Simon Hoffmann
Approaching Current Challenges in Developing a Software Stack for Fully Autonomous Driving
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving is a complex undertaking. A common approach is to break down the driving task into individual subtasks through modularization. These sub-modules are usually developed and published separately. However, if these individually developed algorithms have to be combined again to form a full-stack autonomous driving software, this poses particular challenges. Drawing upon our practical experience in developing the software of TUM Autonomous Motorsport, we have identified and derived these challenges in developing an autonomous driving software stack within a scientific environment. We do not focus on the specific challenges of individual algorithms but on the general difficulties that arise when deploying research algorithms on real-world test vehicles. To overcome these challenges, we introduce strategies that have been effective in our development approach. We additionally provide open-source implementations that enable these concepts on GitHub. As a result, this paper's contributions will simplify future full-stack autonomous driving projects, which are essential for a thorough evaluation of the individual algorithms.
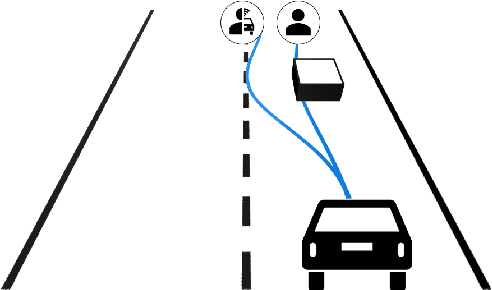
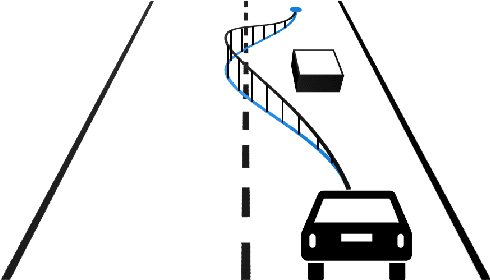
Trajectory Guidance: Enhanced Remote Driving of highly-automated Vehicles
Feb 15, 2024



Abstract:Despite the rapid technological progress, autonomous vehicles still face a wide range of complex driving situations that require human intervention. Teleoperation technology offers a versatile and effective way to address these challenges. The following work puts existing ideas into a modern context and introduces a novel technical implementation of the trajectory guidance teleoperation concept. The presented system was developed within a high-fidelity simulation environment and experimentally validated, demonstrating a realistic ride-hailing mission with prototype autonomous vehicles and onboard passengers. The results indicate that the proposed concept can be a viable alternative to the existing remote driving options, offering a promising way to enhance teleoperation technology and improve overall operation safety.
Survey on Teleoperation Concepts for Automated Vehicles
Aug 18, 2022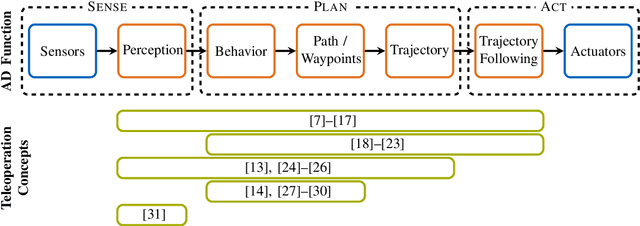
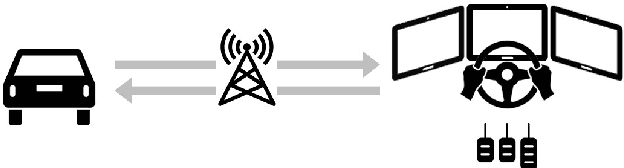
Abstract:In parallel with the advancement of Automated Driving (AD) functions, teleoperation has grown in popularity over recent years. By enabling remote operation of automated vehicles, teleoperation can be established as a reliable fallback solution for operational design domain limits and edge cases of AD functions. Over the years, a variety of different teleoperation concepts as to how a human operator can remotely support or substitute an AD function have been proposed in the literature. This paper presents the results of a literature survey on teleoperation concepts for road vehicles. Furthermore, due to the increasing interest within the industry, insights on patents and overall company activities in the field of teleoperation are presented.
Open Source Software for Teleoperated Driving
Sep 23, 2021

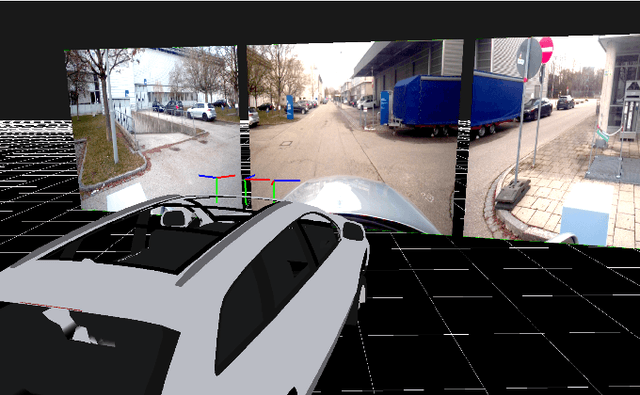

Abstract:Teleoperation allows a human operator to remotely interact with and control a mobile robot in a dangerous or inaccessible area. Besides well-known applications such as space exploration or search and rescue operations, the application of teleoperation in the area of automated driving, i.e., teleoperated driving (ToD), is becoming more popular. Instead of an in-vehicle human fallback driver, a remote operator can connect to the vehicle using cellular networks and resolve situations that are beyond the automated vehicle (AV)'s operational design domain. Teleoperation of AVs, and unmanned ground vehicles in general, introduces different problems, which are the focus of ongoing research. This paper presents an open source ToD software stack, which was developed for the purpose of carrying out this research. As shown in three demonstrations, the software stack can be deployed with minor overheads to control various vehicle systems remotely.
Adaptive Video Configuration and Bitrate Allocation for Teleoperated Driving
Feb 22, 2021
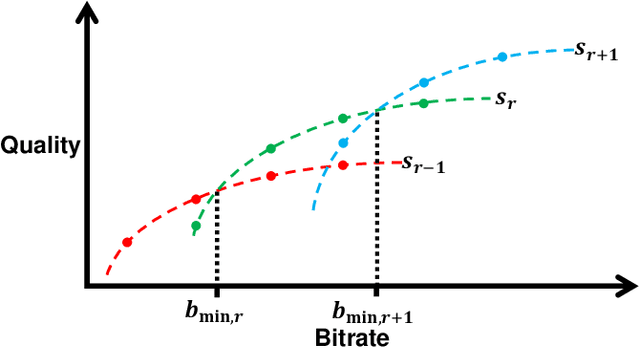
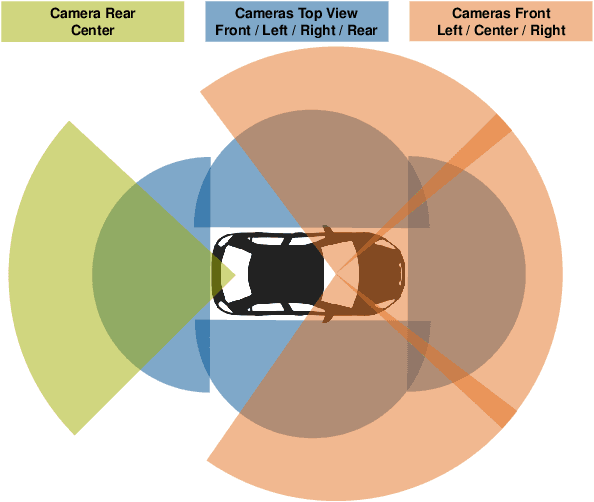

Abstract:Vehicles with autonomous driving capabilities are present on public streets. However, edge cases remain that still require a human in-vehicle driver. Assuming the vehicle manages to come to a safe state in an automated fashion, teleoperated driving technology enables a human to resolve the situation remotely by a control interface connected via a mobile network. While this is a promising solution, it also introduces technical challenges, one of them being the necessity to transmit video data of multiple cameras from the vehicle to the human operator. In this paper, an adaptive video streaming framework specifically designed for teleoperated driving is proposed and demonstrated. The framework enables automatic reconfiguration of the video streams of the multi-camera system at runtime. Predictions of variable transmission service quality are taken into account. With the objective to maximize visual quality, the framework uses so-called rate-quality models to dynamically allocate bitrates and select resolution scaling factors. Results from deploying the proposed framework on an actual teleoperated driving system are presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge