Saruar Alam
An objective validation of polyp and instrument segmentation methods in colonoscopy through Medico 2020 polyp segmentation and MedAI 2021 transparency challenges
Jul 30, 2023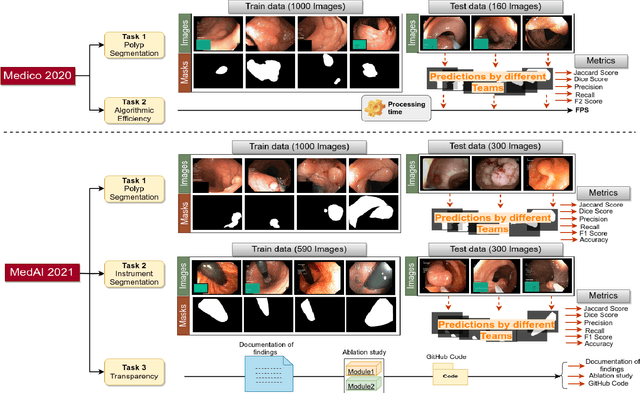
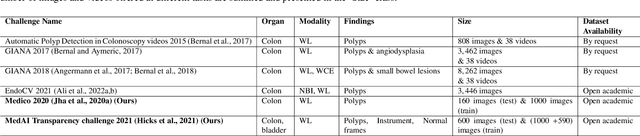
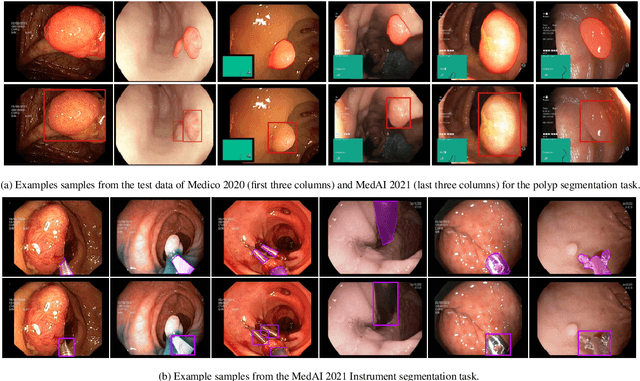
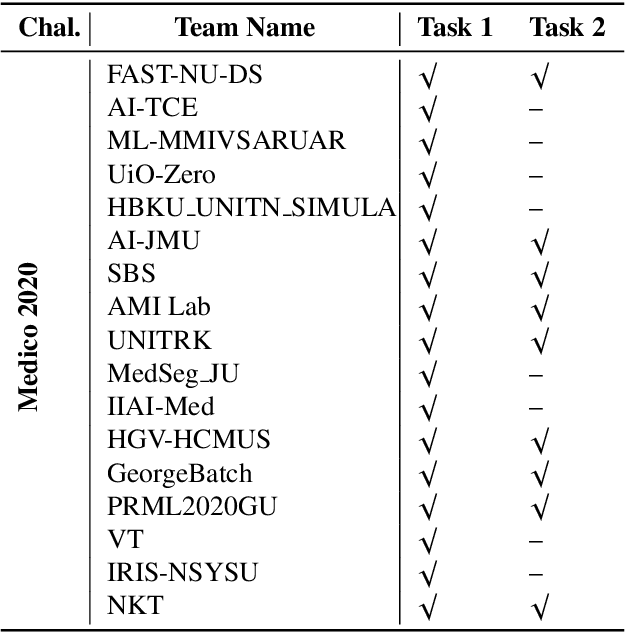
Abstract:Automatic analysis of colonoscopy images has been an active field of research motivated by the importance of early detection of precancerous polyps. However, detecting polyps during the live examination can be challenging due to various factors such as variation of skills and experience among the endoscopists, lack of attentiveness, and fatigue leading to a high polyp miss-rate. Deep learning has emerged as a promising solution to this challenge as it can assist endoscopists in detecting and classifying overlooked polyps and abnormalities in real time. In addition to the algorithm's accuracy, transparency and interpretability are crucial to explaining the whys and hows of the algorithm's prediction. Further, most algorithms are developed in private data, closed source, or proprietary software, and methods lack reproducibility. Therefore, to promote the development of efficient and transparent methods, we have organized the "Medico automatic polyp segmentation (Medico 2020)" and "MedAI: Transparency in Medical Image Segmentation (MedAI 2021)" competitions. We present a comprehensive summary and analyze each contribution, highlight the strength of the best-performing methods, and discuss the possibility of clinical translations of such methods into the clinic. For the transparency task, a multi-disciplinary team, including expert gastroenterologists, accessed each submission and evaluated the team based on open-source practices, failure case analysis, ablation studies, usability and understandability of evaluations to gain a deeper understanding of the models' credibility for clinical deployment. Through the comprehensive analysis of the challenge, we not only highlight the advancements in polyp and surgical instrument segmentation but also encourage qualitative evaluation for building more transparent and understandable AI-based colonoscopy systems.
Automatic Polyp Segmentation using U-Net-ResNet50
Dec 30, 2020
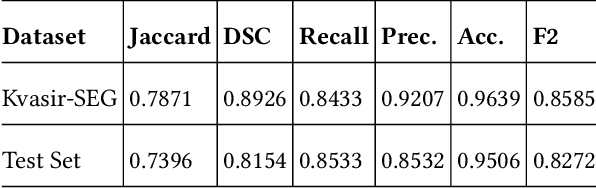
Abstract:Polyps are the predecessors to colorectal cancer which is considered as one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Colonoscopy is the standard procedure for the identification, localization, and removal of colorectal polyps. Due to variability in shape, size, and surrounding tissue similarity, colorectal polyps are often missed by the clinicians during colonoscopy. With the use of an automatic, accurate, and fast polyp segmentation method during the colonoscopy, many colorectal polyps can be easily detected and removed. The ``Medico automatic polyp segmentation challenge'' provides an opportunity to study polyp segmentation and build an efficient and accurate segmentation algorithm. We use the U-Net with pre-trained ResNet50 as the encoder for the polyp segmentation. The model is trained on Kvasir-SEG dataset provided for the challenge and tested on the organizer's dataset and achieves a dice coefficient of 0.8154, Jaccard of 0.7396, recall of 0.8533, precision of 0.8532, accuracy of 0.9506, and F2 score of 0.8272, demonstrating the generalization ability of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge