Shengjian Wu
OD-DETR: Online Distillation for Stabilizing Training of Detection Transformer
Jun 09, 2024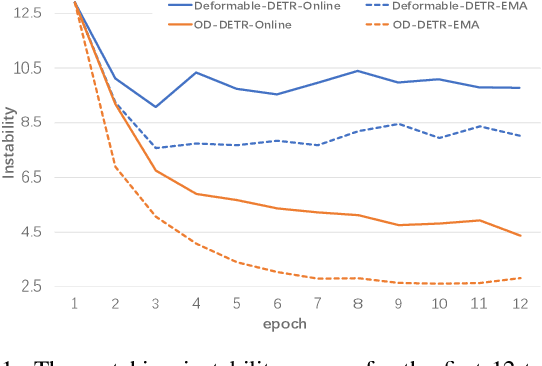
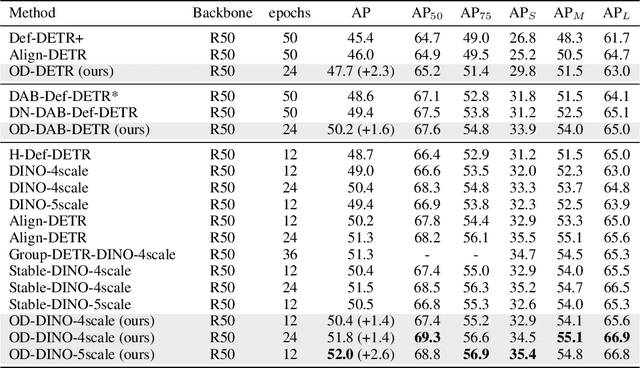
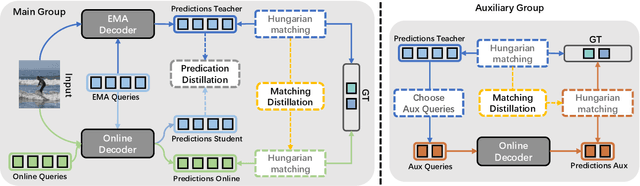
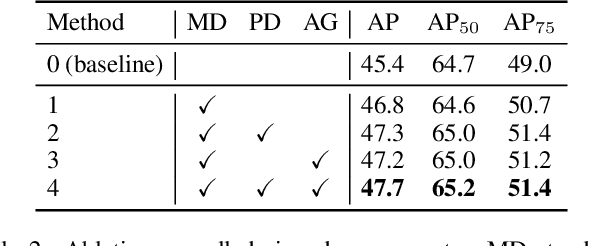
Abstract:DEtection TRansformer (DETR) becomes a dominant paradigm, mainly due to its common architecture with high accuracy and no post-processing. However, DETR suffers from unstable training dynamics. It consumes more data and epochs to converge compared with CNN-based detectors. This paper aims to stabilize DETR training through the online distillation. It utilizes a teacher model, accumulated by Exponential Moving Average (EMA), and distills its knowledge into the online model in following three aspects. First, the matching relation between object queries and ground truth (GT) boxes in the teacher is employed to guide the student, so queries within the student are not only assigned labels based on their own predictions, but also refer to the matching results from the teacher. Second, the teacher's initial query is given to the online student, and its prediction is directly constrained by the corresponding output from the teacher. Finally, the object queries from teacher's different decoding stages are used to build the auxiliary groups to accelerate the convergence. For each GT, two queries with the least matching costs are selected into this extra group, and they predict the GT box and participate the optimization. Extensive experiments show that the proposed OD-DETR successfully stabilizes the training, and significantly increases the performance without bringing in more parameters.
Further Improving Weakly-supervised Object Localization via Causal Knowledge Distillation
Jan 03, 2023



Abstract:Weakly-supervised object localization aims to indicate the category as well as the scope of an object in an image given only the image-level labels. Most of the existing works are based on Class Activation Mapping (CAM) and endeavor to enlarge the discriminative area inside the activation map to perceive the whole object, yet ignore the co-occurrence confounder of the object and context (e.g., fish and water), which makes the model inspection hard to distinguish object boundaries. Besides, the use of CAM also brings a dilemma problem that the classification and localization always suffer from a performance gap and can not reach their highest accuracy simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a casual knowledge distillation method, dubbed KD-CI-CAM, to address these two under-explored issues in one go. More specifically, we tackle the co-occurrence context confounder problem via causal intervention (CI), which explores the causalities among image features, contexts, and categories to eliminate the biased object-context entanglement in the class activation maps. Based on the de-biased object feature, we additionally propose a multi-teacher causal distillation framework to balance the absorption of classification knowledge and localization knowledge during model training. Extensive experiments on several benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of KD-CI-CAM in learning clear object boundaries from confounding contexts and addressing the dilemma problem between classification and localization performance.
IoU-Enhanced Attention for End-to-End Task Specific Object Detection
Oct 05, 2022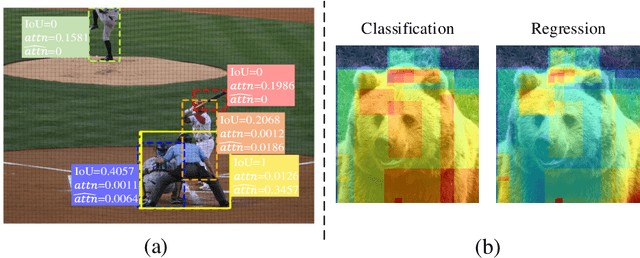
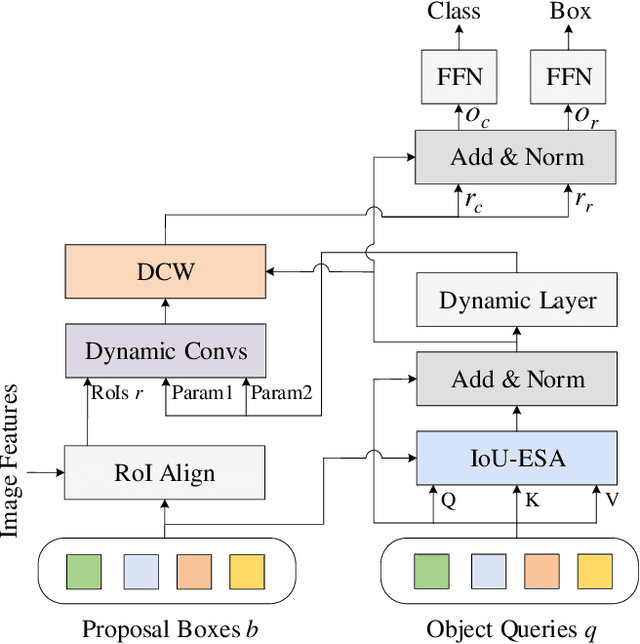
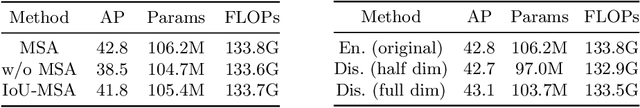
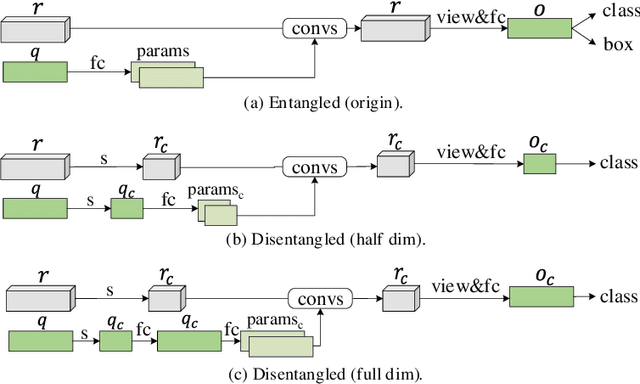
Abstract:Without densely tiled anchor boxes or grid points in the image, sparse R-CNN achieves promising results through a set of object queries and proposal boxes updated in the cascaded training manner. However, due to the sparse nature and the one-to-one relation between the query and its attending region, it heavily depends on the self attention, which is usually inaccurate in the early training stage. Moreover, in a scene of dense objects, the object query interacts with many irrelevant ones, reducing its uniqueness and harming the performance. This paper proposes to use IoU between different boxes as a prior for the value routing in self attention. The original attention matrix multiplies the same size matrix computed from the IoU of proposal boxes, and they determine the routing scheme so that the irrelevant features can be suppressed. Furthermore, to accurately extract features for both classification and regression, we add two lightweight projection heads to provide the dynamic channel masks based on object query, and they multiply with the output from dynamic convs, making the results suitable for the two different tasks. We validate the proposed scheme on different datasets, including MS-COCO and CrowdHuman, showing that it significantly improves the performance and increases the model convergence speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge