Viswanathan Chinnusamy
Image-based phenotyping of diverse Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Genotypes
Apr 06, 2020
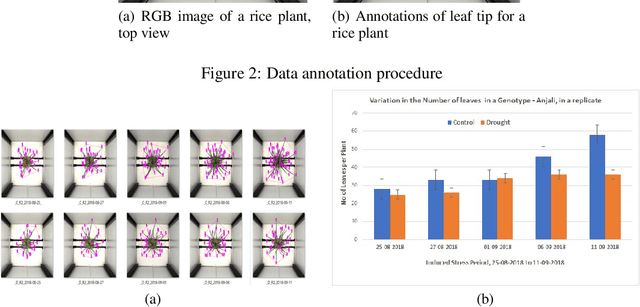
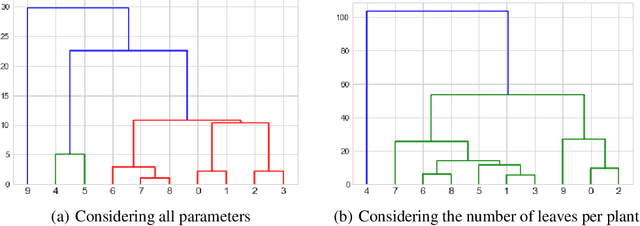
Abstract:Development of either drought-resistant or drought-tolerant varieties in rice (Oryza sativa L.), especially for high yield in the context of climate change, is a crucial task across the world. The need for high yielding rice varieties is a prime concern for developing nations like India, China, and other Asian-African countries where rice is a primary staple food. The present investigation is carried out for discriminating drought tolerant, and susceptible genotypes. A total of 150 genotypes were grown under controlled conditions to evaluate at High Throughput Plant Phenomics facility, Nanaji Deshmukh Plant Phenomics Centre, Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi. A subset of 10 genotypes is taken out of 150 for the current investigation. To discriminate against the genotypes, we considered features such as the number of leaves per plant, the convex hull and convex hull area of a plant-convex hull formed by joining the tips of the leaves, the number of leaves per unit convex hull of a plant, canopy spread - vertical spread, and horizontal spread of a plant. We trained You Only Look Once (YOLO) deep learning algorithm for leaves tips detection and to estimate the number of leaves in a rice plant. With this proposed framework, we screened the genotypes based on selected traits. These genotypes were further grouped among different groupings of drought-tolerant and drought susceptible genotypes using the Ward method of clustering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge