Shima Salarhosseini
Learning based E2E Energy Efficient in Joint Radio and NFV Resource Allocation for 5G and Beyond Networks
Jul 13, 2021
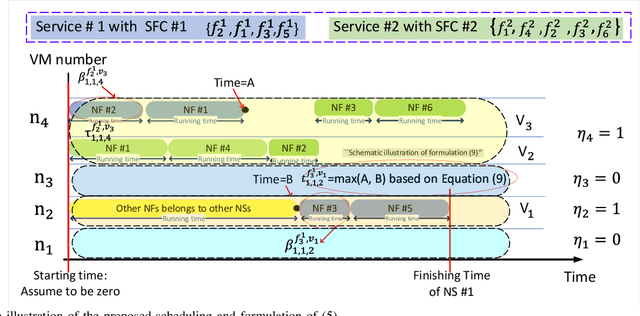
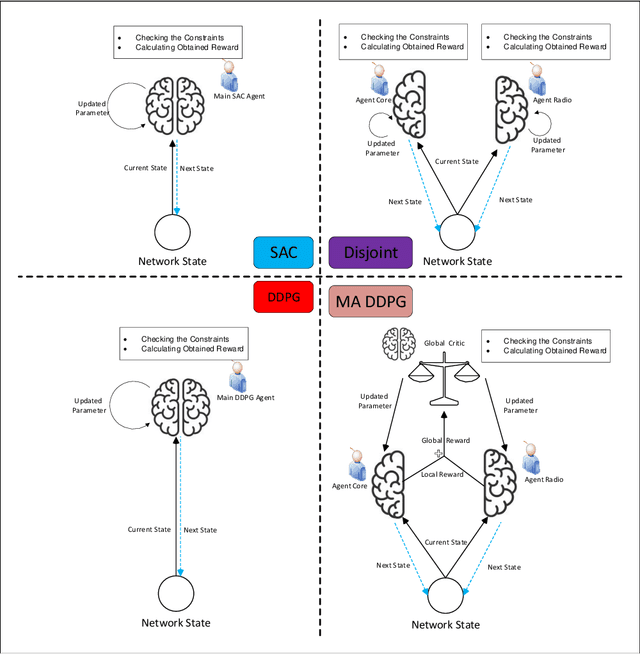
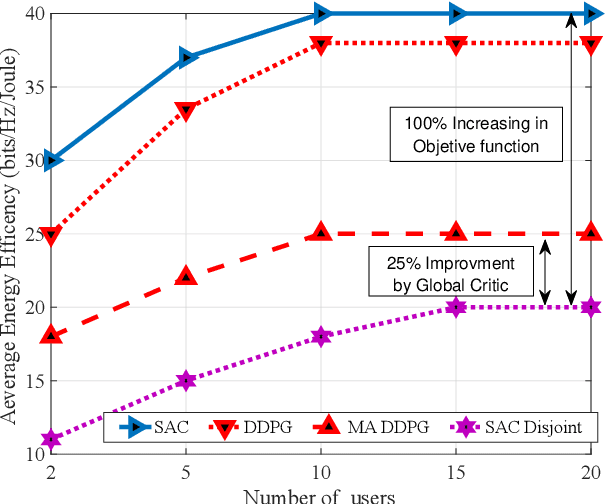
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a joint radio and core resource allocation framework for NFV-enabled networks. In the proposed system model, the goal is to maximize energy efficiency (EE), by guaranteeing end-to-end (E2E) quality of service (QoS) for different service types. To this end, we formulate an optimization problem in which power and spectrum resources are allocated in the radio part. In the core part, the chaining, placement, and scheduling of functions are performed to ensure the QoS of all users. This joint optimization problem is modeled as a Markov decision process (MDP), considering time-varying characteristics of the available resources and wireless channels. A soft actor-critic deep reinforcement learning (SAC-DRL) algorithm based on the maximum entropy framework is subsequently utilized to solve the above MDP. Numerical results reveal that the proposed joint approach based on the SAC-DRL algorithm could significantly reduce energy consumption compared to the case in which R-RA and NFV-RA problems are optimized separately.
AI-Based and Mobility-Aware Energy Efficient Resource Allocation and Trajectory Design for NFV Enabled Aerial Networks
May 21, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel joint intelligent trajectory design and resource allocation algorithm based on user's mobility and their requested services for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) assisted networks, where UAVs act as nodes of a network function virtualization (NFV) enabled network. Our objective is to maximize energy efficiency and minimize the average delay on all services by allocating the limited radio and NFV resources. In addition, due to the traffic conditions and mobility of users, we let some Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) to migrate from their current locations to other locations to satisfy the Quality of Service requirements. We formulate our problem to find near-optimal locations of UAVs, transmit power, subcarrier assignment, placement, and scheduling the requested service's functions over the UAVs and perform suitable VNF migration. Then we propose a novel Hierarchical Hybrid Continuous and Discrete Action (HHCDA) deep reinforcement learning method to solve our problem. Finally, the convergence and computational complexity of the proposed algorithm and its performance analyzed for different parameters. Simulation results show that our proposed HHCDA method decreases the request reject rate and average delay by 31.5% and 20% and increases the energy efficiency by 40% compared to DDPG method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge