieval with a multi modal query greatly enhances the re-identification capability of the system quantitatively as well as qualitatively.
Higher-Degree Stochastic Integration Filtering
Aug 01, 2016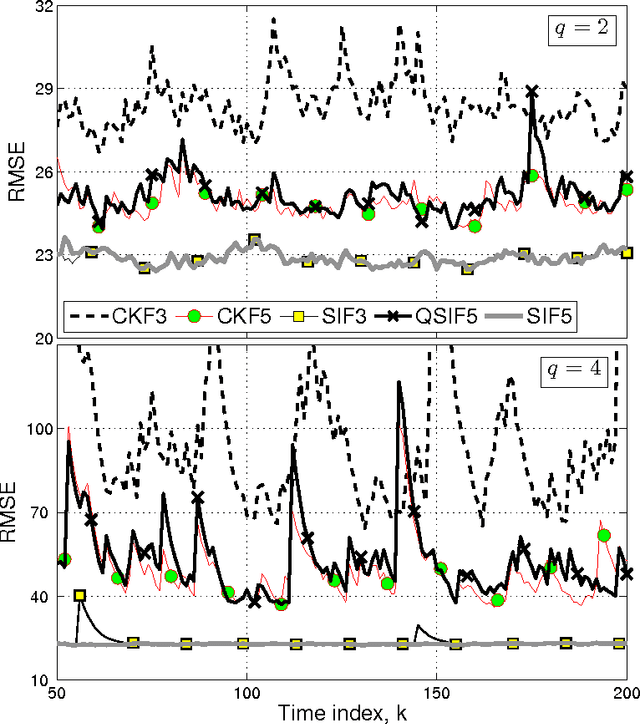
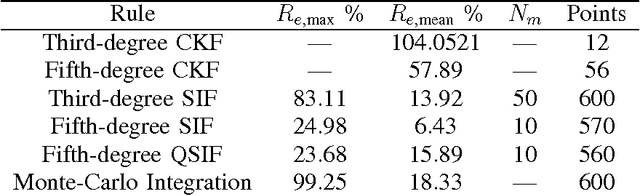
Abstract:We obtain a class of higher-degree stochastic integration filters (SIF) for nonlinear filtering applications. SIF are based on stochastic spherical-radial integration rules that achieve asymptotically exact evaluations of Gaussian weighted multivariate integrals found in nonlinear Bayesian filtering. The superiority of the proposed scheme is demonstrated by comparing the performance of the proposed fifth-degree SIF against a number of existing stochastic, quasi-stochastic and cubature (Kalman) filters. The proposed filter is demonstrated to outperform existing filters in all cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge