Sofia Tolmach
Quality Matters: Evaluating Synthetic Data for Tool-Using LLMs
Sep 26, 2024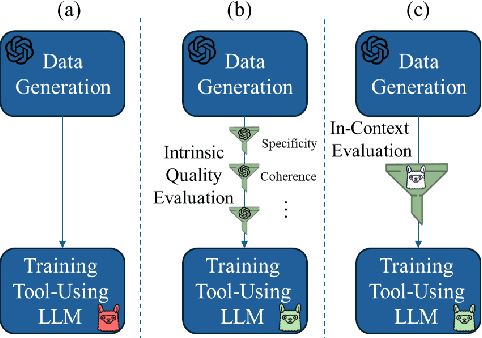
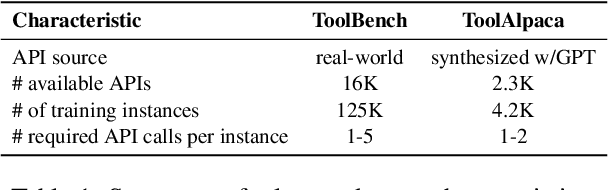

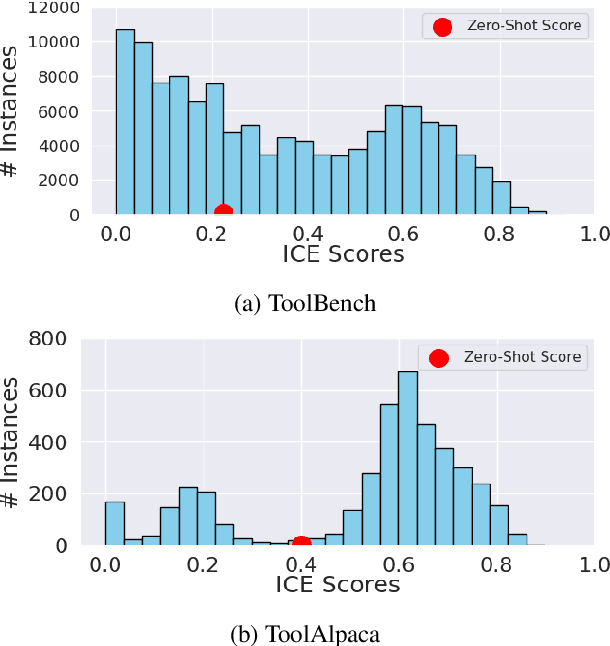
Abstract:Training large language models (LLMs) for external tool usage is a rapidly expanding field, with recent research focusing on generating synthetic data to address the shortage of available data. However, the absence of systematic data quality checks poses complications for properly training and testing models. To that end, we propose two approaches for assessing the reliability of data for training LLMs to use external tools. The first approach uses intuitive, human-defined correctness criteria. The second approach uses a model-driven assessment with in-context evaluation. We conduct a thorough evaluation of data quality on two popular benchmarks, followed by an extrinsic evaluation that showcases the impact of data quality on model performance. Our results demonstrate that models trained on high-quality data outperform those trained on unvalidated data, even when trained with a smaller quantity of data. These findings empirically support the significance of assessing and ensuring the reliability of training data for tool-using LLMs.
"Alexa, what do you do for fun?" Characterizing playful requests with virtual assistants
May 12, 2021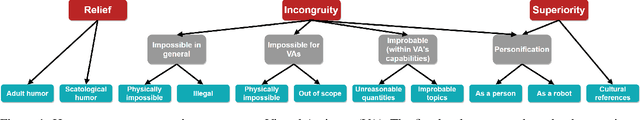

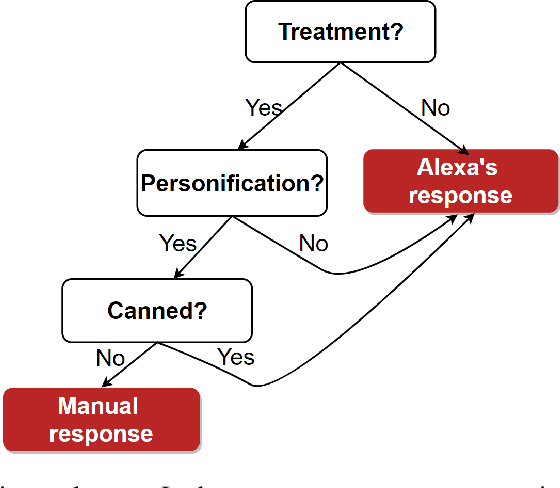

Abstract:Virtual assistants such as Amazon's Alexa, Apple's Siri, Google Home, and Microsoft's Cortana, are becoming ubiquitous in our daily lives and successfully help users in various daily tasks, such as making phone calls or playing music. Yet, they still struggle with playful utterances, which are not meant to be interpreted literally. Examples include jokes or absurd requests or questions such as, "Are you afraid of the dark?", "Who let the dogs out?", or "Order a zillion gummy bears". Today, virtual assistants often return irrelevant answers to such utterances, except for hard-coded ones addressed by canned replies. To address the challenge of automatically detecting playful utterances, we first characterize the different types of playful human-virtual assistant interaction. We introduce a taxonomy of playful requests rooted in theories of humor and refined by analyzing real-world traffic from Alexa. We then focus on one node, personification, where users refer to the virtual assistant as a person ("What do you do for fun?"). Our conjecture is that understanding such utterances will improve user experience with virtual assistants. We conducted a Wizard-of-Oz user study and showed that endowing virtual assistant s with the ability to identify humorous opportunities indeed has the potential to increase user satisfaction. We hope this work will contribute to the understanding of the landscape of the problem and inspire novel ideas and techniques towards the vision of giving virtual assistants a sense of humor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge