Shaqi Luo
Thor: Towards Human-Level Whole-Body Reactions for Intense Contact-Rich Environments
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Humanoids hold great potential for service, industrial, and rescue applications, in which robots must sustain whole-body stability while performing intense, contact-rich interactions with the environment. However, enabling humanoids to generate human-like, adaptive responses under such conditions remains a major challenge. To address this, we propose Thor, a humanoid framework for human-level whole-body reactions in contact-rich environments. Based on the robot's force analysis, we design a force-adaptive torso-tilt (FAT2) reward function to encourage humanoids to exhibit human-like responses during force-interaction tasks. To mitigate the high-dimensional challenges of humanoid control, Thor introduces a reinforcement learning architecture that decouples the upper body, waist, and lower body. Each component shares global observations of the whole body and jointly updates its parameters. Finally, we deploy Thor on the Unitree G1, and it substantially outperforms baselines in force-interaction tasks. Specifically, the robot achieves a peak pulling force of 167.7 N (approximately 48% of the G1's body weight) when moving backward and 145.5 N when moving forward, representing improvements of 68.9% and 74.7%, respectively, compared with the best-performing baseline. Moreover, Thor is capable of pulling a loaded rack (130 N) and opening a fire door with one hand (60 N). These results highlight Thor's effectiveness in enhancing humanoid force-interaction capabilities.
A Unified Interaction Control Framework for Safe Robotic Ultrasound Scanning with Human-Intention-Aware Compliance
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:The ultrasound scanning robot operates in environments where frequent human-robot interactions occur. Most existing control methods for ultrasound scanning address only one specific interaction situation or implement hard switches between controllers for different situations, which compromises both safety and efficiency. In this paper, we propose a unified interaction control framework for ultrasound scanning robots capable of handling all common interactions, distinguishing both human-intended and unintended types, and adapting with appropriate compliance. Specifically, the robot suspends or modulates its ongoing main task if the interaction is intended, e.g., when the doctor grasps the robot to lead the end effector actively. Furthermore, it can identify unintended interactions and avoid potential collision in the null space beforehand. Even if that collision has happened, it can become compliant with the collision in the null space and try to reduce its impact on the main task (where the scan is ongoing) kinematically and dynamically. The multiple situations are integrated into a unified controller with a smooth transition to deal with the interactions by exhibiting human-intention-aware compliance. Experimental results validate the framework's ability to cope with all common interactions including intended intervention and unintended collision in a collaborative carotid artery ultrasound scanning task.
Sequence-aware Pre-training for Echocardiography Probe Guidance
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Cardiac ultrasound probe guidance aims to help novices adjust the 6-DOF probe pose to obtain high-quality sectional images. Cardiac ultrasound faces two major challenges: (1) the inherently complex structure of the heart, and (2) significant individual variations. Previous works have only learned the population-averaged 2D and 3D structures of the heart rather than personalized cardiac structural features, leading to a performance bottleneck. Clinically, we observed that sonographers adjust their understanding of a patient's cardiac structure based on prior scanning sequences, thereby modifying their scanning strategies. Inspired by this, we propose a sequence-aware self-supervised pre-training method. Specifically, our approach learns personalized 2D and 3D cardiac structural features by predicting the masked-out images and actions in a scanning sequence. We hypothesize that if the model can predict the missing content it has acquired a good understanding of the personalized cardiac structure. In the downstream probe guidance task, we also introduced a sequence modeling approach that models individual cardiac structural information based on the images and actions from historical scan data, enabling more accurate navigation decisions. Experiments on a large-scale dataset with 1.36 million samples demonstrated that our proposed sequence-aware paradigm can significantly reduce navigation errors, with translation errors decreasing by 15.90% to 36.87% and rotation errors decreasing by 11.13% to 20.77%, compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Structure-aware World Model for Probe Guidance via Large-scale Self-supervised Pre-train
Jun 28, 2024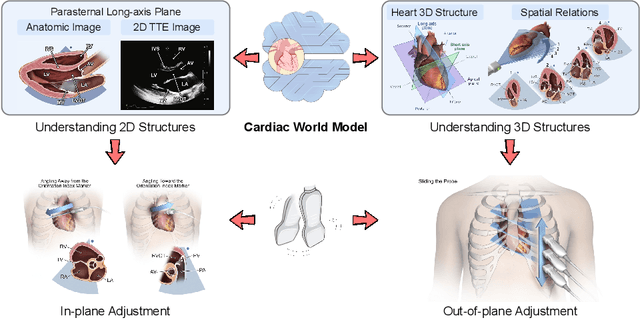
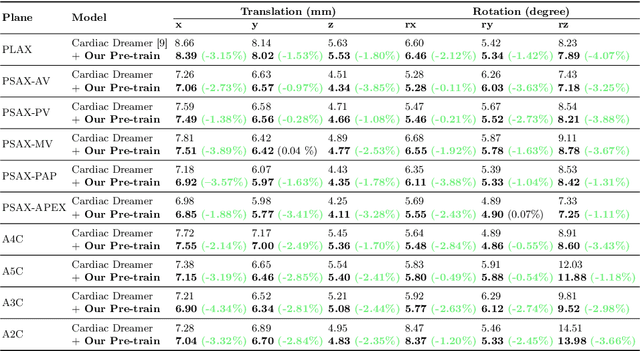
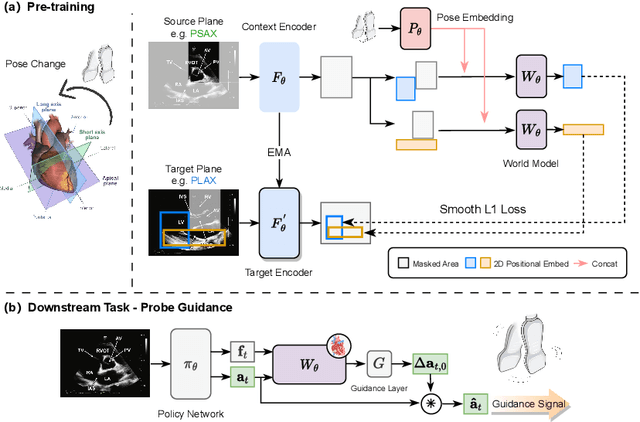

Abstract:The complex structure of the heart leads to significant challenges in echocardiography, especially in acquisition cardiac ultrasound images. Successful echocardiography requires a thorough understanding of the structures on the two-dimensional plane and the spatial relationships between planes in three-dimensional space. In this paper, we innovatively propose a large-scale self-supervised pre-training method to acquire a cardiac structure-aware world model. The core innovation lies in constructing a self-supervised task that requires structural inference by predicting masked structures on a 2D plane and imagining another plane based on pose transformation in 3D space. To support large-scale pre-training, we collected over 1.36 million echocardiograms from ten standard views, along with their 3D spatial poses. In the downstream probe guidance task, we demonstrate that our pre-trained model consistently reduces guidance errors across the ten most common standard views on the test set with 0.29 million samples from 74 routine clinical scans, indicating that structure-aware pre-training benefits the scanning.
Cardiac Copilot: Automatic Probe Guidance for Echocardiography with World Model
Jun 19, 2024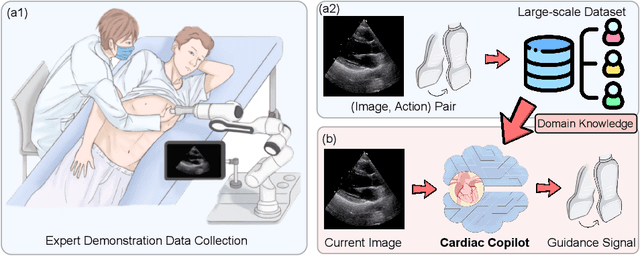
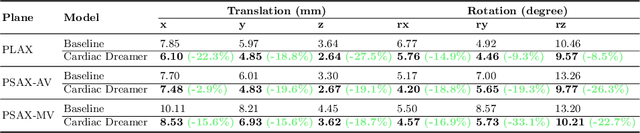
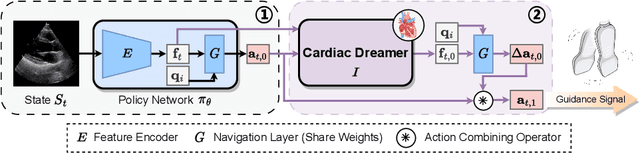
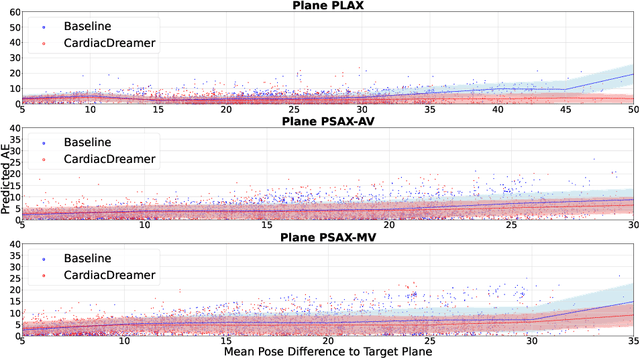
Abstract:Echocardiography is the only technique capable of real-time imaging of the heart and is vital for diagnosing the majority of cardiac diseases. However, there is a severe shortage of experienced cardiac sonographers, due to the heart's complex structure and significant operational challenges. To mitigate this situation, we present a Cardiac Copilot system capable of providing real-time probe movement guidance to assist less experienced sonographers in conducting freehand echocardiography. This system can enable non-experts, especially in primary departments and medically underserved areas, to perform cardiac ultrasound examinations, potentially improving global healthcare delivery. The core innovation lies in proposing a data-driven world model, named Cardiac Dreamer, for representing cardiac spatial structures. This world model can provide structure features of any cardiac planes around the current probe position in the latent space, serving as an precise navigation map for autonomous plane localization. We train our model with real-world ultrasound data and corresponding probe motion from 110 routine clinical scans with 151K sample pairs by three certified sonographers. Evaluations on three standard planes with 37K sample pairs demonstrate that the world model can reduce navigation errors by up to 33\% and exhibit more stable performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge