Sepehr Valipour
A deep level set method for image segmentation
Oct 24, 2017



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel image segmentation approachthat integrates fully convolutional networks (FCNs) with a level setmodel. Compared with a FCN, the integrated method can incorporatesmoothing and prior information to achieve an accurate segmentation.Furthermore, different than using the level set model as a post-processingtool, we integrate it into the training phase to fine-tune the FCN. Thisallows the use of unlabeled data during training in a semi-supervisedsetting. Using two types of medical imaging data (liver CT and left ven-tricle MRI data), we show that the integrated method achieves goodperformance even when little training data is available, outperformingthe FCN or the level set model alone.
Incremental Learning for Robot Perception through HRI
Jan 17, 2017
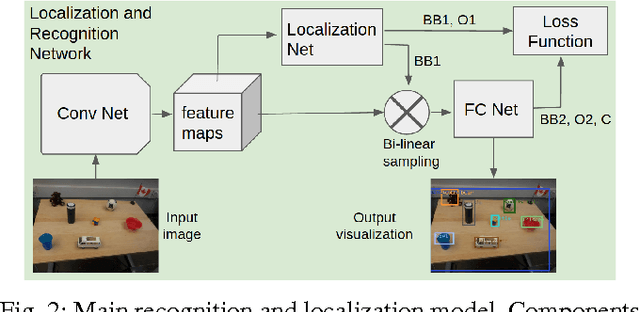


Abstract:Scene understanding and object recognition is a difficult to achieve yet crucial skill for robots. Recently, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), have shown success in this task. However, there is still a gap between their performance on image datasets and real-world robotics scenarios. We present a novel paradigm for incrementally improving a robot's visual perception through active human interaction. In this paradigm, the user introduces novel objects to the robot by means of pointing and voice commands. Given this information, the robot visually explores the object and adds images from it to re-train the perception module. Our base perception module is based on recent development in object detection and recognition using deep learning. Our method leverages state of the art CNNs from off-line batch learning, human guidance, robot exploration and incremental on-line learning.
Convolutional Gated Recurrent Networks for Video Segmentation
Nov 21, 2016



Abstract:Semantic segmentation has recently witnessed major progress, where fully convolutional neural networks have shown to perform well. However, most of the previous work focused on improving single image segmentation. To our knowledge, no prior work has made use of temporal video information in a recurrent network. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to implicitly utilize temporal data in videos for online semantic segmentation. The method relies on a fully convolutional network that is embedded into a gated recurrent architecture. This design receives a sequence of consecutive video frames and outputs the segmentation of the last frame. Convolutional gated recurrent networks are used for the recurrent part to preserve spatial connectivities in the image. Our proposed method can be applied in both online and batch segmentation. This architecture is tested for both binary and semantic video segmentation tasks. Experiments are conducted on the recent benchmarks in SegTrack V2, Davis, CityScapes, and Synthia. Using recurrent fully convolutional networks improved the baseline network performance in all of our experiments. Namely, 5% and 3% improvement of F-measure in SegTrack2 and Davis respectively, 5.7% improvement in mean IoU in Synthia and 3.5% improvement in categorical mean IoU in CityScapes. The performance of the RFCN network depends on its baseline fully convolutional network. Thus RFCN architecture can be seen as a method to improve its baseline segmentation network by exploiting spatiotemporal information in videos.
Recurrent Fully Convolutional Networks for Video Segmentation
Oct 31, 2016



Abstract:Image segmentation is an important step in most visual tasks. While convolutional neural networks have shown to perform well on single image segmentation, to our knowledge, no study has been been done on leveraging recurrent gated architectures for video segmentation. Accordingly, we propose a novel method for online segmentation of video sequences that incorporates temporal data. The network is built from fully convolutional element and recurrent unit that works on a sliding window over the temporal data. We also introduce a novel convolutional gated recurrent unit that preserves the spatial information and reduces the parameters learned. Our method has the advantage that it can work in an online fashion instead of operating over the whole input batch of video frames. The network is tested on the change detection dataset, and proved to have 5.5\% improvement in F-measure over a plain fully convolutional network for per frame segmentation. It was also shown to have improvement of 1.4\% for the F-measure compared to our baseline network that we call FCN 12s.
Parking Stall Vacancy Indicator System Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Jun 30, 2016



Abstract:Parking management systems, and vacancy-indication services in particular, can play a valuable role in reducing traffic and energy waste in large cities. Visual detection methods represent a cost-effective option, since they can take advantage of hardware usually already available in many parking lots, namely cameras. However, visual detection methods can be fragile and not easily generalizable. In this paper, we present a robust detection algorithm based on deep convolutional neural networks. We implemented and tested our algorithm on a large baseline dataset, and also on a set of image feeds from actual cameras already installed in parking lots. We have developed a fully functional system, from server-side image analysis to front-end user interface, to demonstrate the practicality of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge