Shouyong Jiang
Vector Autoregressive Evolution for Dynamic Multi-Objective Optimisation
May 22, 2023



Abstract:Dynamic multi-objective optimisation (DMO) handles optimisation problems with multiple (often conflicting) objectives in varying environments. Such problems pose various challenges to evolutionary algorithms, which have popularly been used to solve complex optimisation problems, due to their dynamic nature and resource restrictions in changing environments. This paper proposes vector autoregressive evolution (VARE) consisting of vector autoregression (VAR) and environment-aware hypermutation to address environmental changes in DMO. VARE builds a VAR model that considers mutual relationship between decision variables to effectively predict the moving solutions in dynamic environments. Additionally, VARE introduces EAH to address the blindness of existing hypermutation strategies in increasing population diversity in dynamic scenarios where predictive approaches are unsuitable. A seamless integration of VAR and EAH in an environment-adaptive manner makes VARE effective to handle a wide range of dynamic environments and competitive with several popular DMO algorithms, as demonstrated in extensive experimental studies. Specially, the proposed algorithm is computationally 50 times faster than two widely-used algorithms (i.e., TrDMOEA and MOEA/D-SVR) while producing significantly better results.
An autoencoder wavelet based deep neural network with attention mechanism for multistep prediction of plant growth
Dec 07, 2020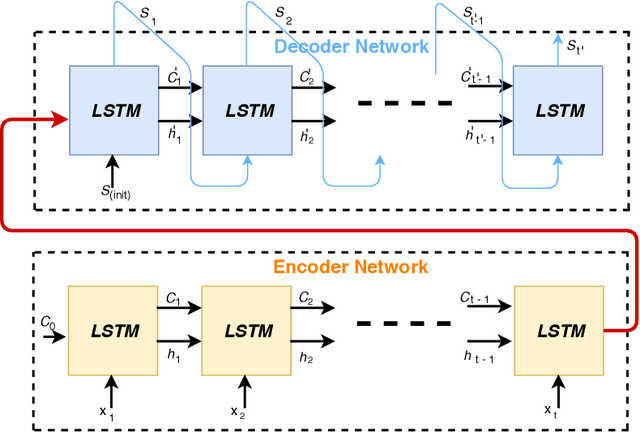
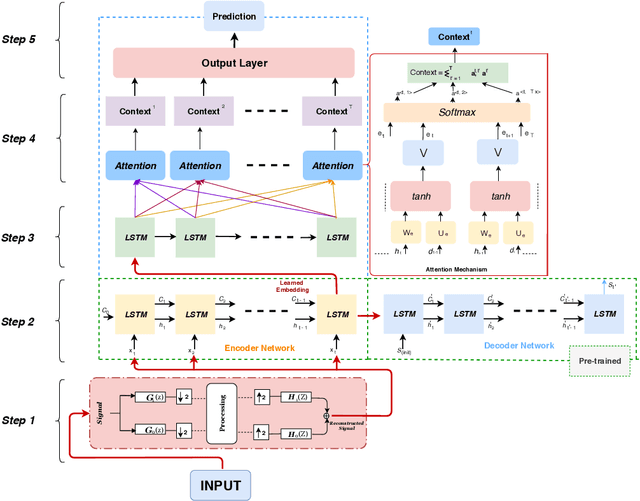
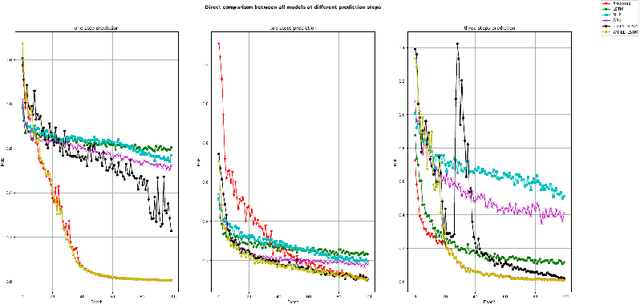
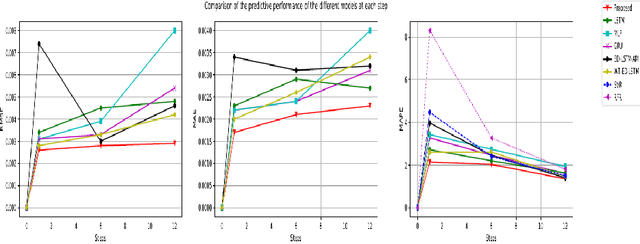
Abstract:Multi-step prediction is considered of major significance for time series analysis in many real life problems. Existing methods mainly focus on one-step-ahead forecasting, since multiple step forecasting generally fails due to accumulation of prediction errors. This paper presents a novel approach for predicting plant growth in agriculture, focusing on prediction of plant Stem Diameter Variations (SDV). The proposed approach consists of three main steps. At first, wavelet decomposition is applied to the original data, as to facilitate model fitting and reduce noise in them. Then an encoder-decoder framework is developed using Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) and used for appropriate feature extraction from the data. Finally, a recurrent neural network including LSTM and an attention mechanism is proposed for modelling long-term dependencies in the time series data. Experimental results are presented which illustrate the good performance of the proposed approach and that it significantly outperforms the existing models, in terms of error criteria such as RMSE, MAE and MAPE.
AREA: Adaptive Reference-set Based Evolutionary Algorithm for Multiobjective Optimisation
Oct 15, 2019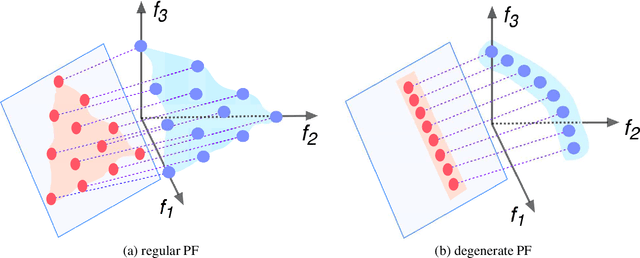
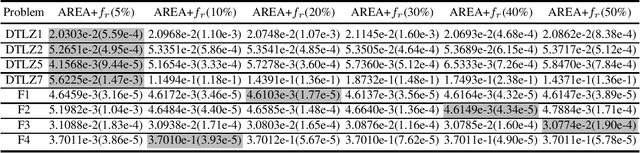
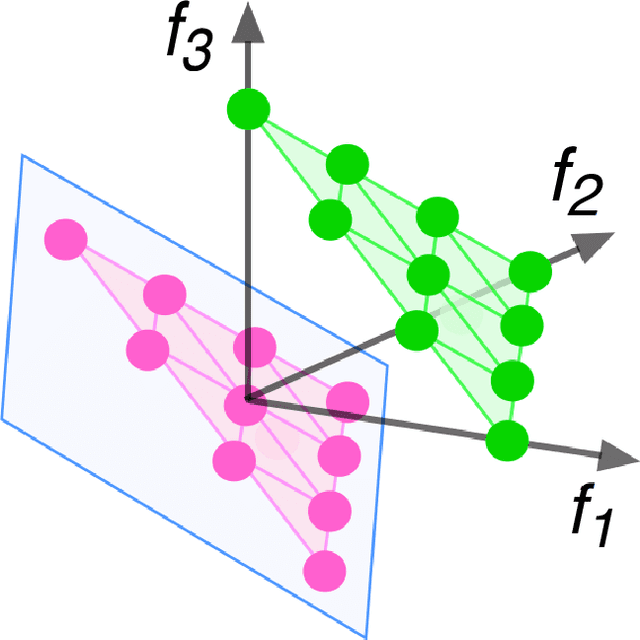
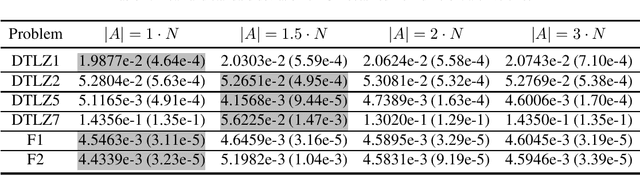
Abstract:Population-based evolutionary algorithms have great potential to handle multiobjective optimisation problems. However, these algorithms depends largely on problem characteristics, and there is a need to improve their performance for a wider range of problems. References, which are often specified by the decision maker's preference in different forms, are a very effective method to improve the performance of algorithms but have not been fully explored in literature. This paper proposes a novel framework for effective use of references to strengthen algorithms. This framework considers references as search targets which can be adjusted based on the information collected during the search. The proposed framework is combined with new strategies, such as reference adaptation and adaptive local mating, to solve different types of problems. The proposed algorithm is compared with state of the arts on a wide range of problems with diverse characteristics. The comparison and extensive sensitivity analysis demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is competitive and robust across different types of problems studied in this paper.
A Scalable Test Suite for Continuous Dynamic Multiobjective Optimisation
Mar 06, 2019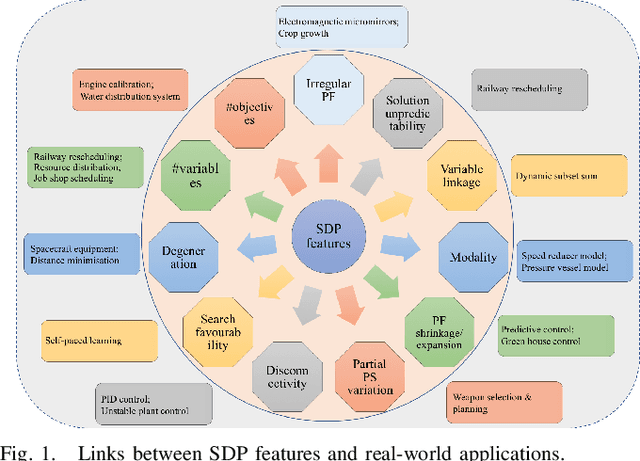
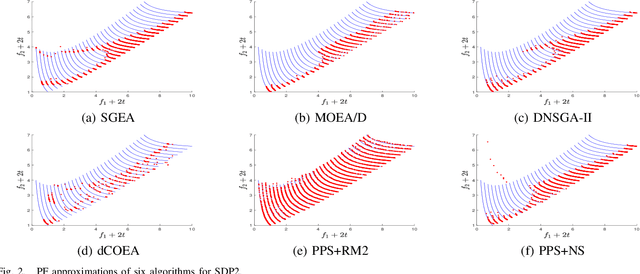
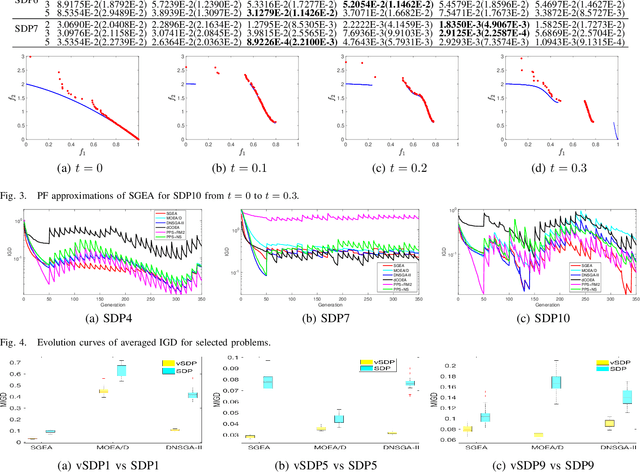
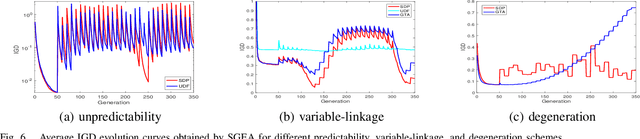
Abstract:Dynamic multiobjective optimisation has gained increasing attention in recent years. Test problems are of great importance in order to facilitate the development of advanced algorithms that can handle dynamic environments well. However, many of existing dynamic multiobjective test problems have not been rigorously constructed and analysed, which may induce some unexpected bias when they are used for algorithmic analysis. In this paper, some of these biases are identified after a review of widely used test problems. These include poor scalability of objectives and, more importantly, problematic overemphasis of static properties rather than dynamics making it difficult to draw accurate conclusion about the strengths and weaknesses of the algorithms studied. A diverse set of dynamics and features is then highlighted that a good test suite should have. We further develop a scalable continuous test suite, which includes a number of dynamics or features that have been rarely considered in literature but frequently occur in real life. It is demonstrated with empirical studies that the proposed test suite is more challenging to the dynamic multiobjective optimisation algorithms found in the literature. The test suite can also test algorithms in ways that existing test suites can not.
* 19 pages, 22 figures and 7 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge