Seyedshams Feyzabadi
daVinciNet: Joint Prediction of Motion and Surgical State in Robot-Assisted Surgery
Sep 24, 2020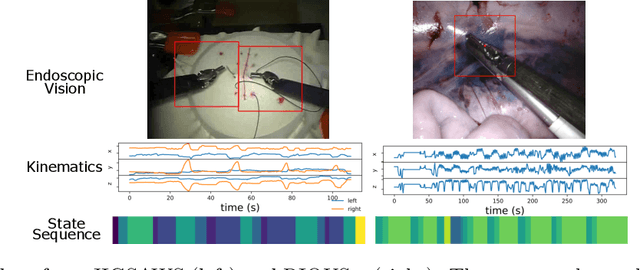
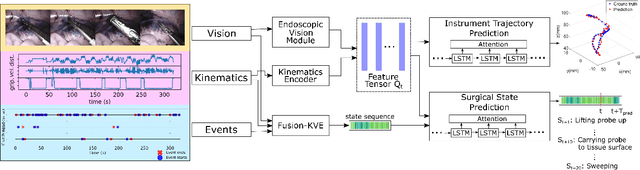
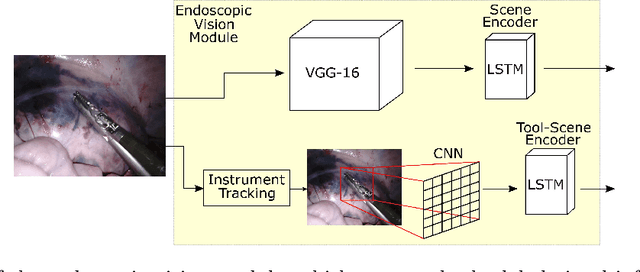
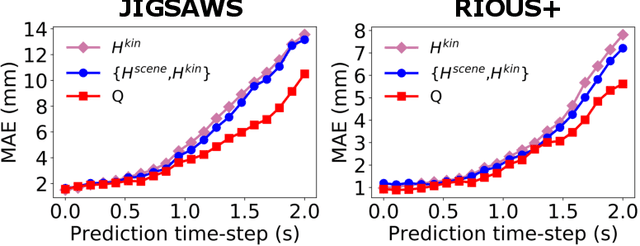
Abstract:This paper presents a technique to concurrently and jointly predict the future trajectories of surgical instruments and the future state(s) of surgical subtasks in robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) using multiple input sources. Such predictions are a necessary first step towards shared control and supervised autonomy of surgical subtasks. Minute-long surgical subtasks, such as suturing or ultrasound scanning, often have distinguishable tool kinematics and visual features, and can be described as a series of fine-grained states with transition schematics. We propose daVinciNet - an end-to-end dual-task model for robot motion and surgical state predictions. daVinciNet performs concurrent end-effector trajectory and surgical state predictions using features extracted from multiple data streams, including robot kinematics, endoscopic vision, and system events. We evaluate our proposed model on an extended Robotic Intra-Operative Ultrasound (RIOUS+) imaging dataset collected on a da Vinci Xi surgical system and the JHU-ISI Gesture and Skill Assessment Working Set (JIGSAWS). Our model achieves up to 93.85% short-term (0.5s) and 82.11% long-term (2s) state prediction accuracy, as well as 1.07mm short-term and 5.62mm long-term trajectory prediction error.
Temporal Segmentation of Surgical Sub-tasks through Deep Learning with Multiple Data Sources
Feb 07, 2020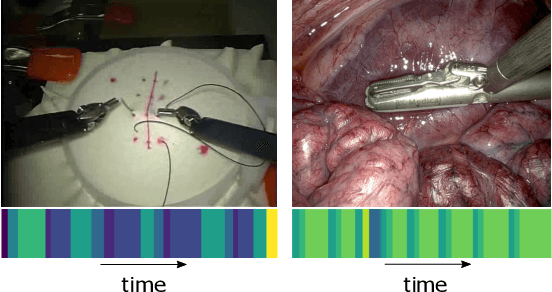

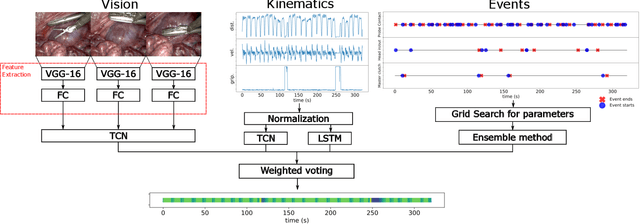
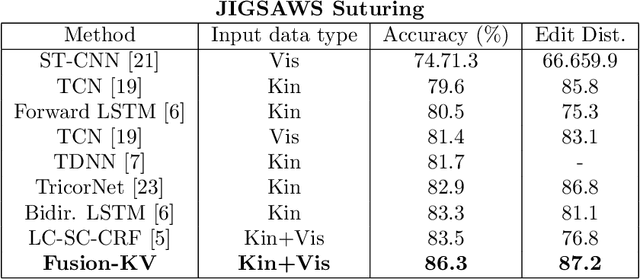
Abstract:Many tasks in robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) can be represented by finite-state machines (FSMs), where each state represents either an action (such as picking up a needle) or an observation (such as bleeding). A crucial step towards the automation of such surgical tasks is the temporal perception of the current surgical scene, which requires a real-time estimation of the states in the FSMs. The objective of this work is to estimate the current state of the surgical task based on the actions performed or events occurred as the task progresses. We propose Fusion-KVE, a unified surgical state estimation model that incorporates multiple data sources including the Kinematics, Vision, and system Events. Additionally, we examine the strengths and weaknesses of different state estimation models in segmenting states with different representative features or levels of granularity. We evaluate our model on the JHU-ISI Gesture and Skill Assessment Working Set (JIGSAWS), as well as a more complex dataset involving robotic intra-operative ultrasound (RIOUS) imaging, created using the da Vinci Xi surgical system. Our model achieves a superior frame-wise state estimation accuracy up to 89.4%, which improves the state-of-the-art surgical state estimation models in both JIGSAWS suturing dataset and our RIOUS dataset.
Joint Deep Learning for Car Detection
Jul 14, 2016



Abstract:Traditional object recognition approaches apply feature extraction, part deformation handling, occlusion handling and classification sequentially while they are independent from each other. Ouyang and Wang proposed a model for jointly learning of all of the mentioned processes using one deep neural network. We utilized, and manipulated their toolbox in order to apply it in car detection scenarios where it had not been tested. Creating a single deep architecture from these components, improves the interaction between them and can enhance the performance of the whole system. We believe that the approach can be used as a general purpose object detection toolbox. We tested the algorithm on UIUC car dataset, and achieved an outstanding result. The accuracy of our method was 97 % while the previously reported results showed an accuracy of up to 91 %. We strongly believe that having an experiment on a larger dataset can show the advantage of using deep models over shallow ones.
Motion Planning with Safety Constraints and High-Level Task Specifications
Jun 14, 2015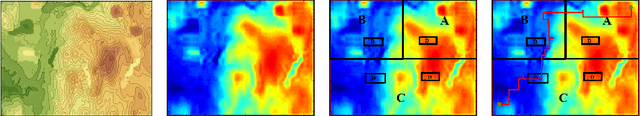
Abstract:We present a method to solve planning problems involving sequential decision making in unpredictable environments while accomplishing a high level task specification expressed using the formalism of linear temporal logic. Our method improves the state of the art by introducing a pruning step that preserves correctness while significantly reducing the time needed to compute an optimal policy. Our theoretical contribution is coupled with simulations substantiating the value of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge