Shubin Xie
DynamicLight: Dynamically Tuning Traffic Signal Duration with DRL
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is becoming increasingly popular in implementing traffic signal control (TSC). However, most existing DRL methods employ fixed control strategies, making traffic signal phase duration less flexible. Additionally, the trend of using more complex DRL models makes real-life deployment more challenging. To address these two challenges, we firstly propose a two-stage DRL framework, named DynamicLight, which uses Max Queue-Length to select the proper phase and employs a deep Q-learning network to determine the duration of the corresponding phase. Based on the design of DynamicLight, we also introduce two variants: (1) DynamicLight-Lite, which addresses the first challenge by using only 19 parameters to achieve dynamic phase duration settings; and (2) DynamicLight-Cycle, which tackles the second challenge by actuating a set of phases in a fixed cyclical order to implement flexible phase duration in the respective cyclical phase structure. Numerical experiments are conducted using both real-world and synthetic datasets, covering four most commonly adopted traffic signal intersections in real life. Experimental results show that: (1) DynamicLight can learn satisfactorily on determining the phase duration and achieve a new state-of-the-art, with improvement up to 6% compared to the baselines in terms of adjusted average travel time; (2) DynamicLight-Lite matches or outperforms most baseline methods with only 19 parameters; and (3) DynamicLight-Cycle demonstrates high performance for current TSC systems without remarkable modification in an actual deployment. Our code is released at Github.
DynLight: Realize dynamic phase duration with multi-level traffic signal control
Apr 20, 2022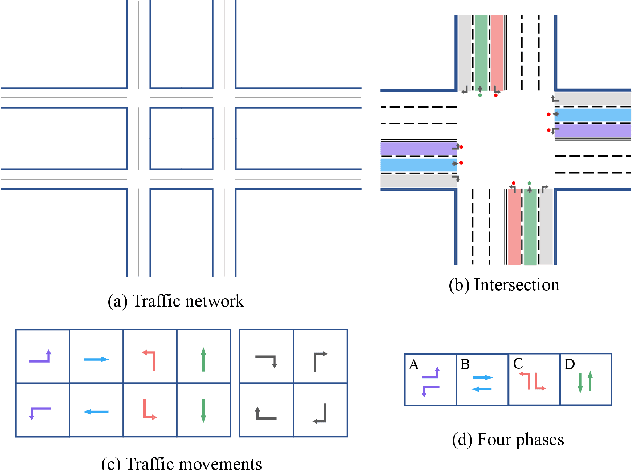

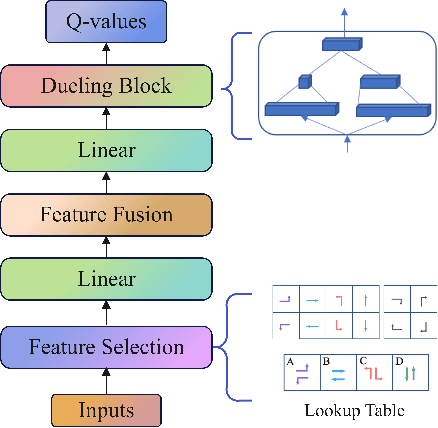

Abstract:Adopting reinforcement learning (RL) for traffic signal control (TSC) is increasingly popular, and RL has become a promising solution for traffic signal control. However, several challenges still need to be overcome. Firstly, most RL methods use fixed action duration and select the green phase for the next state, which makes the phase duration less dynamic and flexible. Secondly, the phase sequence of RL methods can be arbitrary, affecting the real-world deployment which may require a cyclical phase structure. Lastly, the average travel time and throughput are not fair metrics to evaluate TSC performance. To address these challenges, we propose a multi-level traffic signal control framework, DynLight, which uses an optimization method Max-QueueLength (M-QL) to determine the phase and uses a deep Q-network to determine the duration of the corresponding phase. Based on DynLight, we further propose DynLight-C which adopts a well-trained deep Q-network of DynLight and replace M-QL with a cyclical control policy that actuates a set of phases in fixed cyclical order to realize cyclical phase structure. Comprehensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that DynLight achieves a new state-of-the-art. Furthermore, the deep Q-network of DynLight can learn well on determining the phase duration and DynLight-C demonstrates high performance for deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge