Steffen Herbold
Understanding or Memorizing? A Case Study of German Definite Articles in Language Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Language models perform well on grammatical agreement, but it is unclear whether this reflects rule-based generalization or memorization. We study this question for German definite singular articles, whose forms depend on gender and case. Using GRADIEND, a gradient-based interpretability method, we learn parameter update directions for gender-case specific article transitions. We find that updates learned for a specific gender-case article transition frequently affect unrelated gender-case settings, with substantial overlap among the most affected neurons across settings. These results argue against a strictly rule-based encoding of German definite articles, indicating that models at least partly rely on memorized associations rather than abstract grammatical rules.
Criminal Liability of Generative Artificial Intelligence Providers for User-Generated Child Sexual Abuse Material
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The development of more powerful Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has expanded its capabilities and the variety of outputs. This has introduced significant legal challenges, including gray areas in various legal systems, such as the assessment of criminal liability for those responsible for these models. Therefore, we conducted a multidisciplinary study utilizing the statutory interpretation of relevant German laws, which, in conjunction with scenarios, provides a perspective on the different properties of GenAI in the context of Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) generation. We found that generating CSAM with GenAI may have criminal and legal consequences not only for the user committing the primary offense but also for individuals responsible for the models, such as independent software developers, researchers, and company representatives. Additionally, the assessment of criminal liability may be affected by contextual and technical factors, including the type of generated image, content moderation policies, and the model's intended purpose. Based on our findings, we discussed the implications for different roles, as well as the requirements when developing such systems.
Utilizing LLMs for Industrial Process Automation: A Case Study on Modifying RAPID Programs
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:How to best use Large Language Models (LLMs) for software engineering is covered in many publications in recent years. However, most of this work focuses on widely-used general purpose programming languages. The utility of LLMs for software within the industrial process automation domain, with highly-specialized languages that are typically only used in proprietary contexts, is still underexplored. Within this paper, we study enterprises can achieve on their own without investing large amounts of effort into the training of models specific to the domain-specific languages that are used. We show that few-shot prompting approaches are sufficient to solve simple problems in a language that is otherwise not well-supported by an LLM and that is possible on-premise, thereby ensuring the protection of sensitive company data.
SortBench: Benchmarking LLMs based on their ability to sort lists
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Sorting is a tedious but simple task for human intelligence and can be solved fairly easily algorithmically. However, for Large Language Models (LLMs) this task is surprisingly hard, as some properties of sorting are among known weaknesses of LLMs: being faithful to the input data, logical comparisons between values, and strictly differentiating between syntax (used for sorting) and semantics (typically learned by embeddings). Within this paper, we describe the new SortBench benchmark for LLMs that comes with different difficulties and that can be easily scaled in terms of difficulty. We apply this benchmark to seven state-of-the-art LLMs, including current test-time reasoning models. Our results show that while the o3-mini model is very capable at sorting in general, even this can be fooled if strings are defined to mix syntactical and semantical aspects, e.g., by asking to sort numbers written-out as word. Furthermore, all models have problems with the faithfulness to the input of long lists, i.e., they drop items and add new ones. Our results also show that test-time reasoning has a tendency to overthink problems which leads to performance degradation. Finally, models without test-time reasoning like GPT-4o are not much worse than reasoning models.
MAMUT: A Novel Framework for Modifying Mathematical Formulas for the Generation of Specialized Datasets for Language Model Training
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Mathematical formulas are a fundamental and widely used component in various scientific fields, serving as a universal language for expressing complex concepts and relationships. While state-of-the-art transformer models excel in processing and understanding natural language, they encounter challenges with mathematical notation, which involves a complex structure and diverse representations. This study focuses on the development of specialized training datasets to enhance the encoding of mathematical content. We introduce Math Mutator (MAMUT), a framework capable of generating equivalent and falsified versions of a given mathematical formula in LaTeX notation, effectively capturing the mathematical variety in notation of the same concept. Based on MAMUT, we have generated four large mathematical datasets containing diverse notation, which can be used to train language models with enhanced mathematical embeddings.
From Isolates to Families: Using Neural Networks for Automated Language Affiliation
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:In historical linguistics, the affiliation of languages to a common language family is traditionally carried out using a complex workflow that relies on manually comparing individual languages. Large-scale standardized collections of multilingual wordlists and grammatical language structures might help to improve this and open new avenues for developing automated language affiliation workflows. Here, we present neural network models that use lexical and grammatical data from a worldwide sample of more than 1,000 languages with known affiliations to classify individual languages into families. In line with the traditional assumption of most linguists, our results show that models trained on lexical data alone outperform models solely based on grammatical data, whereas combining both types of data yields even better performance. In additional experiments, we show how our models can identify long-ranging relations between entire subgroups, how they can be employed to investigate potential relatives of linguistic isolates, and how they can help us to obtain first hints on the affiliation of so far unaffiliated languages. We conclude that models for automated language affiliation trained on lexical and grammatical data provide comparative linguists with a valuable tool for evaluating hypotheses about deep and unknown language relations.
GRADIEND: Monosemantic Feature Learning within Neural Networks Applied to Gender Debiasing of Transformer Models
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:AI systems frequently exhibit and amplify social biases, including gender bias, leading to harmful consequences in critical areas. This study introduces a novel encoder-decoder approach that leverages model gradients to learn a single monosemantic feature neuron encoding gender information. We show that our method can be used to debias transformer-based language models, while maintaining other capabilities. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach across multiple encoder-only based models and highlight its potential for broader applications.
Perspective of Software Engineering Researchers on Machine Learning Practices Regarding Research, Review, and Education
Nov 28, 2024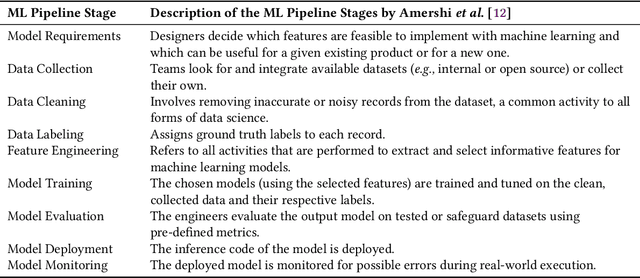
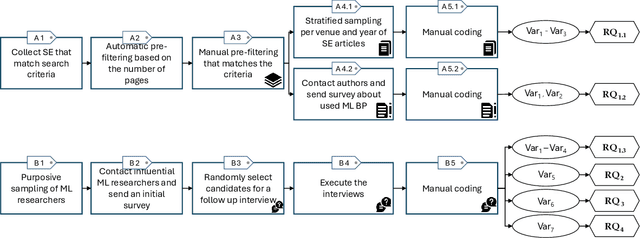
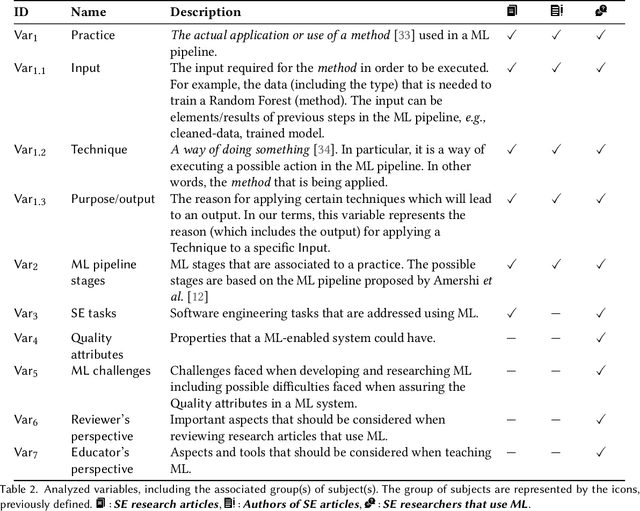
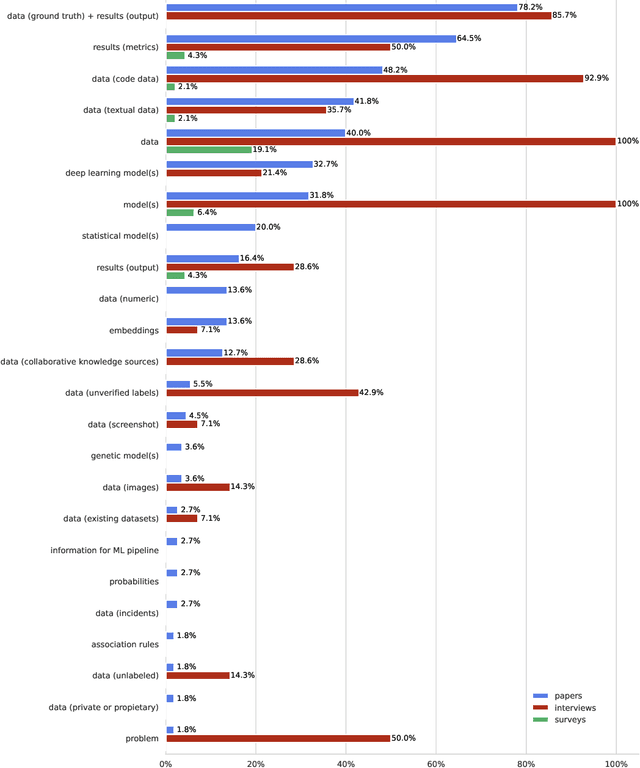
Abstract:Context: Machine Learning (ML) significantly impacts Software Engineering (SE), but studies mainly focus on practitioners, neglecting researchers. This overlooks practices and challenges in teaching, researching, or reviewing ML applications in SE. Objective: This study aims to contribute to the knowledge, about the synergy between ML and SE from the perspective of SE researchers, by providing insights into the practices followed when researching, teaching, and reviewing SE studies that apply ML. Method: We analyzed SE researchers familiar with ML or who authored SE articles using ML, along with the articles themselves. We examined practices, SE tasks addressed with ML, challenges faced, and reviewers' and educators' perspectives using grounded theory coding and qualitative analysis. Results: We found diverse practices focusing on data collection, model training, and evaluation. Some recommended practices (e.g., hyperparameter tuning) appeared in less than 20\% of literature. Common challenges involve data handling, model evaluation (incl. non-functional properties), and involving human expertise in evaluation. Hands-on activities are common in education, though traditional methods persist. Conclusion: Despite accepted practices in applying ML to SE, significant gaps remain. By enhancing guidelines, adopting diverse teaching methods, and emphasizing underrepresented practices, the SE community can bridge these gaps and advance the field.
Legal Aspects for Software Developers Interested in Generative AI Applications
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:Recent successes in Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) have led to new technologies capable of generating high-quality code, natural language, and images. The next step is to integrate GenAI technology into products, a task typically conducted by software developers. Such product development always comes with a certain risk of liability. Within this article, we want to shed light on the current state of two such risks: data protection and copyright. Both aspects are crucial for GenAI. This technology deals with data for both model training and generated output. We summarize key aspects regarding our current knowledge that every software developer involved in product development using GenAI should be aware of to avoid critical mistakes that may expose them to liability claims.
Semantic similarity prediction is better than other semantic similarity measures
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:Semantic similarity between natural language texts is typically measured either by looking at the overlap between subsequences (e.g., BLEU) or by using embeddings (e.g., BERTScore, S-BERT). Within this paper, we argue that when we are only interested in measuring the semantic similarity, it is better to directly predict the similarity using a fine-tuned model for such a task. Using a fine-tuned model for the STS-B from the GLUE benchmark, we define the STSScore approach and show that the resulting similarity is better aligned with our expectations on a robust semantic similarity measure than other approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge