Shifu Yan
Beyond Single Prompts: Synergistic Fusion and Arrangement for VICL
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Vision In-Context Learning (VICL) enables inpainting models to quickly adapt to new visual tasks from only a few prompts. However, existing methods suffer from two key issues: (1) selecting only the most similar prompt discards complementary cues from other high-quality prompts; and (2) failing to exploit the structured information implied by different prompt arrangements. We propose an end-to-end VICL framework to overcome these limitations. Firstly, an adaptive Fusion Module aggregates critical patterns and annotations from multiple prompts to form more precise contextual prompts. Secondly, we introduce arrangement-specific lightweight MLPs to decouple layout priors from the core model, while minimally affecting the overall model. In addition, an bidirectional fine-tuning mechanism swaps the roles of query and prompt, encouraging the model to reconstruct the original prompt from fused context and thus enhancing collaboration between the fusion module and the inpainting model. Experiments on foreground segmentation, single-object detection, and image colorization demonstrate superior results and strong cross-task generalization of our method.
CMMD: Cross-Metric Multi-Dimensional Root Cause Analysis
Mar 30, 2022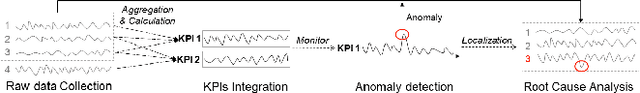
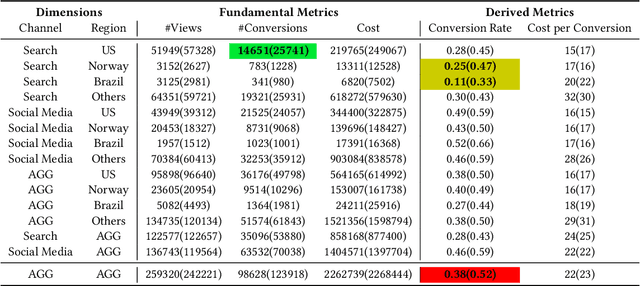
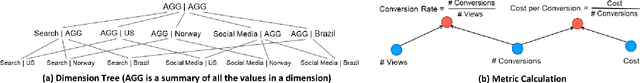

Abstract:In large-scale online services, crucial metrics, a.k.a., key performance indicators (KPIs), are monitored periodically to check their running statuses. Generally, KPIs are aggregated along multiple dimensions and derived by complex calculations among fundamental metrics from the raw data. Once abnormal KPI values are observed, root cause analysis (RCA) can be applied to identify the reasons for anomalies, so that we can troubleshoot quickly. Recently, several automatic RCA techniques were proposed to localize the related dimensions (or a combination of dimensions) to explain the anomalies. However, their analyses are limited to the data on the abnormal metric and ignore the data of other metrics which may be also related to the anomalies, leading to imprecise or even incorrect root causes. To this end, we propose a cross-metric multi-dimensional root cause analysis method, named CMMD, which consists of two key components: 1) relationship modeling, which utilizes graph neural network (GNN) to model the unknown complex calculation among metrics and aggregation function among dimensions from historical data; 2) root cause localization, which adopts the genetic algorithm to efficiently and effectively dive into the raw data and localize the abnormal dimension(s) once the KPI anomalies are detected. Experiments on synthetic datasets, public datasets and online production environment demonstrate the superiority of our proposed CMMD method compared with baselines. Currently, CMMD is running as an online service in Microsoft Azure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge