Anamaria Mojica-Hanke
Criminal Liability of Generative Artificial Intelligence Providers for User-Generated Child Sexual Abuse Material
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The development of more powerful Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has expanded its capabilities and the variety of outputs. This has introduced significant legal challenges, including gray areas in various legal systems, such as the assessment of criminal liability for those responsible for these models. Therefore, we conducted a multidisciplinary study utilizing the statutory interpretation of relevant German laws, which, in conjunction with scenarios, provides a perspective on the different properties of GenAI in the context of Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) generation. We found that generating CSAM with GenAI may have criminal and legal consequences not only for the user committing the primary offense but also for individuals responsible for the models, such as independent software developers, researchers, and company representatives. Additionally, the assessment of criminal liability may be affected by contextual and technical factors, including the type of generated image, content moderation policies, and the model's intended purpose. Based on our findings, we discussed the implications for different roles, as well as the requirements when developing such systems.
Perspective of Software Engineering Researchers on Machine Learning Practices Regarding Research, Review, and Education
Nov 28, 2024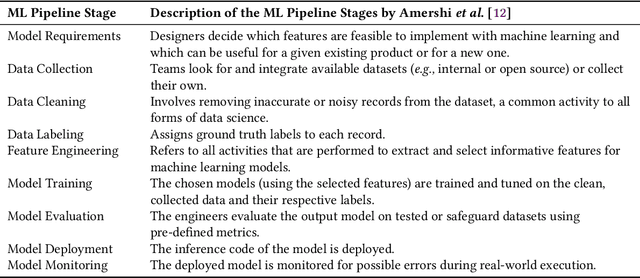
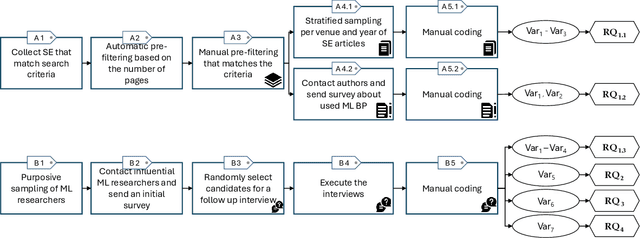
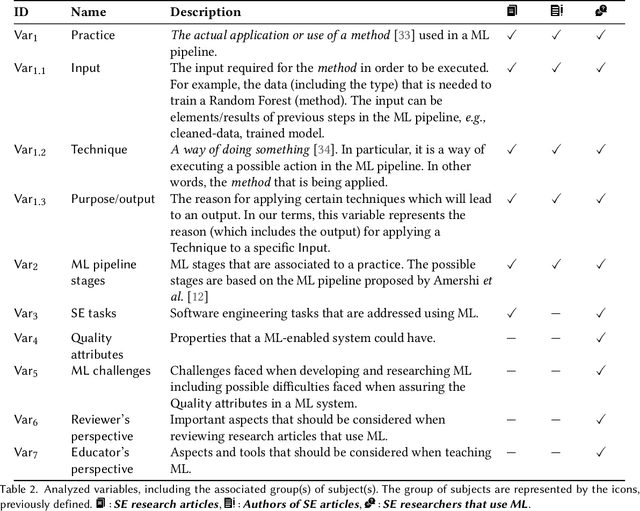
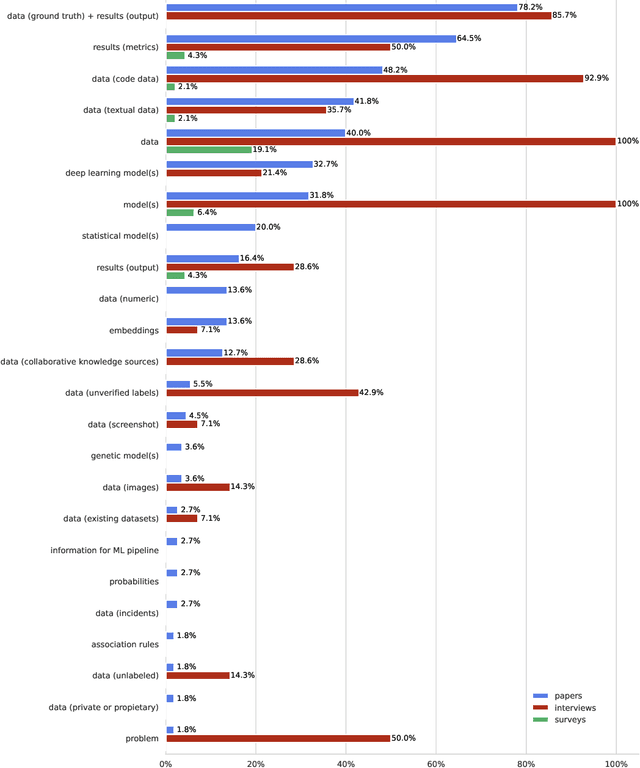
Abstract:Context: Machine Learning (ML) significantly impacts Software Engineering (SE), but studies mainly focus on practitioners, neglecting researchers. This overlooks practices and challenges in teaching, researching, or reviewing ML applications in SE. Objective: This study aims to contribute to the knowledge, about the synergy between ML and SE from the perspective of SE researchers, by providing insights into the practices followed when researching, teaching, and reviewing SE studies that apply ML. Method: We analyzed SE researchers familiar with ML or who authored SE articles using ML, along with the articles themselves. We examined practices, SE tasks addressed with ML, challenges faced, and reviewers' and educators' perspectives using grounded theory coding and qualitative analysis. Results: We found diverse practices focusing on data collection, model training, and evaluation. Some recommended practices (e.g., hyperparameter tuning) appeared in less than 20\% of literature. Common challenges involve data handling, model evaluation (incl. non-functional properties), and involving human expertise in evaluation. Hands-on activities are common in education, though traditional methods persist. Conclusion: Despite accepted practices in applying ML to SE, significant gaps remain. By enhancing guidelines, adopting diverse teaching methods, and emphasizing underrepresented practices, the SE community can bridge these gaps and advance the field.
Legal Aspects for Software Developers Interested in Generative AI Applications
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:Recent successes in Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) have led to new technologies capable of generating high-quality code, natural language, and images. The next step is to integrate GenAI technology into products, a task typically conducted by software developers. Such product development always comes with a certain risk of liability. Within this article, we want to shed light on the current state of two such risks: data protection and copyright. Both aspects are crucial for GenAI. This technology deals with data for both model training and generated output. We summarize key aspects regarding our current knowledge that every software developer involved in product development using GenAI should be aware of to avoid critical mistakes that may expose them to liability claims.
Towards machine learning guided by best practices
May 06, 2023Abstract:Nowadays, machine learning (ML) is being used in software systems with multiple application fields, from medicine to software engineering (SE). On the one hand, the popularity of ML in the industry can be seen in the statistics showing its growth and adoption. On the other hand, its popularity can also be seen in research, particularly in SE, where not only have multiple studies been published in SE conferences and journals but also in the multiple workshops and co-located conferences in software engineering conferences. At the same time, researchers and practitioners have shown that machine learning has some particular challenges and pitfalls. In particular, research has shown that ML-enabled systems have a different development process than traditional SE, which also describes some of the challenges of ML applications. In order to mitigate some of the identified challenges and pitfalls, white and gray literature has proposed a set of recommendations based on their own experiences and focused on their domain (e.g., biomechanics), but for the best of our knowledge, there is no guideline focused on the SE community. This thesis aims to reduce this gap by answering research questions that help to understand the practices used and discussed by practitioners and researchers in the SE community by analyzing possible sources of practices such as question and answer communities and also previous research studies to present a set of practices with an SE perspective.
What are the Machine Learning best practices reported by practitioners on Stack Exchange?
Jan 25, 2023



Abstract:Machine Learning (ML) is being used in multiple disciplines due to its powerful capability to infer relationships within data. In particular, Software Engineering (SE) is one of those disciplines in which ML has been used for multiple tasks, like software categorization, bugs prediction, and testing. In addition to the multiple ML applications, some studies have been conducted to detect and understand possible pitfalls and issues when using ML. However, to the best of our knowledge, only a few studies have focused on presenting ML best practices or guidelines for the application of ML in different domains. In addition, the practices and literature presented in previous literature (i) are domain-specific (e.g., concrete practices in biomechanics), (ii) describe few practices, or (iii) the practices lack rigorous validation and are presented in gray literature. In this paper, we present a study listing 127 ML best practices systematically mining 242 posts of 14 different Stack Exchange (STE) websites and validated by four independent ML experts. The list of practices is presented in a set of categories related to different stages of the implementation process of an ML-enabled system; for each practice, we include explanations and examples. In all the practices, the provided examples focus on SE tasks. We expect this list of practices could help practitioners to understand better the practices and use ML in a more informed way, in particular newcomers to this new area that sits at the intersection of software engineering and machine learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge