Socayna Jouide
medigan: A Python Library of Pretrained Generative Models for Enriched Data Access in Medical Imaging
Sep 28, 2022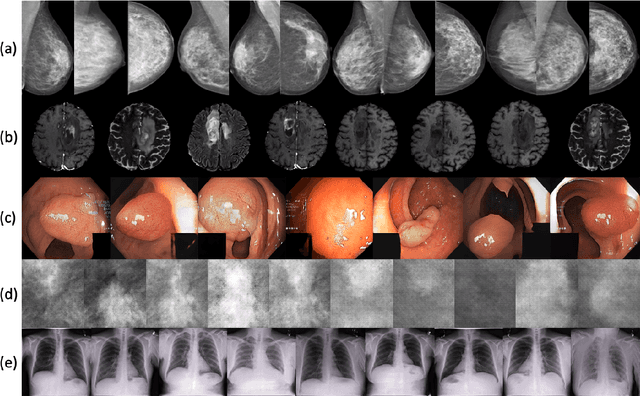
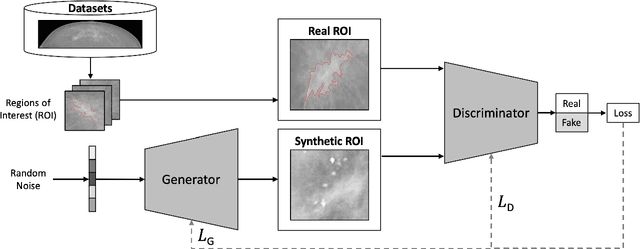
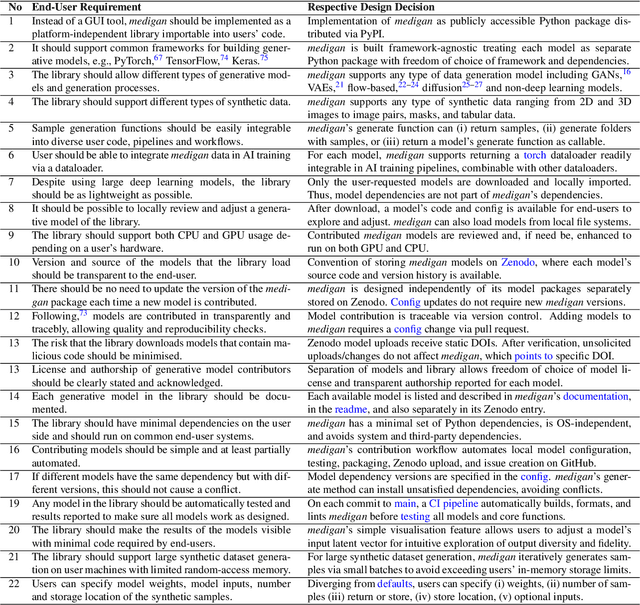
Abstract:Synthetic data generated by generative models can enhance the performance and capabilities of data-hungry deep learning models in medical imaging. However, there is (1) limited availability of (synthetic) datasets and (2) generative models are complex to train, which hinders their adoption in research and clinical applications. To reduce this entry barrier, we propose medigan, a one-stop shop for pretrained generative models implemented as an open-source framework-agnostic Python library. medigan allows researchers and developers to create, increase, and domain-adapt their training data in just a few lines of code. Guided by design decisions based on gathered end-user requirements, we implement medigan based on modular components for generative model (i) execution, (ii) visualisation, (iii) search & ranking, and (iv) contribution. The library's scalability and design is demonstrated by its growing number of integrated and readily-usable pretrained generative models consisting of 21 models utilising 9 different Generative Adversarial Network architectures trained on 11 datasets from 4 domains, namely, mammography, endoscopy, x-ray, and MRI. Furthermore, 3 applications of medigan are analysed in this work, which include (a) enabling community-wide sharing of restricted data, (b) investigating generative model evaluation metrics, and (c) improving clinical downstream tasks. In (b), extending on common medical image synthesis assessment and reporting standards, we show Fr\'echet Inception Distance variability based on image normalisation and radiology-specific feature extraction.
Domain generalization in deep learning-based mass detection in mammography: A large-scale multi-center study
Jan 27, 2022



Abstract:Computer-aided detection systems based on deep learning have shown great potential in breast cancer detection. However, the lack of domain generalization of artificial neural networks is an important obstacle to their deployment in changing clinical environments. In this work, we explore the domain generalization of deep learning methods for mass detection in digital mammography and analyze in-depth the sources of domain shift in a large-scale multi-center setting. To this end, we compare the performance of eight state-of-the-art detection methods, including Transformer-based models, trained in a single domain and tested in five unseen domains. Moreover, a single-source mass detection training pipeline is designed to improve the domain generalization without requiring images from the new domain. The results show that our workflow generalizes better than state-of-the-art transfer learning-based approaches in four out of five domains while reducing the domain shift caused by the different acquisition protocols and scanner manufacturers. Subsequently, an extensive analysis is performed to identify the covariate shifts with bigger effects on the detection performance, such as due to differences in patient age, breast density, mass size, and mass malignancy. Ultimately, this comprehensive study provides key insights and best practices for future research on domain generalization in deep learning-based breast cancer detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge