Soyoung Park
FnRGNN: Distribution-aware Fairness in Graph Neural Network
Oct 22, 2025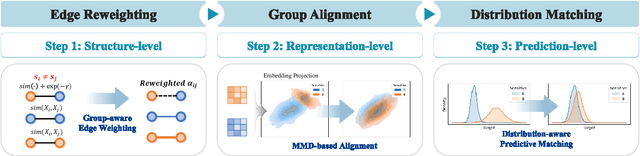
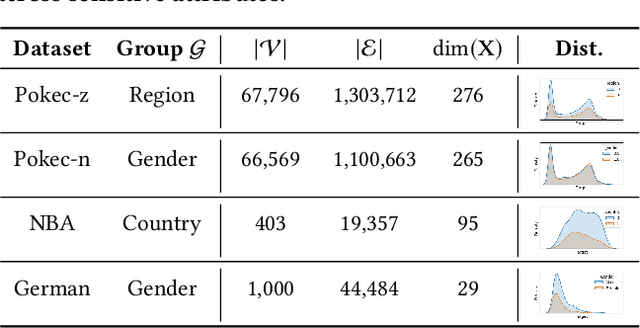
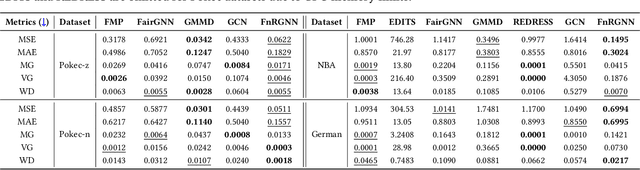
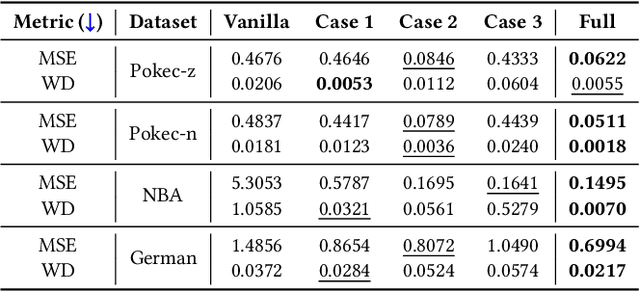
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel at learning from structured data, yet fairness in regression tasks remains underexplored. Existing approaches mainly target classification and representation-level debiasing, which cannot fully address the continuous nature of node-level regression. We propose FnRGNN, a fairness-aware in-processing framework for GNN-based node regression that applies interventions at three levels: (i) structure-level edge reweighting, (ii) representation-level alignment via MMD, and (iii) prediction-level normalization through Sinkhorn-based distribution matching. This multi-level strategy ensures robust fairness under complex graph topologies. Experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate that FnRGNN reduces group disparities without sacrificing performance. Code is available at https://github.com/sybeam27/FnRGNN.
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
Automated Precision Localization of Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter Tip through Model-Agnostic Multi-Stage Networks
Jun 14, 2022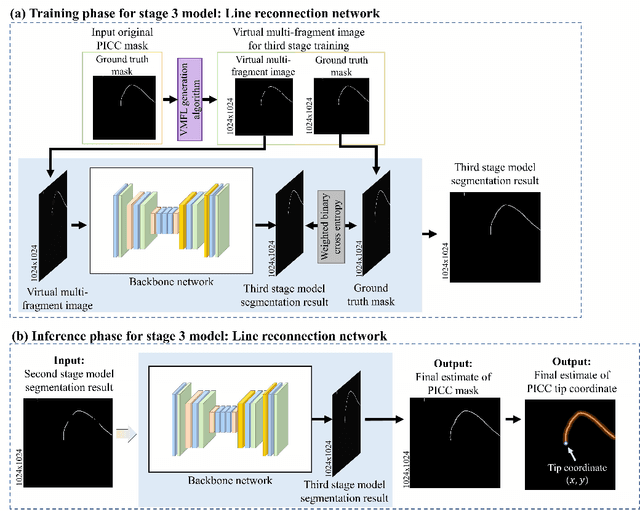

Abstract:Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs) have been widely used as one of the representative central venous lines (CVCs) due to their long-term intravascular access with low infectivity. However, PICCs have a fatal drawback of a high frequency of tip mispositions, increasing the risk of puncture, embolism, and complications such as cardiac arrhythmias. To automatically and precisely detect it, various attempts have been made by using the latest deep learning (DL) technologies. However, even with these approaches, it is still practically difficult to determine the tip location because the multiple fragments phenomenon (MFP) occurs in the process of predicting and extracting the PICC line required before predicting the tip. This study aimed to develop a system generally applied to existing models and to restore the PICC line more exactly by removing the MFs of the model output, thereby precisely localizing the actual tip position for detecting its disposition. To achieve this, we proposed a multi-stage DL-based framework post-processing the PICC line extraction result of the existing technology. The performance was compared by each root mean squared error (RMSE) and MFP incidence rate according to whether or not MFCN is applied to five conventional models. In internal validation, when MFCN was applied to the existing single model, MFP was improved by an average of 45%. The RMSE was improved by over 63% from an average of 26.85mm (17.16 to 35.80mm) to 9.72mm (9.37 to 10.98mm). In external validation, when MFCN was applied, the MFP incidence rate decreased by an average of 32% and the RMSE decreased by an average of 65\%. Therefore, by applying the proposed MFCN, we observed the significant/consistent detection performance improvement of PICC tip location compared to the existing model.
Technologies for AI-Driven Fashion Social Networking Service with E-Commerce
Mar 11, 2022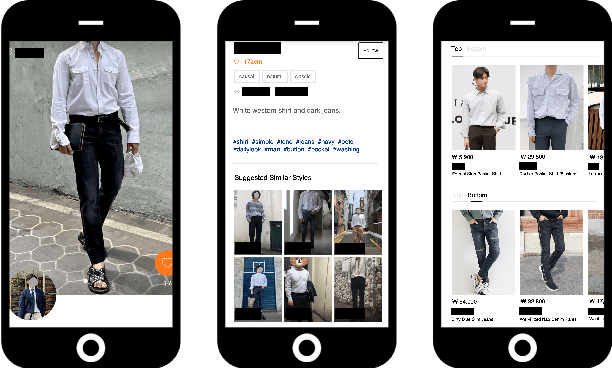
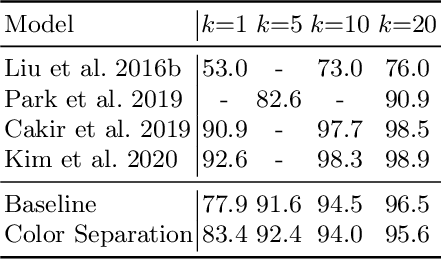
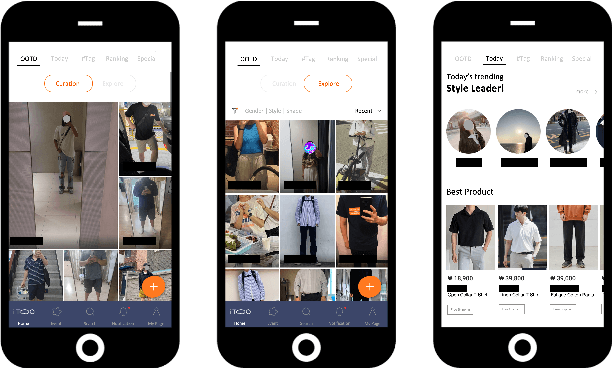

Abstract:The rapid growth of the online fashion market brought demands for innovative fashion services and commerce platforms. With the recent success of deep learning, many applications employ AI technologies such as visual search and recommender systems to provide novel and beneficial services. In this paper, we describe applied technologies for AI-driven fashion social networking service that incorporate fashion e-commerce. In the application, people can share and browse their outfit-of-the-day (OOTD) photos, while AI analyzes them and suggests similar style OOTDs and related products. To this end, we trained deep learning based AI models for fashion and integrated them to build a fashion visual search system and a recommender system for OOTD. With aforementioned technologies, the AI-driven fashion SNS platform, iTOO, has been successfully launched.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge