Suhaib A. Fahmy
Configurable p-Neurons Using Modular p-Bits
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Probabilistic bits (p-bits) have recently been employed in neural networks (NNs) as stochastic neurons with sigmoidal probabilistic activation functions. Nonetheless, there remain a wealth of other probabilistic activation functions that are yet to be explored. Here we re-engineer the p-bit by decoupling its stochastic signal path from its input data path, giving rise to a modular p-bit that enables the realization of probabilistic neurons (p-neurons) with a range of configurable probabilistic activation functions, including a probabilistic version of the widely used Logistic Sigmoid, Tanh and Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation functions. We present spintronic (CMOS + sMTJ) designs that show wide and tunable probabilistic ranges of operation. Finally, we experimentally implement digital-CMOS versions on an FPGA, with stochastic unit sharing, and demonstrate an order of magnitude (10x) saving in required hardware resources compared to conventional digital p-bit implementations.
MAESTRO: Multi-Agent Evaluation Suite for Testing, Reliability, and Observability
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:We present MAESTRO, an evaluation suite for the testing, reliability, and observability of LLM-based MAS. MAESTRO standardizes MAS configuration and execution through a unified interface, supports integrating both native and third-party MAS via a repository of examples and lightweight adapters, and exports framework-agnostic execution traces together with system-level signals (e.g., latency, cost, and failures). We instantiate MAESTRO with 12 representative MAS spanning popular agentic frameworks and interaction patterns, and conduct controlled experiments across repeated runs, backend models, and tool configurations. Our case studies show that MAS executions can be structurally stable yet temporally variable, leading to substantial run-to-run variance in performance and reliability. We further find that MAS architecture is the dominant driver of resource profiles, reproducibility, and cost-latency-accuracy trade-off, often outweighing changes in backend models or tool settings. Overall, MAESTRO enables systematic evaluation and provides empirical guidance for designing and optimizing agentic systems.
Resource-Efficient Federated Learning
Nov 01, 2021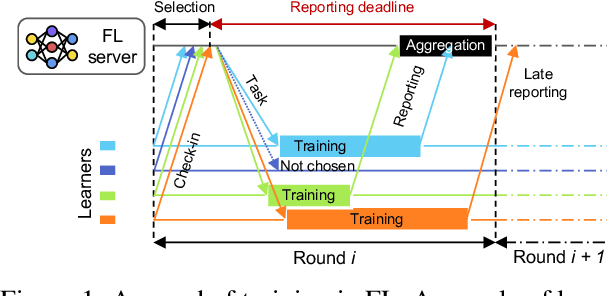
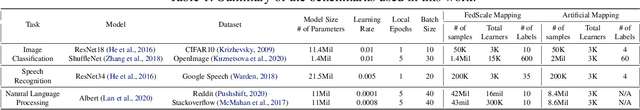
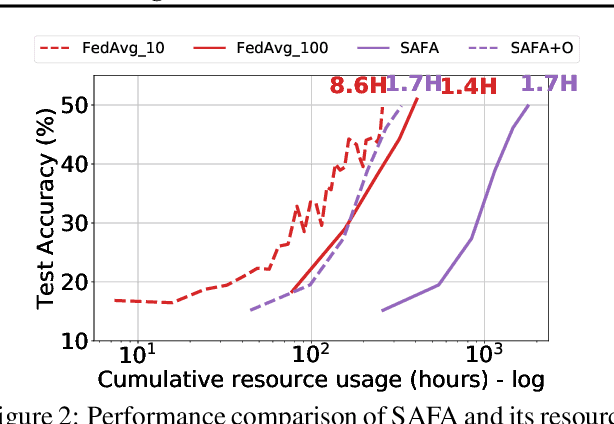
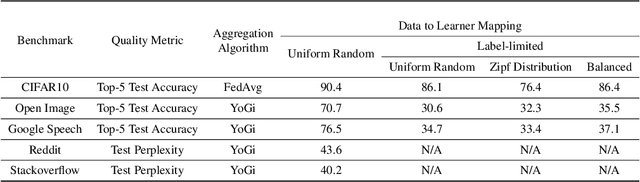
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables distributed training by learners using local data, thereby enhancing privacy and reducing communication. However, it presents numerous challenges relating to the heterogeneity of the data distribution, device capabilities, and participant availability as deployments scale, which can impact both model convergence and bias. Existing FL schemes use random participant selection to improve fairness; however, this can result in inefficient use of resources and lower quality training. In this work, we systematically address the question of resource efficiency in FL, showing the benefits of intelligent participant selection, and incorporation of updates from straggling participants. We demonstrate how these factors enable resource efficiency while also improving trained model quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge