Shiyu Yi
Adaptive Transfer Learning of Multi-View Time Series Classification
Oct 14, 2019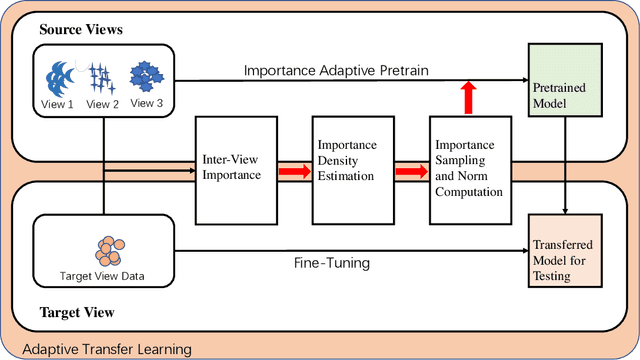
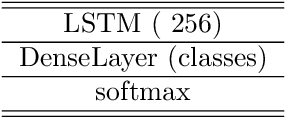
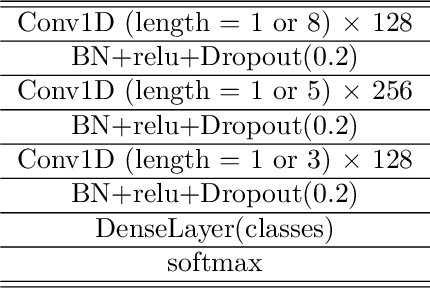
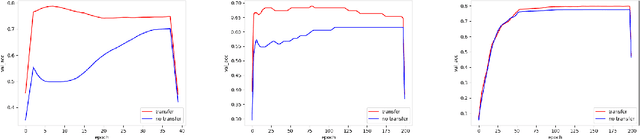
Abstract:Time Series Classification (TSC) has been an important and challenging task in data mining, especially on multivariate time series and multi-view time series data sets. Meanwhile, transfer learning has been widely applied in computer vision and natural language processing applications to improve deep neural network's generalization capabilities. However, very few previous works applied transfer learning framework to time series mining problems. Particularly, the technique of measuring similarities between source domain and target domain based on dynamic representation such as density estimation with importance sampling has never been combined with transfer learning framework. In this paper, we first proposed a general adaptive transfer learning framework for multi-view time series data, which shows strong ability in storing inter-view importance value in the process of knowledge transfer. Next, we represented inter-view importance through some time series similarity measurements and approximated the posterior distribution in latent space for the importance sampling via density estimation techniques. We then computed the matrix norm of sampled importance value, which controls the degree of knowledge transfer in pre-training process. We further evaluated our work, applied it to many other time series classification tasks, and observed that our architecture maintained desirable generalization ability. Finally, we concluded that our framework could be adapted with deep learning techniques to receive significant model performance improvements.
FIS-GAN: GAN with Flow-based Importance Sampling
Oct 06, 2019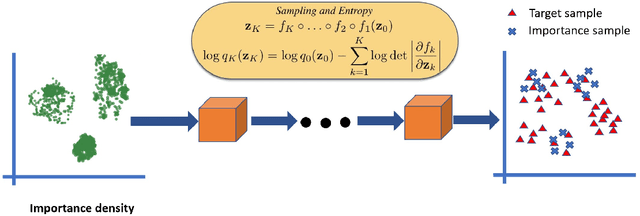
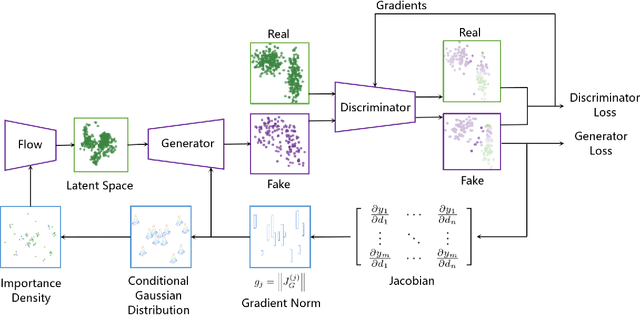
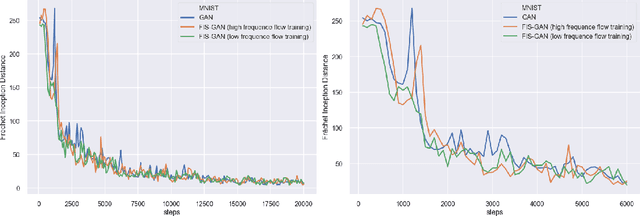
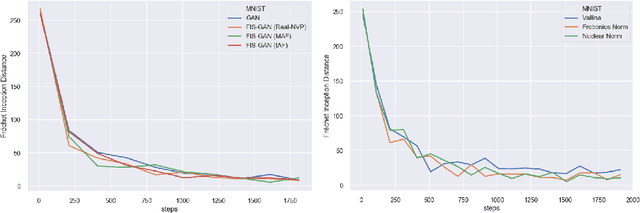
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) training process, in most cases, apply uniform and Gaussian sampling methods in latent space, which probably spends most of the computation on examples that can be properly handled and easy to generate. Theoretically, importance sampling speeds up stochastic gradient algorithms for supervised learning by prioritizing training examples. In this paper, we explore the possibility for adapting importance sampling into adversarial learning. We use importance sampling to replace uniform and Gaussian sampling methods in latent space and combine normalizing flow with importance sampling to approximate latent space posterior distribution by density estimation. Empirically, results on MNIST and Fashion-MNIST demonstrate that our method significantly accelerates the convergence of generative process while retaining visual fidelity in generated samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge