Sungjin Choi
DRAC: Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis Challenge with Ultra-Wide Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Images
Apr 05, 2023



Abstract:Computer-assisted automatic analysis of diabetic retinopathy (DR) is of great importance in reducing the risks of vision loss and even blindness. Ultra-wide optical coherence tomography angiography (UW-OCTA) is a non-invasive and safe imaging modality in DR diagnosis system, but there is a lack of publicly available benchmarks for model development and evaluation. To promote further research and scientific benchmarking for diabetic retinopathy analysis using UW-OCTA images, we organized a challenge named "DRAC - Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis Challenge" in conjunction with the 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022). The challenge consists of three tasks: segmentation of DR lesions, image quality assessment and DR grading. The scientific community responded positively to the challenge, with 11, 12, and 13 teams from geographically diverse institutes submitting different solutions in these three tasks, respectively. This paper presents a summary and analysis of the top-performing solutions and results for each task of the challenge. The obtained results from top algorithms indicate the importance of data augmentation, model architecture and ensemble of networks in improving the performance of deep learning models. These findings have the potential to enable new developments in diabetic retinopathy analysis. The challenge remains open for post-challenge registrations and submissions for benchmarking future methodology developments.
Tunable Image Quality Control of 3-D Ultrasound using Switchable CycleGAN
Dec 06, 2021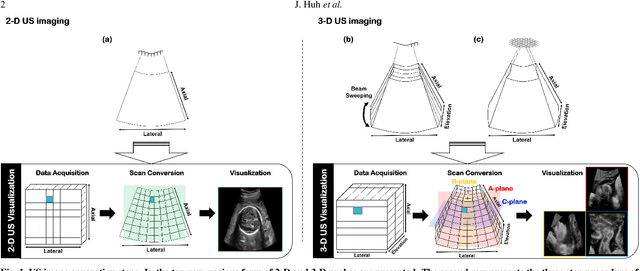
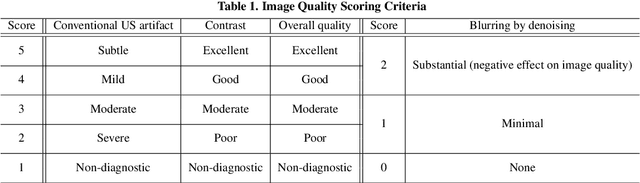
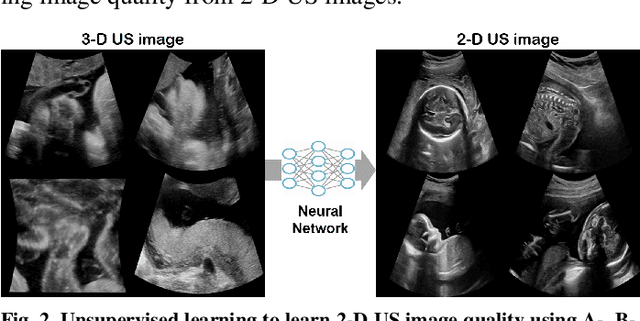
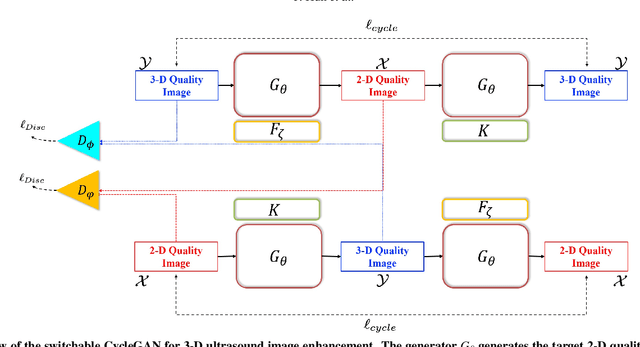
Abstract:In contrast to 2-D ultrasound (US) for uniaxial plane imaging, a 3-D US imaging system can visualize a volume along three axial planes. This allows for a full view of the anatomy, which is useful for gynecological (GYN) and obstetrical (OB) applications. Unfortunately, the 3-D US has an inherent limitation in resolution compared to the 2-D US. In the case of 3-D US with a 3-D mechanical probe, for example, the image quality is comparable along the beam direction, but significant deterioration in image quality is often observed in the other two axial image planes. To address this, here we propose a novel unsupervised deep learning approach to improve 3-D US image quality. In particular, using {\em unmatched} high-quality 2-D US images as a reference, we trained a recently proposed switchable CycleGAN architecture so that every mapping plane in 3-D US can learn the image quality of 2-D US images. Thanks to the switchable architecture, our network can also provide real-time control of image enhancement level based on user preference, which is ideal for a user-centric scanner setup. Extensive experiments with clinical evaluation confirm that our method offers significantly improved image quality as well user-friendly flexibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge