Bashar Alhnaity
An autoencoder wavelet based deep neural network with attention mechanism for multistep prediction of plant growth
Dec 07, 2020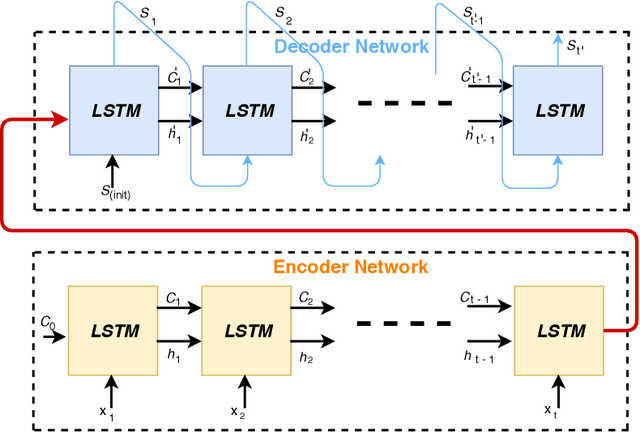
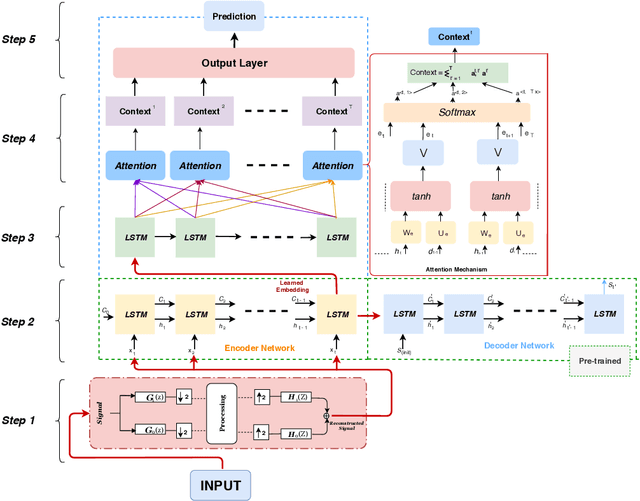
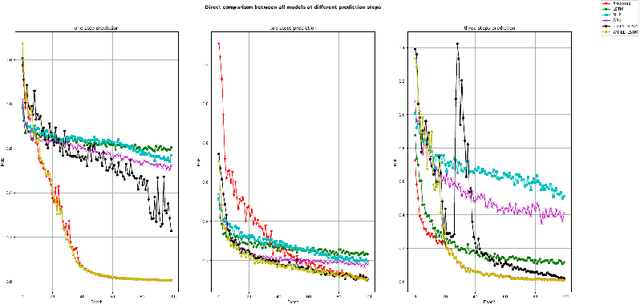
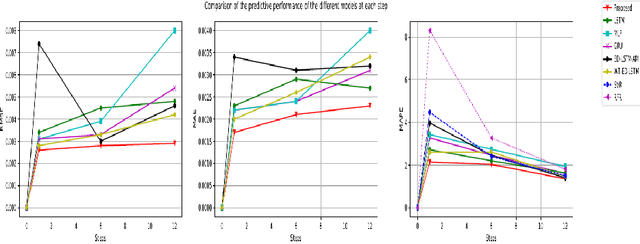
Abstract:Multi-step prediction is considered of major significance for time series analysis in many real life problems. Existing methods mainly focus on one-step-ahead forecasting, since multiple step forecasting generally fails due to accumulation of prediction errors. This paper presents a novel approach for predicting plant growth in agriculture, focusing on prediction of plant Stem Diameter Variations (SDV). The proposed approach consists of three main steps. At first, wavelet decomposition is applied to the original data, as to facilitate model fitting and reduce noise in them. Then an encoder-decoder framework is developed using Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) and used for appropriate feature extraction from the data. Finally, a recurrent neural network including LSTM and an attention mechanism is proposed for modelling long-term dependencies in the time series data. Experimental results are presented which illustrate the good performance of the proposed approach and that it significantly outperforms the existing models, in terms of error criteria such as RMSE, MAE and MAPE.
Using Deep Learning to Predict Plant Growth and Yield in Greenhouse Environments
Jul 01, 2019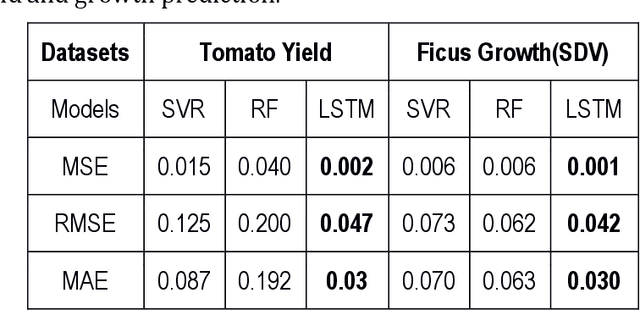
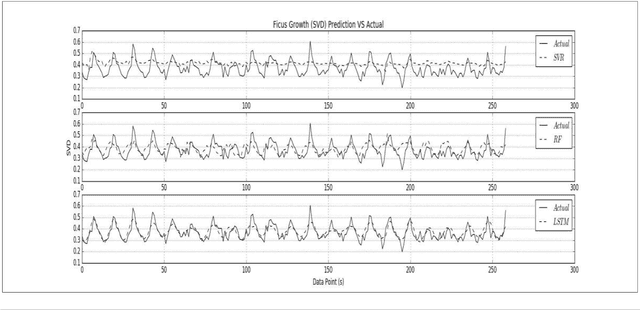
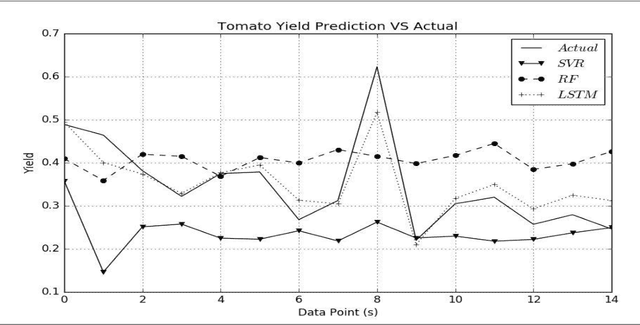
Abstract:Effective plant growth and yield prediction is an essential task for greenhouse growers and for agriculture in general. Developing models which can effectively model growth and yield can help growers improve the environmental control for better production, match supply and market demand and lower costs. Recent developments in Machine Learning (ML) and, in particular, Deep Learning (DL) can provide powerful new analytical tools. The proposed study utilises ML and DL techniques to predict yield and plant growth variation across two different scenarios, tomato yield forecasting and Ficus benjamina stem growth, in controlled greenhouse environments. We deploy a new deep recurrent neural network (RNN), using the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neuron model, in the prediction formulations. Both the former yield, growth and stem diameter values, as well as the microclimate conditions, are used by the RNN architecture to model the targeted growth parameters. A comparative study is presented, using ML methods, such as support vector regression and random forest regression, utilising the mean square error criterion, in order to evaluate the performance achieved by the different methods. Very promising results, based on data that have been obtained from two greenhouses, in Belgium and the UK, in the framework of the EU Interreg SMARTGREEN project (2017-2021), are presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge