Sheshansh Agrawal
BLITZRANK: Principled Zero-shot Ranking Agents with Tournament Graphs
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models have emerged as powerful zero-shot rerankers for retrieval-augmented generation, offering strong generalization without task-specific training. However, existing LLM reranking methods either rely on heuristics that fail to fully exploit the information revealed by each ranking decision or are inefficient when they do. We introduce a tournament graph framework that provides a principled foundation for $k$-wise reranking. Our key observation is that each $k$-document comparison reveals a complete tournament of $\binom{k}{2}$ pairwise preferences. These tournaments are aggregated into a global preference graph, whose transitive closure yields many additional orderings without further model invocations. We formalize when a candidate's rank is certifiably determined and design a query schedule that greedily maximizes information gain towards identifying the top-$m$ items. Our framework also gracefully handles non-transitive preferences - cycles induced by LLM judgments - by collapsing them into equivalence classes that yield principled tiered rankings. Empirically, across 14 benchmarks and 5 LLMs, our method achieves Pareto dominance over existing methods: matching or exceeding accuracy while requiring 25-40% fewer tokens than comparable approaches, and 7$\times$ fewer than pairwise methods at near-identical quality.
DECAF: Deep Extreme Classification with Label Features
Aug 01, 2021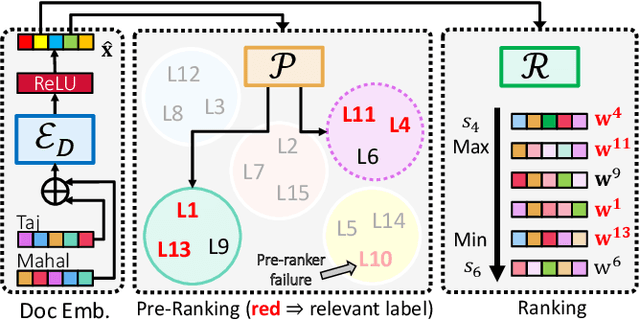
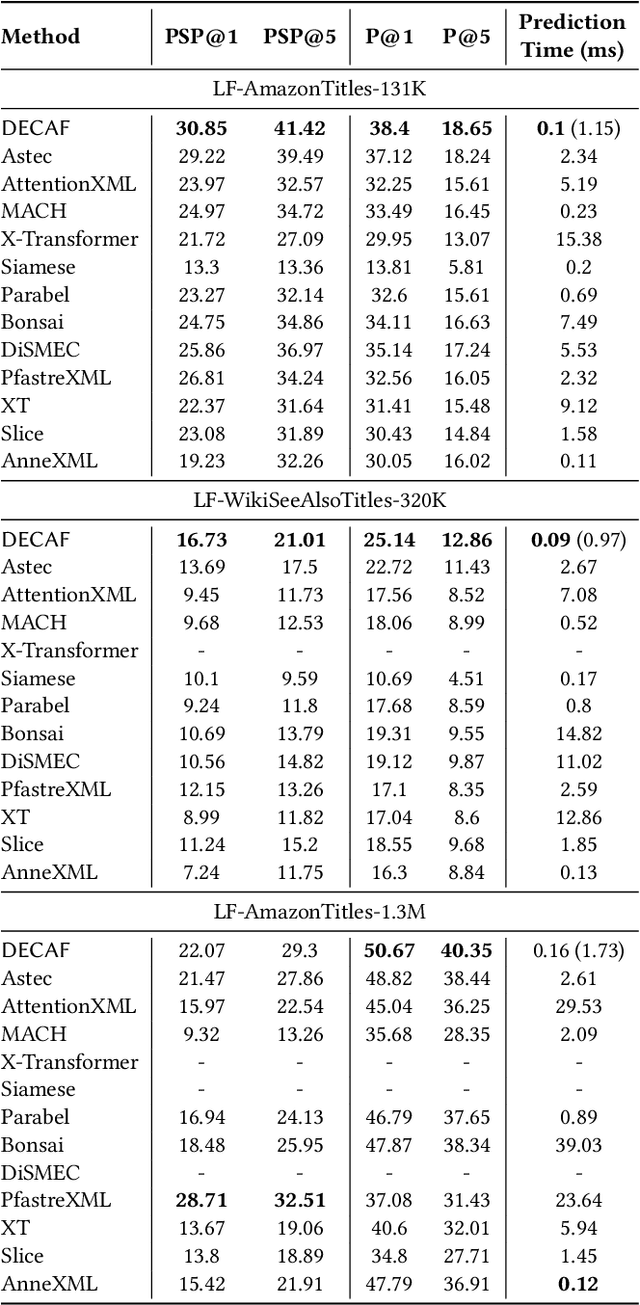
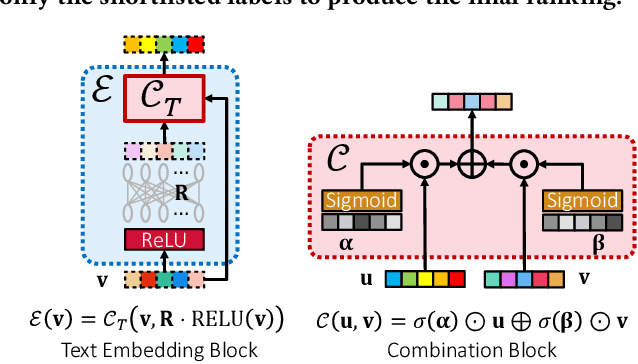
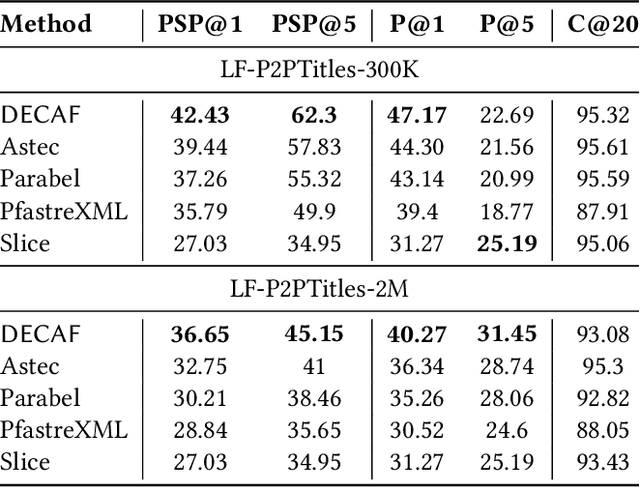
Abstract:Extreme multi-label classification (XML) involves tagging a data point with its most relevant subset of labels from an extremely large label set, with several applications such as product-to-product recommendation with millions of products. Although leading XML algorithms scale to millions of labels, they largely ignore label meta-data such as textual descriptions of the labels. On the other hand, classical techniques that can utilize label metadata via representation learning using deep networks struggle in extreme settings. This paper develops the DECAF algorithm that addresses these challenges by learning models enriched by label metadata that jointly learn model parameters and feature representations using deep networks and offer accurate classification at the scale of millions of labels. DECAF makes specific contributions to model architecture design, initialization, and training, enabling it to offer up to 2-6% more accurate prediction than leading extreme classifiers on publicly available benchmark product-to-product recommendation datasets, such as LF-AmazonTitles-1.3M. At the same time, DECAF was found to be up to 22x faster at inference than leading deep extreme classifiers, which makes it suitable for real-time applications that require predictions within a few milliseconds. The code for DECAF is available at the following URL https://github.com/Extreme-classification/DECAF.
ECLARE: Extreme Classification with Label Graph Correlations
Jul 31, 2021
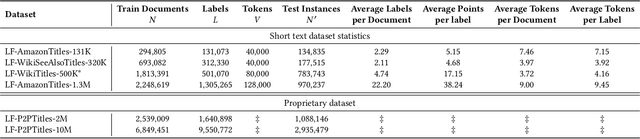
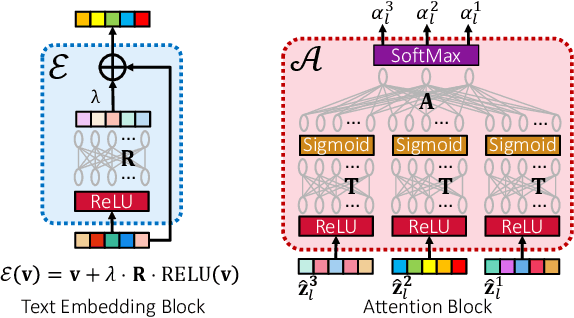
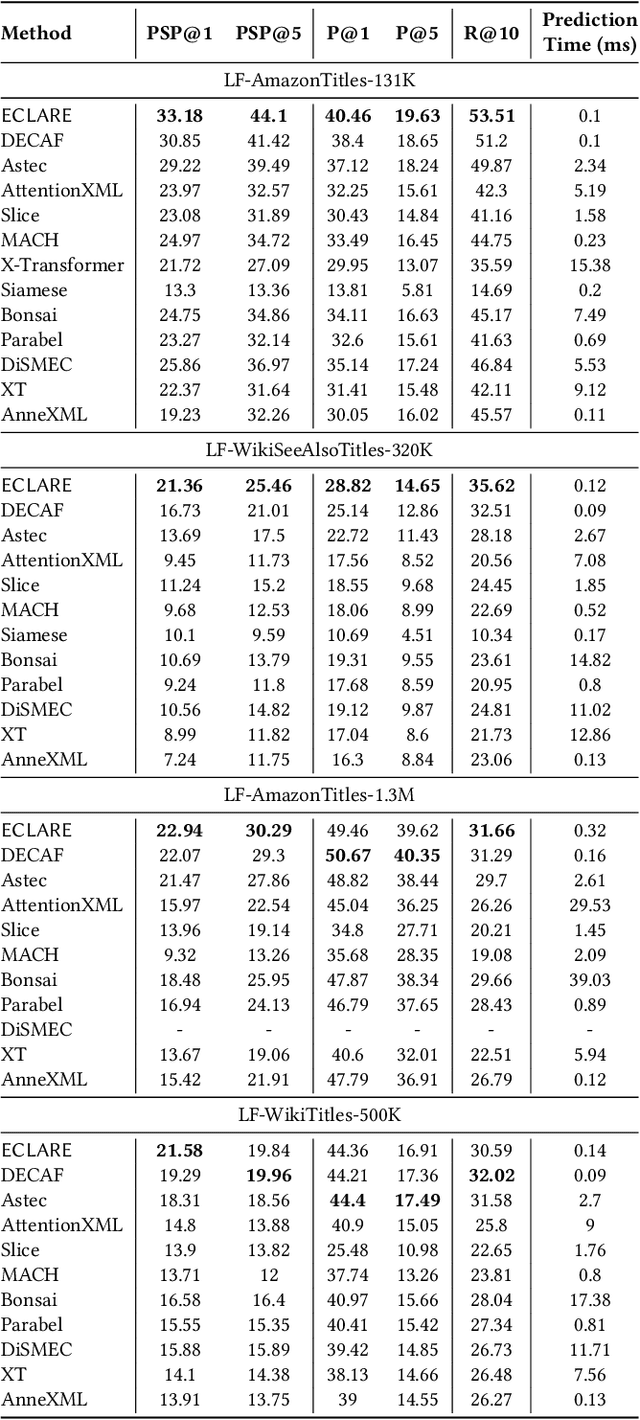
Abstract:Deep extreme classification (XC) seeks to train deep architectures that can tag a data point with its most relevant subset of labels from an extremely large label set. The core utility of XC comes from predicting labels that are rarely seen during training. Such rare labels hold the key to personalized recommendations that can delight and surprise a user. However, the large number of rare labels and small amount of training data per rare label offer significant statistical and computational challenges. State-of-the-art deep XC methods attempt to remedy this by incorporating textual descriptions of labels but do not adequately address the problem. This paper presents ECLARE, a scalable deep learning architecture that incorporates not only label text, but also label correlations, to offer accurate real-time predictions within a few milliseconds. Core contributions of ECLARE include a frugal architecture and scalable techniques to train deep models along with label correlation graphs at the scale of millions of labels. In particular, ECLARE offers predictions that are 2 to 14% more accurate on both publicly available benchmark datasets as well as proprietary datasets for a related products recommendation task sourced from the Bing search engine. Code for ECLARE is available at https://github.com/Extreme-classification/ECLARE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge