Stephan Mühlbacher-Karrer
Proximity Perception in Human-Centered Robotics: A Survey on Sensing Systems and Applications
Aug 17, 2021



Abstract:Proximity perception is a technology that has the potential to play an essential role in the future of robotics. It can fulfill the promise of safe, robust, and autonomous systems in industry and everyday life, alongside humans, as well as in remote locations in space and underwater. In this survey paper, we cover the developments of this field from the early days up to the present, with a focus on human-centered robotics. Here, proximity sensors are typically deployed in two scenarios: first, on the exterior of manipulator arms to support safety and interaction functionality, and second, on the inside of grippers or hands to support grasping and exploration. Starting from this observation, we propose a categorization for the approaches found in the literature. To provide a basis for understanding these approaches, we devote effort to present the technologies and different measuring principles that were developed over the years, also providing a summary in form of a table. Then, we show the diversity of applications that have been presented in the literature. Finally, we give an overview of the most important trends that will shape the future of this domain.
robo-gym -- An Open Source Toolkit for Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning on Real and Simulated Robots
Jul 06, 2020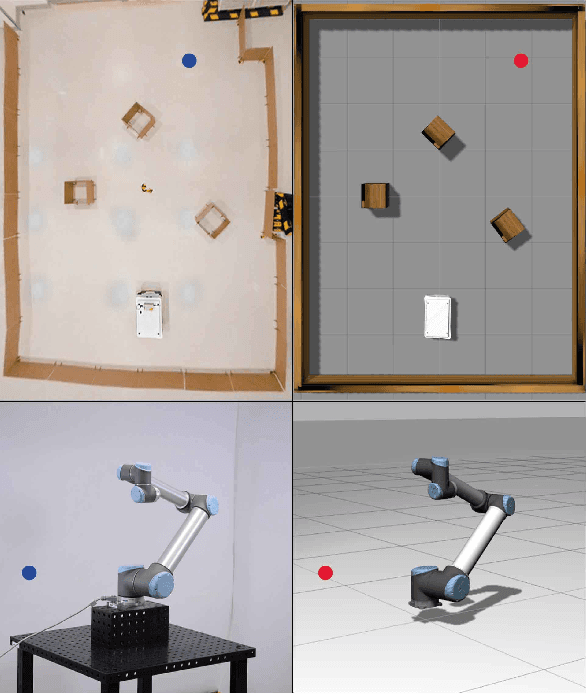
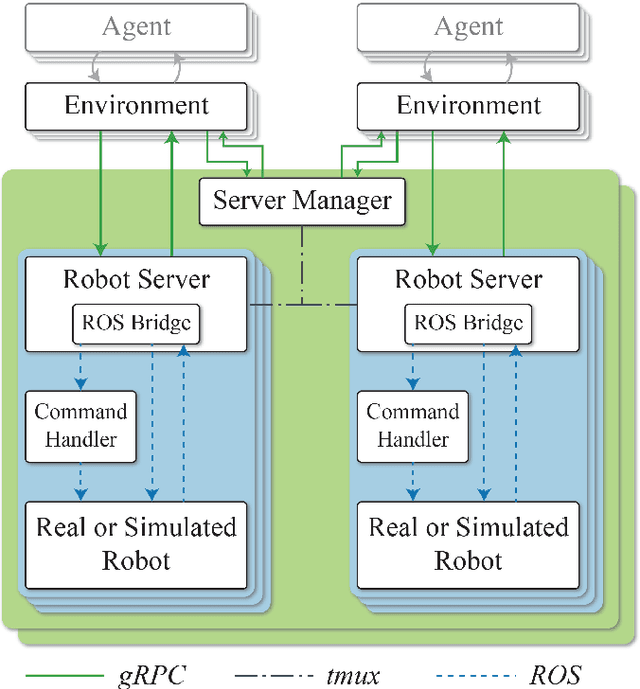
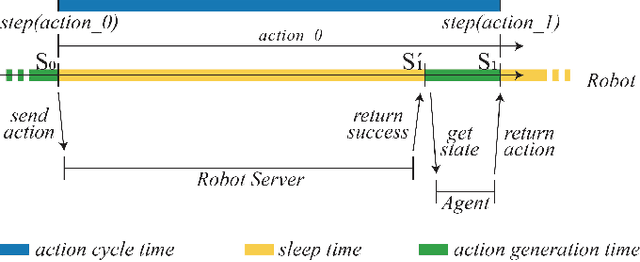
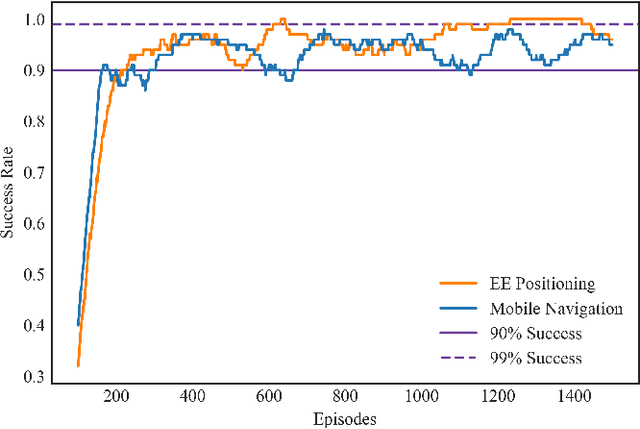
Abstract:Applying Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to complex tasks in the field of robotics has proven to be very successful in the recent years. However, most of the publications focus either on applying it to a task in simulation or to a task in a real world setup. Although there are great examples of combining the two worlds with the help of transfer learning, it often requires a lot of additional work and fine-tuning to make the setup work effectively. In order to increase the use of DRL with real robots and reduce the gap between simulation and real world robotics, we propose an open source toolkit: robo-gym. We demonstrate a unified setup for simulation and real environments which enables a seamless transfer from training in simulation to application on the robot. We showcase the capabilities and the effectiveness of the framework with two real world applications featuring industrial robots: a mobile robot and a robot arm. The distributed capabilities of the framework enable several advantages like using distributed algorithms, separating the workload of simulation and training on different physical machines as well as enabling the future opportunity to train in simulation and real world at the same time. Finally we offer an overview and comparison of robo-gym with other frequently used state-of-the-art DRL frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge