Shunyao Zhang
Celine
Compressive Sensing Photoacoustic Imaging Receiver with Matrix-Vector-Multiplication SAR ADC
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Wearable photoacoustic imaging devices hold great promise for continuous health monitoring and point-of-care diagnostics. However, the large data volume generated by high-density transducer arrays presents a major challenge for realizing compact and power-efficient wearable systems. This paper presents a photoacoustic imaging receiver (RX) that embeds compressive sensing directly into the hardware to address this bottleneck. The RX integrates 16 AFEs and four matrix-vector-multiplication (MVM) SAR ADCs that perform energy- and area-efficient analog-domain compression. The architecture achieves a 4-8x reduction in output data rate while preserving low-loss full-array information. The MVM SAR ADC executes passive and accurate MVM using user-defined programmable ternary weights. Two signal reconstruction methods are implemented: (1) an optimization approach using the fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm, and (2) a learning-based approach employing implicit neural representation. Fabricated in 65 nm CMOS, the chip achieves an ADC's SNDR of 57.5 dB at 20.41 MS/s, with an AFE input-referred noise of 3.5 nV/sqrt(Hz). MVM linearity measurements show R^2 > 0.999 across a wide range of weights and input amplitudes. The system is validated through phantom imaging experiments, demonstrating high-fidelity image reconstruction under up to 8x compression. The RX consumes 5.83 mW/channel and supports a general ternary-weighted measurement matrix, offering a compelling solution for next-generation miniaturized, wearable PA imaging systems.
NetDistiller: Empowering Tiny Deep Learning via In-Situ Distillation
Oct 24, 2023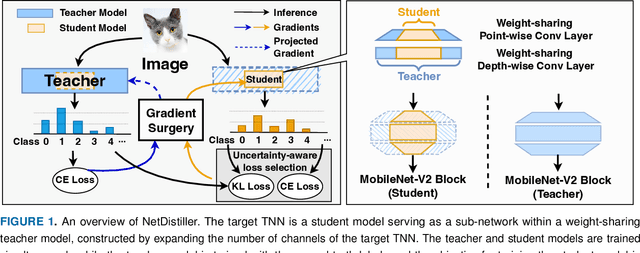
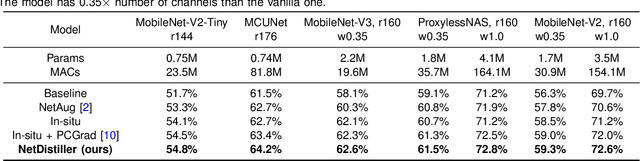
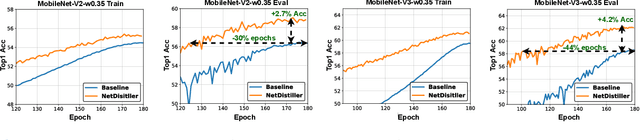
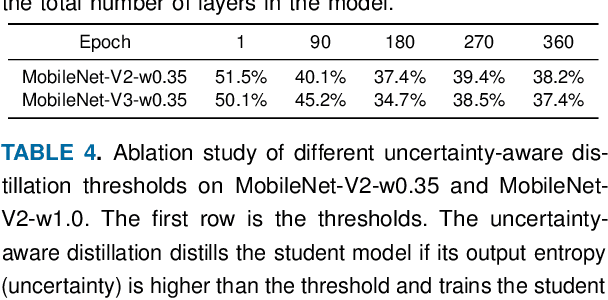
Abstract:Boosting the task accuracy of tiny neural networks (TNNs) has become a fundamental challenge for enabling the deployments of TNNs on edge devices which are constrained by strict limitations in terms of memory, computation, bandwidth, and power supply. To this end, we propose a framework called NetDistiller to boost the achievable accuracy of TNNs by treating them as sub-networks of a weight-sharing teacher constructed by expanding the number of channels of the TNN. Specifically, the target TNN model is jointly trained with the weight-sharing teacher model via (1) gradient surgery to tackle the gradient conflicts between them and (2) uncertainty-aware distillation to mitigate the overfitting of the teacher model. Extensive experiments across diverse tasks validate NetDistiller's effectiveness in boosting TNNs' achievable accuracy over state-of-the-art methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/GATECH-EIC/NetDistiller.
NeRFool: Uncovering the Vulnerability of Generalizable Neural Radiance Fields against Adversarial Perturbations
Jun 10, 2023



Abstract:Generalizable Neural Radiance Fields (GNeRF) are one of the most promising real-world solutions for novel view synthesis, thanks to their cross-scene generalization capability and thus the possibility of instant rendering on new scenes. While adversarial robustness is essential for real-world applications, little study has been devoted to understanding its implication on GNeRF. We hypothesize that because GNeRF is implemented by conditioning on the source views from new scenes, which are often acquired from the Internet or third-party providers, there are potential new security concerns regarding its real-world applications. Meanwhile, existing understanding and solutions for neural networks' adversarial robustness may not be applicable to GNeRF, due to its 3D nature and uniquely diverse operations. To this end, we present NeRFool, which to the best of our knowledge is the first work that sets out to understand the adversarial robustness of GNeRF. Specifically, NeRFool unveils the vulnerability patterns and important insights regarding GNeRF's adversarial robustness. Built upon the above insights gained from NeRFool, we further develop NeRFool+, which integrates two techniques capable of effectively attacking GNeRF across a wide range of target views, and provide guidelines for defending against our proposed attacks. We believe that our NeRFool/NeRFool+ lays the initial foundation for future innovations in developing robust real-world GNeRF solutions. Our codes are available at: https://github.com/GATECH-EIC/NeRFool.
Hint-Aug: Drawing Hints from Foundation Vision Transformers Towards Boosted Few-Shot Parameter-Efficient Tuning
Apr 26, 2023Abstract:Despite the growing demand for tuning foundation vision transformers (FViTs) on downstream tasks, fully unleashing FViTs' potential under data-limited scenarios (e.g., few-shot tuning) remains a challenge due to FViTs' data-hungry nature. Common data augmentation techniques fall short in this context due to the limited features contained in the few-shot tuning data. To tackle this challenge, we first identify an opportunity for FViTs in few-shot tuning: pretrained FViTs themselves have already learned highly representative features from large-scale pretraining data, which are fully preserved during widely used parameter-efficient tuning. We thus hypothesize that leveraging those learned features to augment the tuning data can boost the effectiveness of few-shot FViT tuning. To this end, we propose a framework called Hint-based Data Augmentation (Hint-Aug), which aims to boost FViT in few-shot tuning by augmenting the over-fitted parts of tuning samples with the learned features of pretrained FViTs. Specifically, Hint-Aug integrates two key enablers: (1) an Attentive Over-fitting Detector (AOD) to detect over-confident patches of foundation ViTs for potentially alleviating their over-fitting on the few-shot tuning data and (2) a Confusion-based Feature Infusion (CFI) module to infuse easy-to-confuse features from the pretrained FViTs with the over-confident patches detected by the above AOD in order to enhance the feature diversity during tuning. Extensive experiments and ablation studies on five datasets and three parameter-efficient tuning techniques consistently validate Hint-Aug's effectiveness: 0.04% ~ 32.91% higher accuracy over the state-of-the-art (SOTA) data augmentation method under various low-shot settings. For example, on the Pet dataset, Hint-Aug achieves a 2.22% higher accuracy with 50% less training data over SOTA data augmentation methods.
Gen-NeRF: Efficient and Generalizable Neural Radiance Fields via Algorithm-Hardware Co-Design
Apr 25, 2023

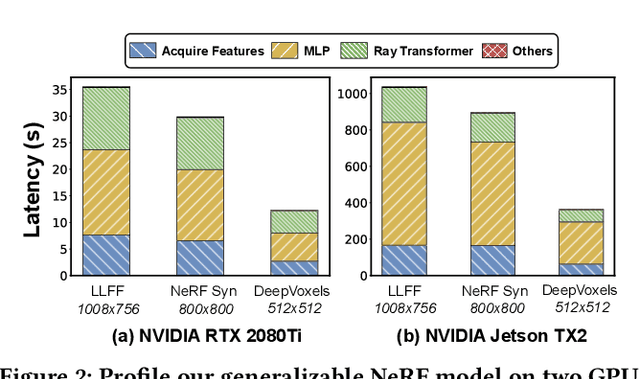
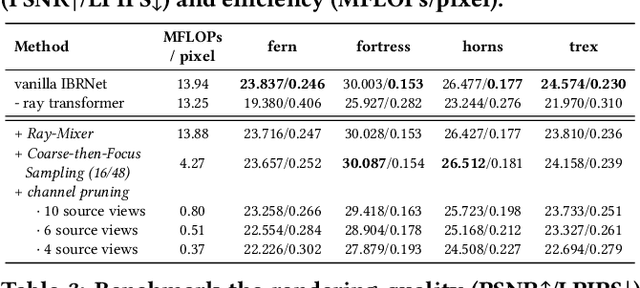
Abstract:Novel view synthesis is an essential functionality for enabling immersive experiences in various Augmented- and Virtual-Reality (AR/VR) applications, for which generalizable Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have gained increasing popularity thanks to their cross-scene generalization capability. Despite their promise, the real-device deployment of generalizable NeRFs is bottlenecked by their prohibitive complexity due to the required massive memory accesses to acquire scene features, causing their ray marching process to be memory-bounded. To this end, we propose Gen-NeRF, an algorithm-hardware co-design framework dedicated to generalizable NeRF acceleration, which for the first time enables real-time generalizable NeRFs. On the algorithm side, Gen-NeRF integrates a coarse-then-focus sampling strategy, leveraging the fact that different regions of a 3D scene contribute differently to the rendered pixel, to enable sparse yet effective sampling. On the hardware side, Gen-NeRF highlights an accelerator micro-architecture to maximize the data reuse opportunities among different rays by making use of their epipolar geometric relationship. Furthermore, our Gen-NeRF accelerator features a customized dataflow to enhance data locality during point-to-hardware mapping and an optimized scene feature storage strategy to minimize memory bank conflicts. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed Gen-NeRF framework in enabling real-time and generalizable novel view synthesis.
Patch-Fool: Are Vision Transformers Always Robust Against Adversarial Perturbations?
Apr 05, 2022



Abstract:Vision transformers (ViTs) have recently set off a new wave in neural architecture design thanks to their record-breaking performance in various vision tasks. In parallel, to fulfill the goal of deploying ViTs into real-world vision applications, their robustness against potential malicious attacks has gained increasing attention. In particular, recent works show that ViTs are more robust against adversarial attacks as compared with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and conjecture that this is because ViTs focus more on capturing global interactions among different input/feature patches, leading to their improved robustness to local perturbations imposed by adversarial attacks. In this work, we ask an intriguing question: "Under what kinds of perturbations do ViTs become more vulnerable learners compared to CNNs?" Driven by this question, we first conduct a comprehensive experiment regarding the robustness of both ViTs and CNNs under various existing adversarial attacks to understand the underlying reason favoring their robustness. Based on the drawn insights, we then propose a dedicated attack framework, dubbed Patch-Fool, that fools the self-attention mechanism by attacking its basic component (i.e., a single patch) with a series of attention-aware optimization techniques. Interestingly, our Patch-Fool framework shows for the first time that ViTs are not necessarily more robust than CNNs against adversarial perturbations. In particular, we find that ViTs are more vulnerable learners compared with CNNs against our Patch-Fool attack which is consistent across extensive experiments, and the observations from Sparse/Mild Patch-Fool, two variants of Patch-Fool, indicate an intriguing insight that the perturbation density and strength on each patch seem to be the key factors that influence the robustness ranking between ViTs and CNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge