Sarah Schulz
QURATOR: Innovative Technologies for Content and Data Curation
Apr 25, 2020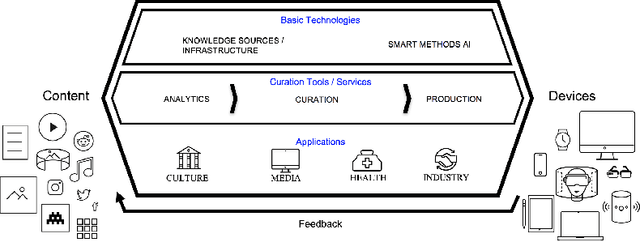
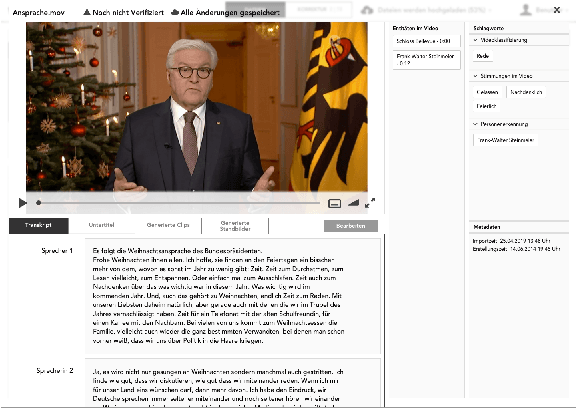
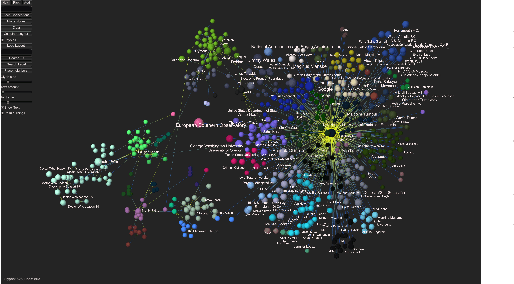
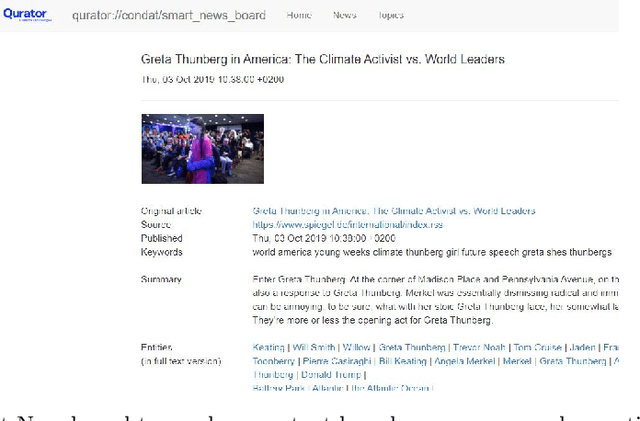
Abstract:In all domains and sectors, the demand for intelligent systems to support the processing and generation of digital content is rapidly increasing. The availability of vast amounts of content and the pressure to publish new content quickly and in rapid succession requires faster, more efficient and smarter processing and generation methods. With a consortium of ten partners from research and industry and a broad range of expertise in AI, Machine Learning and Language Technologies, the QURATOR project, funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, develops a sustainable and innovative technology platform that provides services to support knowledge workers in various industries to address the challenges they face when curating digital content. The project's vision and ambition is to establish an ecosystem for content curation technologies that significantly pushes the current state of the art and transforms its region, the metropolitan area Berlin-Brandenburg, into a global centre of excellence for curation technologies.
Named Entities in Medical Case Reports: Corpus and Experiments
Mar 29, 2020
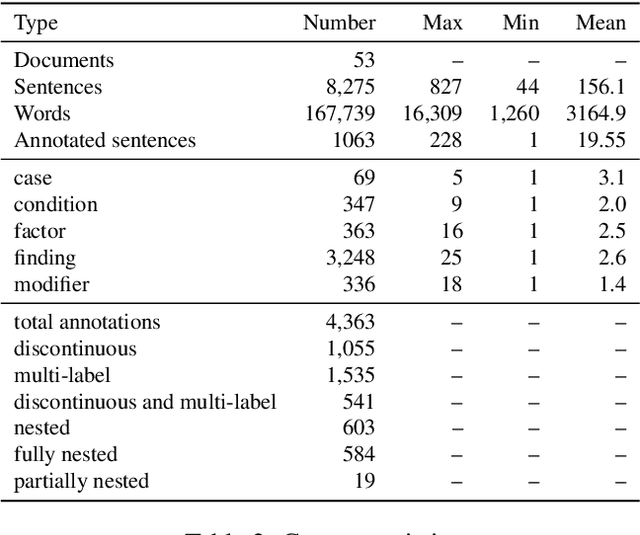

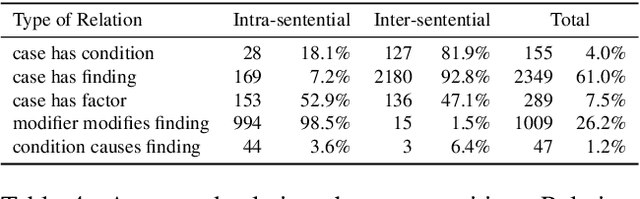
Abstract:We present a new corpus comprising annotations of medical entities in case reports, originating from PubMed Central's open access library. In the case reports, we annotate cases, conditions, findings, factors and negation modifiers. Moreover, where applicable, we annotate relations between these entities. As such, this is the first corpus of this kind made available to the scientific community in English. It enables the initial investigation of automatic information extraction from case reports through tasks like Named Entity Recognition, Relation Extraction and (sentence/paragraph) relevance detection. Additionally, we present four strong baseline systems for the detection of medical entities made available through the annotated dataset.
What Does Explainable AI Really Mean? A New Conceptualization of Perspectives
Oct 02, 2017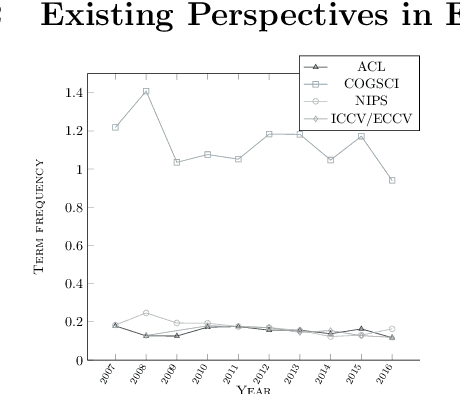
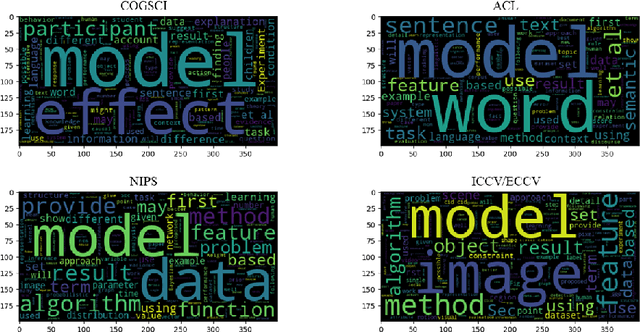
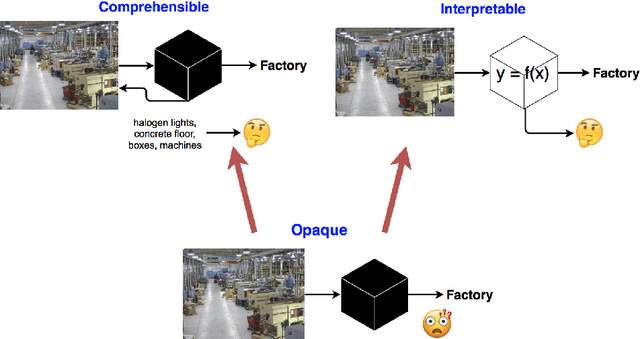
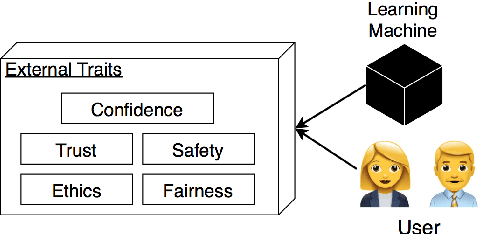
Abstract:We characterize three notions of explainable AI that cut across research fields: opaque systems that offer no insight into its algo- rithmic mechanisms; interpretable systems where users can mathemat- ically analyze its algorithmic mechanisms; and comprehensible systems that emit symbols enabling user-driven explanations of how a conclusion is reached. The paper is motivated by a corpus analysis of NIPS, ACL, COGSCI, and ICCV/ECCV paper titles showing differences in how work on explainable AI is positioned in various fields. We close by introducing a fourth notion: truly explainable systems, where automated reasoning is central to output crafted explanations without requiring human post processing as final step of the generative process.
Challenges of Computational Processing of Code-Switching
Oct 07, 2016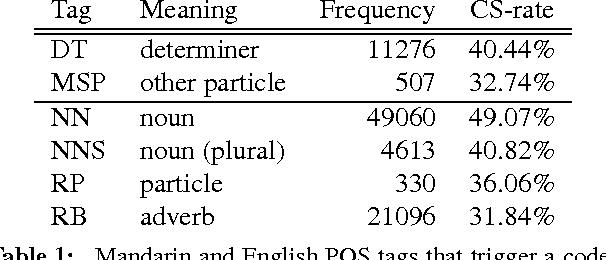
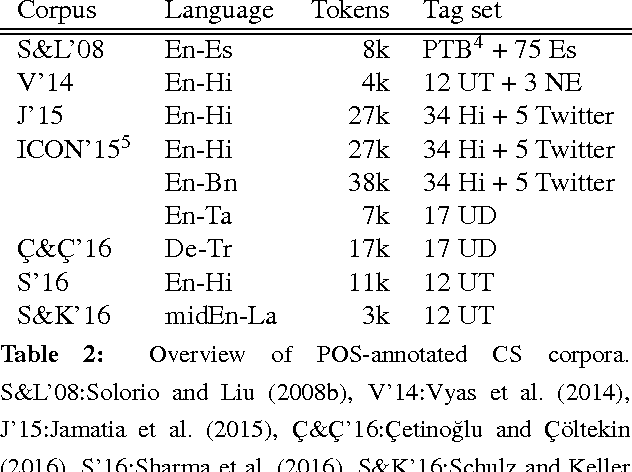
Abstract:This paper addresses challenges of Natural Language Processing (NLP) on non-canonical multilingual data in which two or more languages are mixed. It refers to code-switching which has become more popular in our daily life and therefore obtains an increasing amount of attention from the research community. We report our experience that cov- ers not only core NLP tasks such as normalisation, language identification, language modelling, part-of-speech tagging and dependency parsing but also more downstream ones such as machine translation and automatic speech recognition. We highlight and discuss the key problems for each of the tasks with supporting examples from different language pairs and relevant previous work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge