Shuoxi Zhang
Enhancing Pre-Trained Model-Based Class-Incremental Learning through Neural Collapse
Apr 25, 2025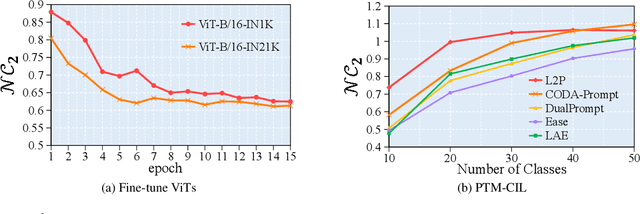
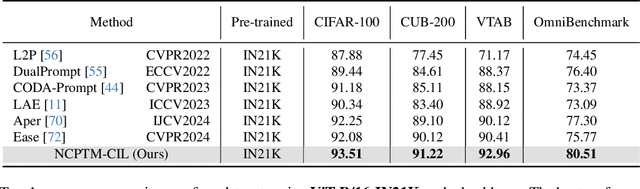
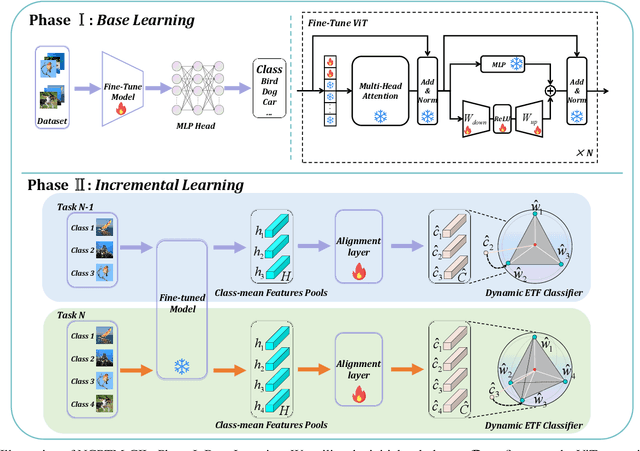
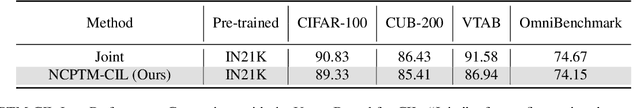
Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) is a critical capability for real-world applications, enabling learning systems to adapt to new tasks while retaining knowledge from previous ones. Recent advancements in pre-trained models (PTMs) have significantly advanced the field of CIL, demonstrating superior performance over traditional methods. However, understanding how features evolve and are distributed across incremental tasks remains an open challenge. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to modeling feature evolution in PTM-based CIL through the lens of neural collapse (NC), a striking phenomenon observed in the final phase of training, which leads to a well-separated, equiangular feature space. We explore the connection between NC and CIL effectiveness, showing that aligning feature distributions with the NC geometry enhances the ability to capture the dynamic behavior of continual learning. Based on this insight, we introduce Neural Collapse-inspired Pre-Trained Model-based CIL (NCPTM-CIL), a method that dynamically adjusts the feature space to conform to the elegant NC structure, thereby enhancing the continual learning process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that NCPTM-CIL outperforms state-of-the-art methods across four benchmark datasets. Notably, when initialized with ViT-B/16-IN1K, NCPTM-CIL surpasses the runner-up method by 6.73% on VTAB, 1.25% on CIFAR-100, and 2.5% on OmniBenchmark.
Neural Collapse Inspired Knowledge Distillation
Dec 16, 2024
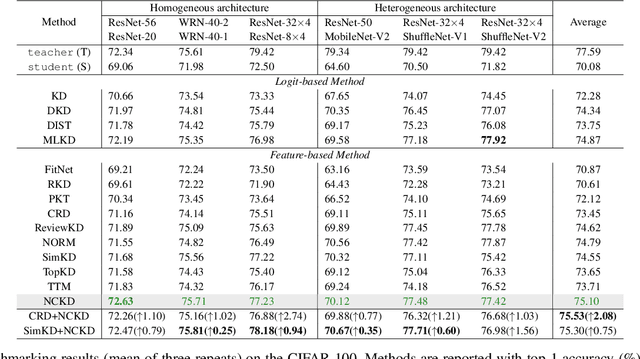


Abstract:Existing knowledge distillation (KD) methods have demonstrated their ability in achieving student network performance on par with their teachers. However, the knowledge gap between the teacher and student remains significant and may hinder the effectiveness of the distillation process. In this work, we introduce the structure of Neural Collapse (NC) into the KD framework. NC typically occurs in the final phase of training, resulting in a graceful geometric structure where the last-layer features form a simplex equiangular tight frame. Such phenomenon has improved the generalization of deep network training. We hypothesize that NC can also alleviate the knowledge gap in distillation, thereby enhancing student performance. This paper begins with an empirical analysis to bridge the connection between knowledge distillation and neural collapse. Through this analysis, we establish that transferring the teacher's NC structure to the student benefits the distillation process. Therefore, instead of merely transferring instance-level logits or features, as done by existing distillation methods, we encourage students to learn the teacher's NC structure. Thereby, we propose a new distillation paradigm termed Neural Collapse-inspired Knowledge Distillation (NCKD). Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that NCKD is simple yet effective, improving the generalization of all distilled student models and achieving state-of-the-art accuracy performance.
You Only Need Less Attention at Each Stage in Vision Transformers
Jun 01, 2024Abstract:The advent of Vision Transformers (ViTs) marks a substantial paradigm shift in the realm of computer vision. ViTs capture the global information of images through self-attention modules, which perform dot product computations among patchified image tokens. While self-attention modules empower ViTs to capture long-range dependencies, the computational complexity grows quadratically with the number of tokens, which is a major hindrance to the practical application of ViTs. Moreover, the self-attention mechanism in deep ViTs is also susceptible to the attention saturation issue. Accordingly, we argue against the necessity of computing the attention scores in every layer, and we propose the Less-Attention Vision Transformer (LaViT), which computes only a few attention operations at each stage and calculates the subsequent feature alignments in other layers via attention transformations that leverage the previously calculated attention scores. This novel approach can mitigate two primary issues plaguing traditional self-attention modules: the heavy computational burden and attention saturation. Our proposed architecture offers superior efficiency and ease of implementation, merely requiring matrix multiplications that are highly optimized in contemporary deep learning frameworks. Moreover, our architecture demonstrates exceptional performance across various vision tasks including classification, detection and segmentation.
Knowledge Distillation via Token-level Relationship Graph
Jun 20, 2023Abstract:Knowledge distillation is a powerful technique for transferring knowledge from a pre-trained teacher model to a student model. However, the true potential of knowledge transfer has not been fully explored. Existing approaches primarily focus on distilling individual information or instance-level relationships, overlooking the valuable information embedded in token-level relationships, which may be particularly affected by the long-tail effects. To address the above limitations, we propose a novel method called Knowledge Distillation with Token-level Relationship Graph (TRG) that leverages the token-wise relational knowledge to enhance the performance of knowledge distillation. By employing TRG, the student model can effectively emulate higher-level semantic information from the teacher model, resulting in improved distillation results. To further enhance the learning process, we introduce a token-wise contextual loss called contextual loss, which encourages the student model to capture the inner-instance semantic contextual of the teacher model. We conduct experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method against several state-of-the-art approaches. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of TRG across various visual classification tasks, including those involving imbalanced data. Our method consistently outperforms the existing baselines, establishing a new state-of-the-art performance in the field of knowledge distillation.
Class-aware Information for Logit-based Knowledge Distillation
Nov 27, 2022



Abstract:Knowledge distillation aims to transfer knowledge to the student model by utilizing the predictions/features of the teacher model, and feature-based distillation has recently shown its superiority over logit-based distillation. However, due to the cumbersome computation and storage of extra feature transformation, the training overhead of feature-based methods is much higher than that of logit-based distillation. In this work, we revisit the logit-based knowledge distillation, and observe that the existing logit-based distillation methods treat the prediction logits only in the instance level, while many other useful semantic information is overlooked. To address this issue, we propose a Class-aware Logit Knowledge Distillation (CLKD) method, that extents the logit distillation in both instance-level and class-level. CLKD enables the student model mimic higher semantic information from the teacher model, hence improving the distillation performance. We further introduce a novel loss called Class Correlation Loss to force the student learn the inherent class-level correlation of the teacher. Empirical comparisons demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over several prevailing logit-based methods and feature-based methods, in which CLKD achieves compelling results on various visual classification tasks and outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines.
Generating Pseudo-labels Adaptively for Few-shot Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning
Jul 09, 2022
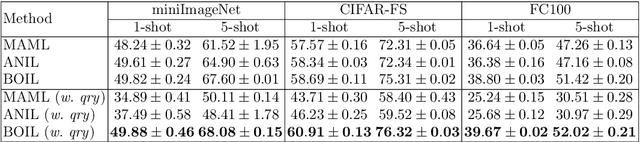
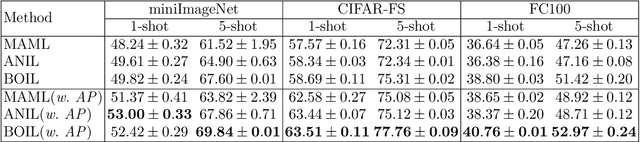
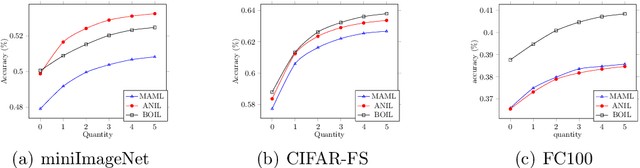
Abstract:Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) is a famous few-shot learning method that has inspired many follow-up efforts, such as ANIL and BOIL. However, as an inductive method, MAML is unable to fully utilize the information of query set, limiting its potential of gaining higher generality. To address this issue, we propose a simple yet effective method that generates psuedo-labels adaptively and could boost the performance of the MAML family. The proposed methods, dubbed Generative Pseudo-label based MAML (GP-MAML), GP-ANIL and GP-BOIL, leverage statistics of the query set to improve the performance on new tasks. Specifically, we adaptively add pseudo labels and pick samples from the query set, then re-train the model using the picked query samples together with the support set. The GP series can also use information from the pseudo query set to re-train the network during the meta-testing. While some transductive methods, such as Transductive Propagation Network (TPN), struggle to achieve this goal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge