Sayedmohammadreza Rastegari
Grasp the Graph (GtG) 2.0: Ensemble of GNNs for High-Precision Grasp Pose Detection in Clutter
May 05, 2025Abstract:Grasp pose detection in cluttered, real-world environments remains a significant challenge due to noisy and incomplete sensory data combined with complex object geometries. This paper introduces Grasp the Graph 2.0 (GtG 2.0) method, a lightweight yet highly effective hypothesis-and-test robotics grasping framework which leverages an ensemble of Graph Neural Networks for efficient geometric reasoning from point cloud data. Building on the success of GtG 1.0, which demonstrated the potential of Graph Neural Networks for grasp detection but was limited by assumptions of complete, noise-free point clouds and 4-Dof grasping, GtG 2.0 employs a conventional Grasp Pose Generator to efficiently produce 7-Dof grasp candidates. Candidates are assessed with an ensemble Graph Neural Network model which includes points within the gripper jaws (inside points) and surrounding contextual points (outside points). This improved representation boosts grasp detection performance over previous methods using the same generator. GtG 2.0 shows up to a 35% improvement in Average Precision on the GraspNet-1Billion benchmark compared to hypothesis-and-test and Graph Neural Network-based methods, ranking it among the top three frameworks. Experiments with a 3-Dof Delta Parallel robot and Kinect-v1 camera show a success rate of 91% and a clutter completion rate of 100%, demonstrating its flexibility and reliability.
Interpretable Multimodal Learning for Tumor Protein-Metal Binding: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:In cancer therapeutics, protein-metal binding mechanisms critically govern drug pharmacokinetics and targeting efficacy, thereby fundamentally shaping the rational design of anticancer metallodrugs. While conventional laboratory methods used to study such mechanisms are often costly, low throughput, and limited in capturing dynamic biological processes, machine learning (ML) has emerged as a promising alternative. Despite increasing efforts to develop protein-metal binding datasets and ML algorithms, the application of ML in tumor protein-metal binding remains limited. Key challenges include a shortage of high-quality, tumor-specific datasets, insufficient consideration of multiple data modalities, and the complexity of interpreting results due to the ''black box'' nature of complex ML models. This paper summarizes recent progress and ongoing challenges in using ML to predict tumor protein-metal binding, focusing on data, modeling, and interpretability. We present multimodal protein-metal binding datasets and outline strategies for acquiring, curating, and preprocessing them for training ML models. Moreover, we explore the complementary value provided by different data modalities and examine methods for their integration. We also review approaches for improving model interpretability to support more trustworthy decisions in cancer research. Finally, we offer our perspective on research opportunities and propose strategies to address the scarcity of tumor protein data and the limited number of predictive models for tumor protein-metal binding. We also highlight two promising directions for effective metal-based drug design: integrating protein-protein interaction data to provide structural insights into metal-binding events and predicting structural changes in tumor proteins after metal binding.
Co-evolution-based Metal-binding Residue Prediction with Graph Neural Networks
Feb 22, 2025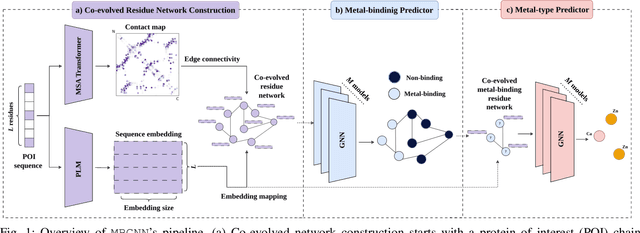
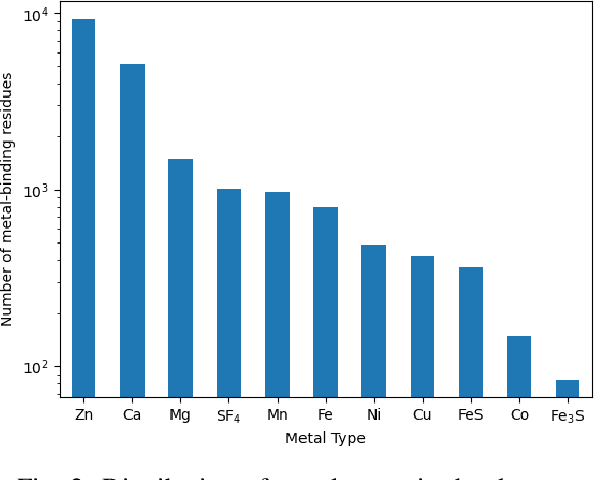
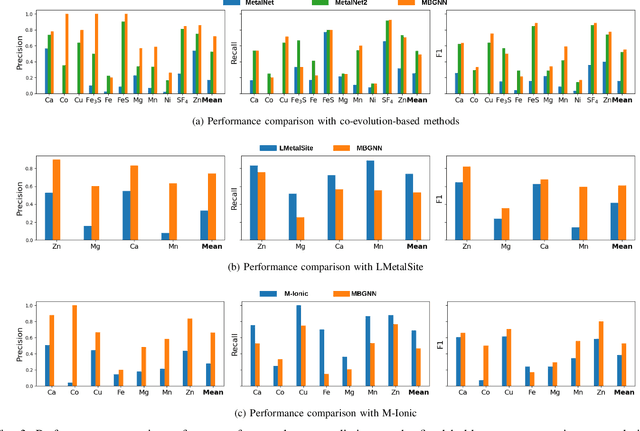
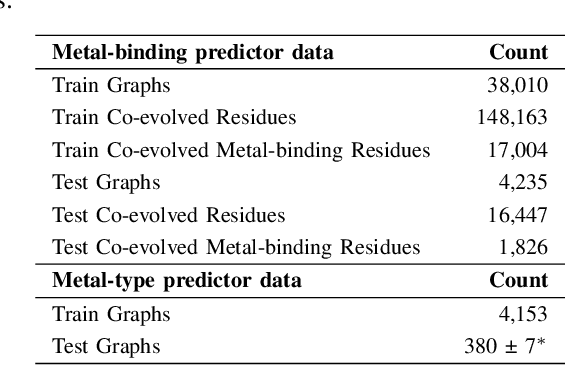
Abstract:In computational structural biology, predicting metal-binding sites and their corresponding metal types is challenging due to the complexity of protein structures and interactions. Conventional sequence- and structure-based prediction approaches cannot capture the complex evolutionary relationships driving these interactions to facilitate understanding, while recent co-evolution-based approaches do not fully consider the entire structure of the co-evolved residue network. In this paper, we introduce MBGNN (Metal-Binding Graph Neural Network) that utilizes the entire co-evolved residue network and effectively captures the complex dependencies within protein structures via graph neural networks to enhance the prediction of co-evolved metal-binding residues and their associated metal types. Experimental results on a public dataset show that MBGNN outperforms existing co-evolution-based metal-binding prediction methods, and it is also competitive against recent sequence-based methods, showing the potential of integrating co-evolutionary insights with advanced machine learning to deepen our understanding of protein-metal interactions. The MBGNN code is publicly available at https://github.com/SRastegari/MBGNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge