Holim Lim
Technologies for AI-Driven Fashion Social Networking Service with E-Commerce
Mar 11, 2022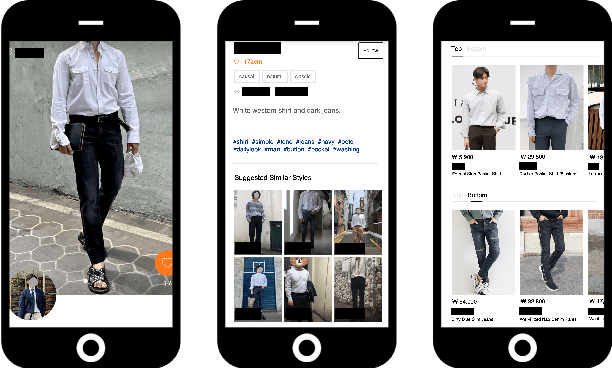
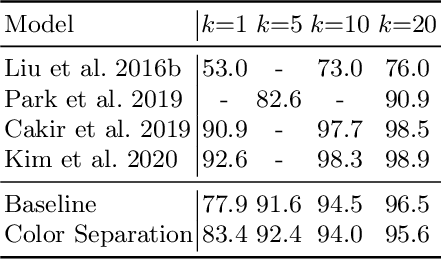
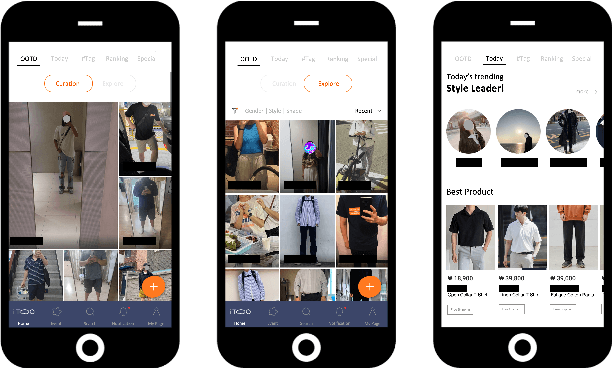

Abstract:The rapid growth of the online fashion market brought demands for innovative fashion services and commerce platforms. With the recent success of deep learning, many applications employ AI technologies such as visual search and recommender systems to provide novel and beneficial services. In this paper, we describe applied technologies for AI-driven fashion social networking service that incorporate fashion e-commerce. In the application, people can share and browse their outfit-of-the-day (OOTD) photos, while AI analyzes them and suggests similar style OOTDs and related products. To this end, we trained deep learning based AI models for fashion and integrated them to build a fashion visual search system and a recommender system for OOTD. With aforementioned technologies, the AI-driven fashion SNS platform, iTOO, has been successfully launched.
False Negative Distillation and Contrastive Learning for Personalized Outfit Recommendation
Oct 13, 2021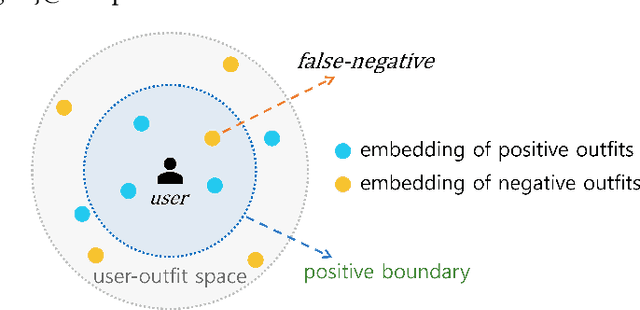
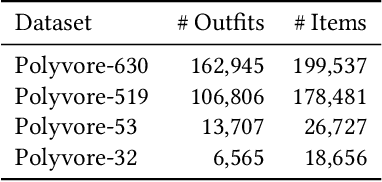
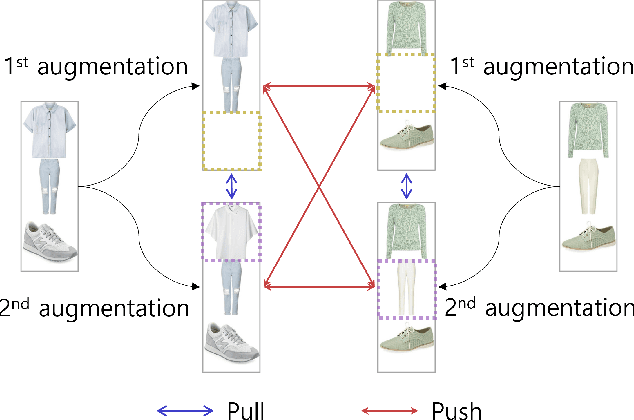
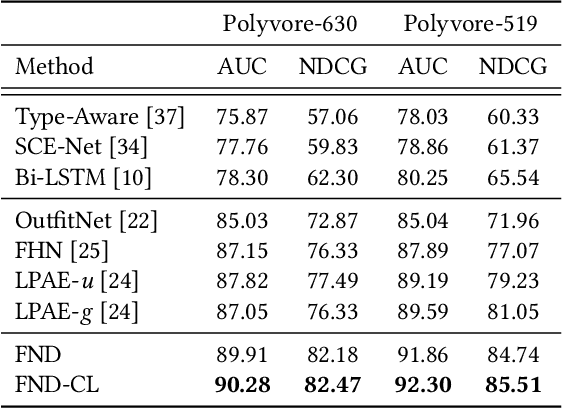
Abstract:Personalized outfit recommendation has recently been in the spotlight with the rapid growth of the online fashion industry. However, recommending outfits has two significant challenges that should be addressed. The first challenge is that outfit recommendation often requires a complex and large model that utilizes visual information, incurring huge memory and time costs. One natural way to mitigate this problem is to compress such a cumbersome model with knowledge distillation (KD) techniques that leverage knowledge from a pretrained teacher model. However, it is hard to apply existing KD approaches in recommender systems (RS) to the outfit recommendation because they require the ranking of all possible outfits while the number of outfits grows exponentially to the number of consisting clothing items. Therefore, we propose a new KD framework for outfit recommendation, called False Negative Distillation (FND), which exploits false-negative information from the teacher model while not requiring the ranking of all candidates. The second challenge is that the explosive number of outfit candidates amplifying the data sparsity problem, often leading to poor outfit representation. To tackle this issue, inspired by the recent success of contrastive learning (CL), we introduce a CL framework for outfit representation learning with two proposed data augmentation methods. Quantitative and qualitative experiments on outfit recommendation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and soundness of our proposed methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge