Sijie Niu
Senior Member, IEEE
Learning Language-Driven Sequence-Level Modal-Invariant Representations for Video-Based Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:The core of video-based visible-infrared person re-identification (VVI-ReID) lies in learning sequence-level modal-invariant representations across different modalities. Recent research tends to use modality-shared language prompts generated by CLIP to guide the learning of modal-invariant representations. Despite achieving optimal performance, such methods still face limitations in efficient spatial-temporal modeling, sufficient cross-modal interaction, and explicit modality-level loss guidance. To address these issues, we propose the language-driven sequence-level modal-invariant representation learning (LSMRL) method, which includes spatial-temporal feature learning (STFL) module, semantic diffusion (SD) module and cross-modal interaction (CMI) module. To enable parameter- and computation-efficient spatial-temporal modeling, the STFL module is built upon CLIP with minimal modifications. To achieve sufficient cross-modal interaction and enhance the learning of modal-invariant features, the SD module is proposed to diffuse modality-shared language prompts into visible and infrared features to establish preliminary modal consistency. The CMI module is further developed to leverage bidirectional cross-modal self-attention to eliminate residual modality gaps and refine modal-invariant representations. To explicitly enhance the learning of modal-invariant representations, two modality-level losses are introduced to improve the features' discriminative ability and their generalization to unseen categories. Extensive experiments on large-scale VVI-ReID datasets demonstrate the superiority of LSMRL over AOTA methods.
CLIP4VI-ReID: Learning Modality-shared Representations via CLIP Semantic Bridge for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a novel CLIP-driven modality-shared representation learning network named CLIP4VI-ReID for VI-ReID task, which consists of Text Semantic Generation (TSG), Infrared Feature Embedding (IFE), and High-level Semantic Alignment (HSA). Specifically, considering the huge gap in the physical characteristics between natural images and infrared images, the TSG is designed to generate text semantics only for visible images, thereby enabling preliminary visible-text modality alignment. Then, the IFE is proposed to rectify the feature embeddings of infrared images using the generated text semantics. This process injects id-related semantics into the shared image encoder, enhancing its adaptability to the infrared modality. Besides, with text serving as a bridge, it enables indirect visible-infrared modality alignment. Finally, the HSA is established to refine the high-level semantic alignment. This process ensures that the fine-tuned text semantics only contain id-related information, thereby achieving more accurate cross-modal alignment and enhancing the discriminability of the learned modal-shared representations. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed CLIP4VI-ReID achieves superior performance than other state-of-the-art methods on some widely used VI-ReID datasets.
Discriminative Feature Learning Framework with Gradient Preference for Anomaly Detection
Apr 23, 2022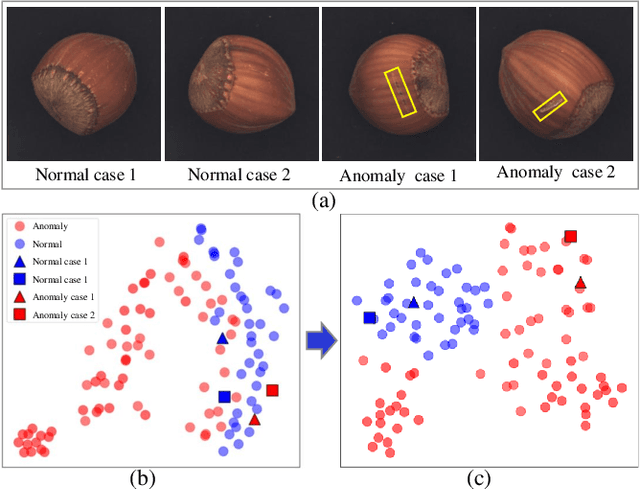
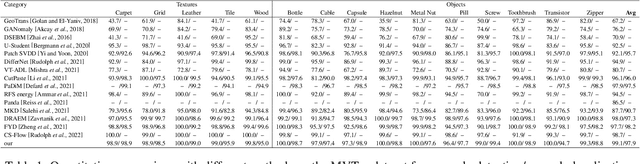
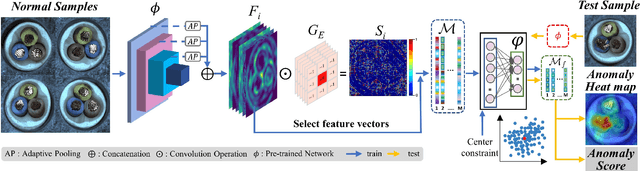
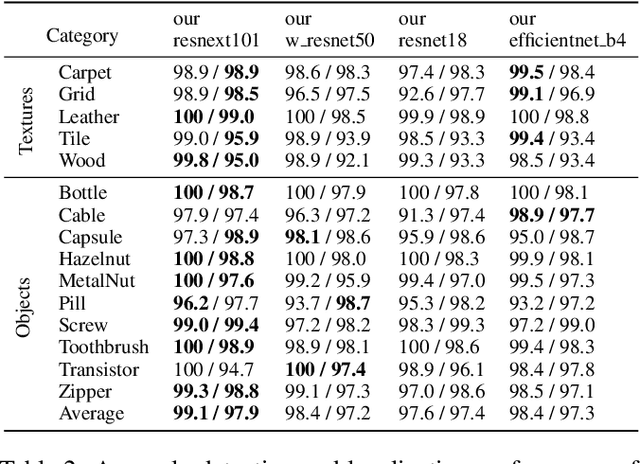
Abstract:Unsupervised representation learning has been extensively employed in anomaly detection, achieving impressive performance. Extracting valuable feature vectors that can remarkably improve the performance of anomaly detection are essential in unsupervised representation learning. To this end, we propose a novel discriminative feature learning framework with gradient preference for anomaly detection. Specifically, we firstly design a gradient preference based selector to store powerful feature points in space and then construct a feature repository, which alleviate the interference of redundant feature vectors and improve inference efficiency. To overcome the looseness of feature vectors, secondly, we present a discriminative feature learning with center constrain to map the feature repository to a compact subspace, so that the anomalous samples are more distinguishable from the normal ones. Moreover, our method can be easily extended to anomaly localization. Extensive experiments on popular industrial and medical anomaly detection datasets demonstrate our proposed framework can achieve competitive results in both anomaly detection and localization. More important, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art in few shot anomaly detection.
Multi-Site Infant Brain Segmentation Algorithms: The iSeg-2019 Challenge
Jul 11, 2020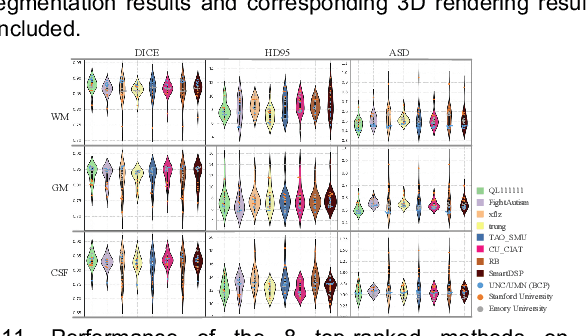
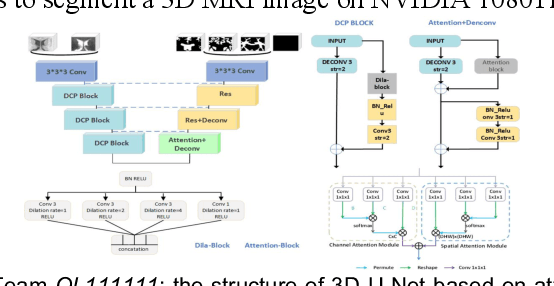
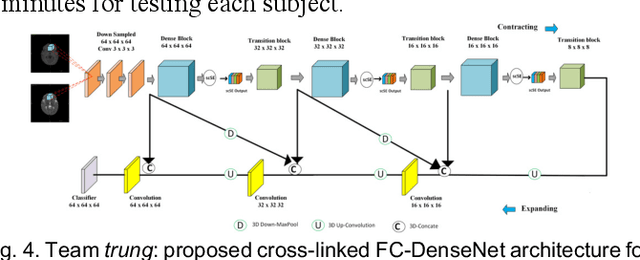
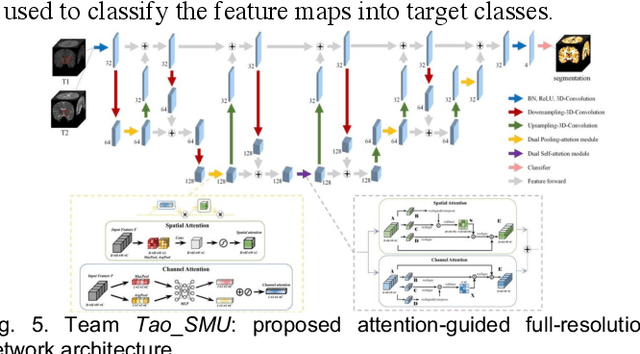
Abstract:To better understand early brain growth patterns in health and disorder, it is critical to accurately segment infant brain magnetic resonance (MR) images into white matter (WM), gray matter (GM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Deep learning-based methods have achieved state-of-the-art performance; however, one of major limitations is that the learning-based methods may suffer from the multi-site issue, that is, the models trained on a dataset from one site may not be applicable to the datasets acquired from other sites with different imaging protocols/scanners. To promote methodological development in the community, iSeg-2019 challenge (http://iseg2019.web.unc.edu) provides a set of 6-month infant subjects from multiple sites with different protocols/scanners for the participating methods. Training/validation subjects are from UNC (MAP) and testing subjects are from UNC/UMN (BCP), Stanford University, and Emory University. By the time of writing, there are 30 automatic segmentation methods participating in iSeg-2019. We review the 8 top-ranked teams by detailing their pipelines/implementations, presenting experimental results and evaluating performance in terms of the whole brain, regions of interest, and gyral landmark curves. We also discuss their limitations and possible future directions for the multi-site issue. We hope that the multi-site dataset in iSeg-2019 and this review article will attract more researchers on the multi-site issue.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge