Sudhir Kumar
Health Sentinel: An AI Pipeline For Real-time Disease Outbreak Detection
Jun 24, 2025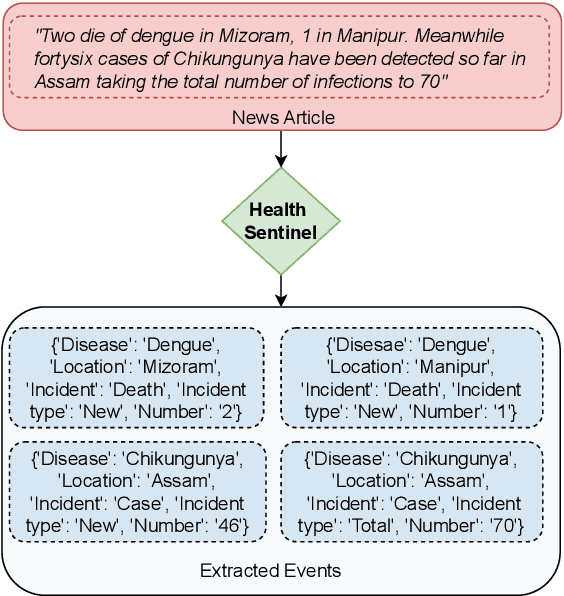
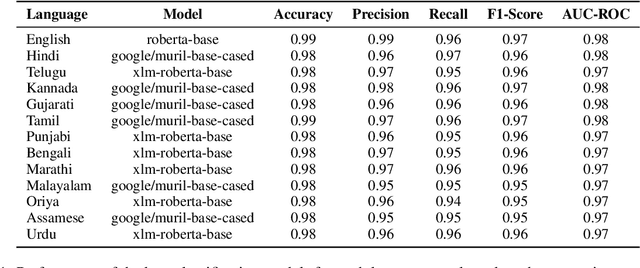
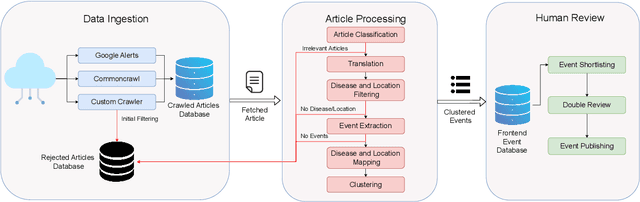
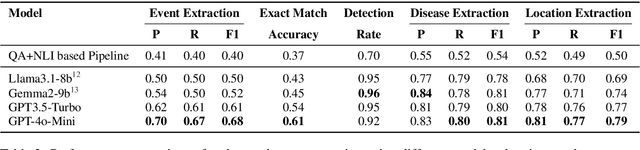
Abstract:Early detection of disease outbreaks is crucial to ensure timely intervention by the health authorities. Due to the challenges associated with traditional indicator-based surveillance, monitoring informal sources such as online media has become increasingly popular. However, owing to the number of online articles getting published everyday, manual screening of the articles is impractical. To address this, we propose Health Sentinel. It is a multi-stage information extraction pipeline that uses a combination of ML and non-ML methods to extract events-structured information concerning disease outbreaks or other unusual health events-from online articles. The extracted events are made available to the Media Scanning and Verification Cell (MSVC) at the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), Delhi for analysis, interpretation and further dissemination to local agencies for timely intervention. From April 2022 till date, Health Sentinel has processed over 300 million news articles and identified over 95,000 unique health events across India of which over 3,500 events were shortlisted by the public health experts at NCDC as potential outbreaks.
Deep Low-Shot Learning for Biological Image Classification and Visualization from Limited Training Samples
Oct 20, 2020



Abstract:Predictive modeling is useful but very challenging in biological image analysis due to the high cost of obtaining and labeling training data. For example, in the study of gene interaction and regulation in Drosophila embryogenesis, the analysis is most biologically meaningful when in situ hybridization (ISH) gene expression pattern images from the same developmental stage are compared. However, labeling training data with precise stages is very time-consuming even for evelopmental biologists. Thus, a critical challenge is how to build accurate computational models for precise developmental stage classification from limited training samples. In addition, identification and visualization of developmental landmarks are required to enable biologists to interpret prediction results and calibrate models. To address these challenges, we propose a deep two-step low-shot learning framework to accurately classify ISH images using limited training images. Specifically, to enable accurate model training on limited training samples, we formulate the task as a deep low-shot learning problem and develop a novel two-step learning approach, including data-level learning and feature-level learning. We use a deep residual network as our base model and achieve improved performance in the precise stage prediction task of ISH images. Furthermore, the deep model can be interpreted by computing saliency maps, which consist of pixel-wise contributions of an image to its prediction result. In our task, saliency maps are used to assist the identification and visualization of developmental landmarks. Our experimental results show that the proposed model can not only make accurate predictions, but also yield biologically meaningful interpretations. We anticipate our methods to be easily generalizable to other biological image classification tasks with small training datasets.
Image-based phenotyping of diverse Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Genotypes
Apr 06, 2020
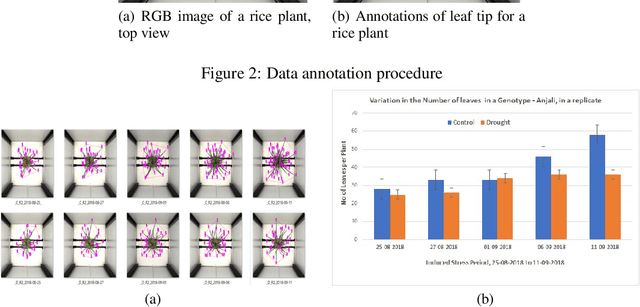
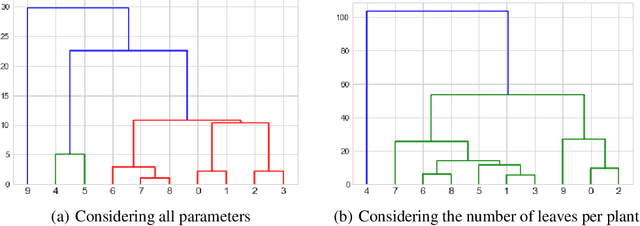
Abstract:Development of either drought-resistant or drought-tolerant varieties in rice (Oryza sativa L.), especially for high yield in the context of climate change, is a crucial task across the world. The need for high yielding rice varieties is a prime concern for developing nations like India, China, and other Asian-African countries where rice is a primary staple food. The present investigation is carried out for discriminating drought tolerant, and susceptible genotypes. A total of 150 genotypes were grown under controlled conditions to evaluate at High Throughput Plant Phenomics facility, Nanaji Deshmukh Plant Phenomics Centre, Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi. A subset of 10 genotypes is taken out of 150 for the current investigation. To discriminate against the genotypes, we considered features such as the number of leaves per plant, the convex hull and convex hull area of a plant-convex hull formed by joining the tips of the leaves, the number of leaves per unit convex hull of a plant, canopy spread - vertical spread, and horizontal spread of a plant. We trained You Only Look Once (YOLO) deep learning algorithm for leaves tips detection and to estimate the number of leaves in a rice plant. With this proposed framework, we screened the genotypes based on selected traits. These genotypes were further grouped among different groupings of drought-tolerant and drought susceptible genotypes using the Ward method of clustering.
$c^+$GAN: Complementary Fashion Item Recommendation
Jun 13, 2019
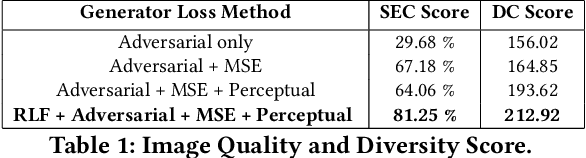

Abstract:We present a conditional generative adversarial model to draw realistic samples from paired fashion clothing distribution and provide real samples to pair with arbitrary fashion units. More concretely, given an image of a shirt, obtained from a fashion magazine, a brochure or even any random click on ones phone, we draw realistic samples from a parameterized conditional distribution learned as a conditional generative adversarial network ($c^+$GAN) to generate the possible pants which can go with the shirt. We start with a classical cGAN model as proposed by Mirza and Osindero \cite{MirzaO14} and modify both the generator and discriminator to work on captured-in-the-wild data with no human alignment. We gather a dataset from web crawled data, systematically develop a method which counters the problems inherent to such data, and finally present plausible results based on our technique. We propose simple ideas to evaluate how these techniques can conquer the cognitive gap that exists when arbitrary clothing articles need to be paired with another relevant article, based on similarity of search results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge