Stephen Ash
RoboPhD: Self-Improving Text-to-SQL Through Autonomous Agent Evolution
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:We present RoboPhD, a system where AI agents autonomously conduct research to improve Text-to-SQL performance. RoboPhD implements a closed-loop evolution cycle with two coordinated components: a SQL Generation agent composed of a database analysis script and SQL generation instructions, and an Evolution agent that designs new versions based on performance feedback. Central to the framework is an ELO-based selection mechanism enabling survival-of-the-fittest dynamics while handling non-transitivity in performance. Starting from a naive 70-line baseline, RoboPhD evolves agents through iterative cross-pollination, discovering effective techniques without any external guidance on the Text-to-SQL domain. Our best agent, evolved to 1500 lines over 18 iterations, autonomously discovered strategies such as size-adaptive database analysis that adjusts depth based on schema complexity and SQL generation patterns for column selection, evidence interpretation, and aggregation. Evolution provides the largest gains on cheaper models: while we improve by 2.3 points over a strong Claude Opus 4.5 naive baseline, we show an improvement of 8.9 points over the weaker Claude Haiku model. This enables 'skip a tier' deployment: evolved Haiku exceeds naive Sonnet accuracy, and evolved Sonnet exceeds naive Opus, both at lower cost. The full system achieves 73.67% accuracy on the BIRD test set, demonstrating that AI can autonomously build a strong agentic system with only a trivial human-provided starting point.
UNITE: A Unified Benchmark for Text-to-SQL Evaluation
May 26, 2023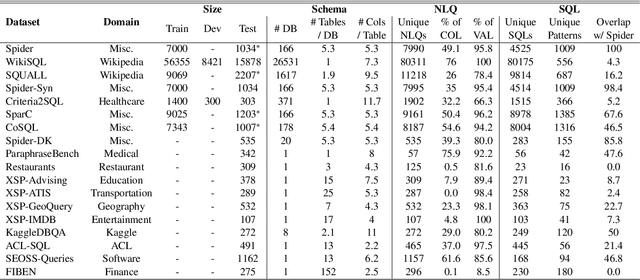
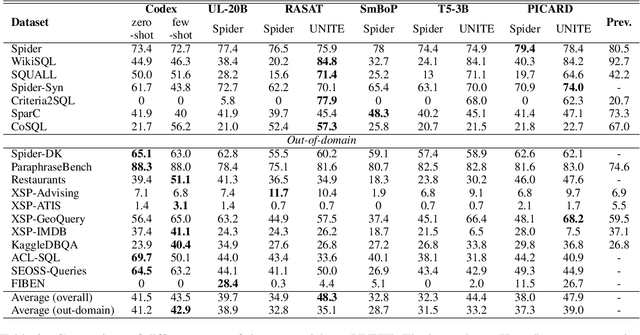
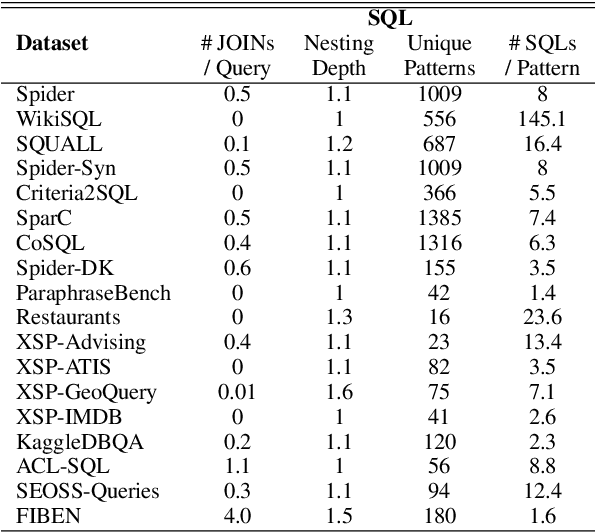
Abstract:A practical text-to-SQL system should generalize well on a wide variety of natural language questions, unseen database schemas, and novel SQL query structures. To comprehensively evaluate text-to-SQL systems, we introduce a \textbf{UNI}fied benchmark for \textbf{T}ext-to-SQL \textbf{E}valuation (UNITE). It is composed of publicly available text-to-SQL datasets, containing natural language questions from more than 12 domains, SQL queries from more than 3.9K patterns, and 29K databases. Compared to the widely used Spider benchmark \cite{yu-etal-2018-spider}, we introduce $\sim$120K additional examples and a threefold increase in SQL patterns, such as comparative and boolean questions. We conduct a systematic study of six state-of-the-art (SOTA) text-to-SQL parsers on our new benchmark and show that: 1) Codex performs surprisingly well on out-of-domain datasets; 2) specially designed decoding methods (e.g. constrained beam search) can improve performance for both in-domain and out-of-domain settings; 3) explicitly modeling the relationship between questions and schemas further improves the Seq2Seq models. More importantly, our benchmark presents key challenges towards compositional generalization and robustness issues -- which these SOTA models cannot address well. \footnote{Our code and data processing script will be available at \url{https://github.com/XXXX.}}
Design Challenges in Named Entity Transliteration
Aug 07, 2018



Abstract:We analyze some of the fundamental design challenges that impact the development of a multilingual state-of-the-art named entity transliteration system, including curating bilingual named entity datasets and evaluation of multiple transliteration methods. We empirically evaluate the transliteration task using traditional weighted finite state transducer (WFST) approach against two neural approaches: the encoder-decoder recurrent neural network method and the recent, non-sequential Transformer method. In order to improve availability of bilingual named entity transliteration datasets, we release personal name bilingual dictionaries minded from Wikidata for English to Russian, Hebrew, Arabic and Japanese Katakana. Our code and dictionaries are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge