Stefan Wild
Recursive Two-Step Lookahead Expected Payoff for Time-Dependent Bayesian Optimization
Jun 14, 2020
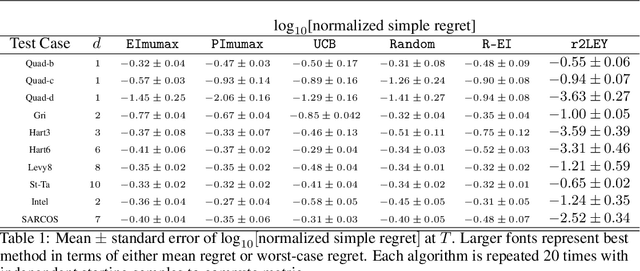


Abstract:We propose a novel Bayesian method to solve the maximization of a time-dependent expensive-to-evaluate oracle. We are interested in the decision that maximizes the oracle at a finite time horizon, when relatively few noisy evaluations can be performed before the horizon. Our recursive, two-step lookahead expected payoff ($\texttt{r2LEY}$) acquisition function makes nonmyopic decisions at every stage by maximizing the estimated expected value of the oracle at the horizon. $\texttt{r2LEY}$ circumvents the evaluation of the expensive multistep (more than two steps) lookahead acquisition function by recursively optimizing a two-step lookahead acquisition function at every stage; unbiased estimators of this latter function and its gradient are utilized for efficient optimization. $\texttt{r2LEY}$ is shown to exhibit natural exploration properties far from the time horizon, enabling accurate emulation of the oracle, which is exploited in the final decision made at the horizon. To demonstrate the utility of $\texttt{r2LEY}$, we compare it with time-dependent extensions of popular myopic acquisition functions via both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Scalable Reinforcement-Learning-Based Neural Architecture Search for Cancer Deep Learning Research
Sep 01, 2019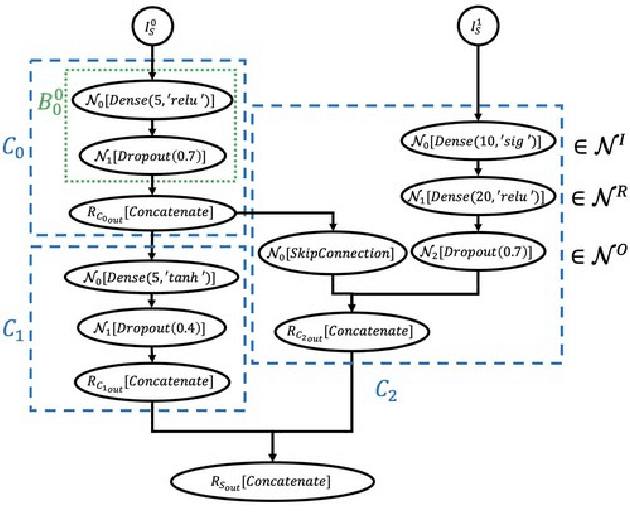
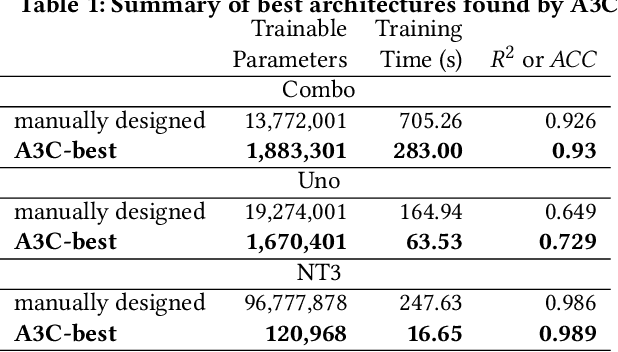
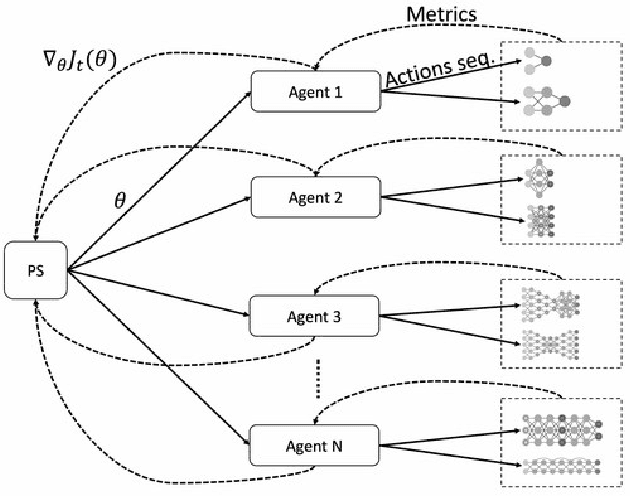
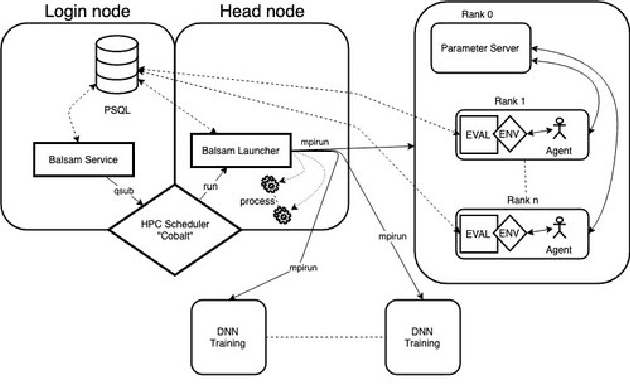
Abstract:Cancer is a complex disease, the understanding and treatment of which are being aided through increases in the volume of collected data and in the scale of deployed computing power. Consequently, there is a growing need for the development of data-driven and, in particular, deep learning methods for various tasks such as cancer diagnosis, detection, prognosis, and prediction. Despite recent successes, however, designing high-performing deep learning models for nonimage and nontext cancer data is a time-consuming, trial-and-error, manual task that requires both cancer domain and deep learning expertise. To that end, we develop a reinforcement-learning-based neural architecture search to automate deep-learning-based predictive model development for a class of representative cancer data. We develop custom building blocks that allow domain experts to incorporate the cancer-data-specific characteristics. We show that our approach discovers deep neural network architectures that have significantly fewer trainable parameters, shorter training time, and accuracy similar to or higher than those of manually designed architectures. We study and demonstrate the scalability of our approach on up to 1,024 Intel Knights Landing nodes of the Theta supercomputer at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge